Contact Details
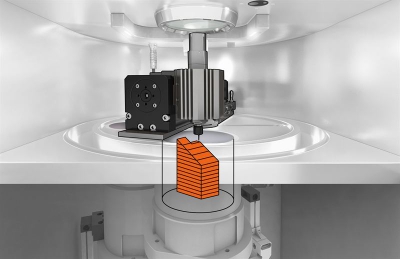
The ORLAS CREATOR hybrid 3D printing and milling machine from O.R. Lasertechnology Inc. brings together the benefits of both additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing within a single platform to offer a comprehensive manufacturing solution. The advantages of 3D printing complex metal components using the direct AM powder melting process in combination with the OR LASER’s advanced milling capabilities for precision finishing ensure that the ORLAS CREATOR hybrid is a compelling manufacturing solution at an accessible price point for SMEs.
Moreover, the ORLAS CREATOR hybrid goes beyond the capabilities of classical milling and machining, whereby structures and surfaces that are not normally reachable, such as inside contours, undercuts or hidden cooling channels, can be milled effectively. The ORLAS CREATOR hybrid offers all of the 3D printing features of the classic CREATOR , including the full laser power of 250W at a spot of 40 μm; laser processing speeds of 3,500 mm/sec. and a build platform 110 mm (diameter) with a maximum Z-axis of 100 mm.
Related Glossary Terms
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- lapping compound( powder)
lapping compound( powder)
Light, abrasive material used for finishing a surface.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- milling machine ( mill)
milling machine ( mill)
Runs endmills and arbor-mounted milling cutters. Features include a head with a spindle that drives the cutters; a column, knee and table that provide motion in the three Cartesian axes; and a base that supports the components and houses the cutting-fluid pump and reservoir. The work is mounted on the table and fed into the rotating cutter or endmill to accomplish the milling steps; vertical milling machines also feed endmills into the work by means of a spindle-mounted quill. Models range from small manual machines to big bed-type and duplex mills. All take one of three basic forms: vertical, horizontal or convertible horizontal/vertical. Vertical machines may be knee-type (the table is mounted on a knee that can be elevated) or bed-type (the table is securely supported and only moves horizontally). In general, horizontal machines are bigger and more powerful, while vertical machines are lighter but more versatile and easier to set up and operate.





