Taking a look at live tooling
Taking a look at live tooling
A review is given of this machining method, its basic concepts and developments in the technology.
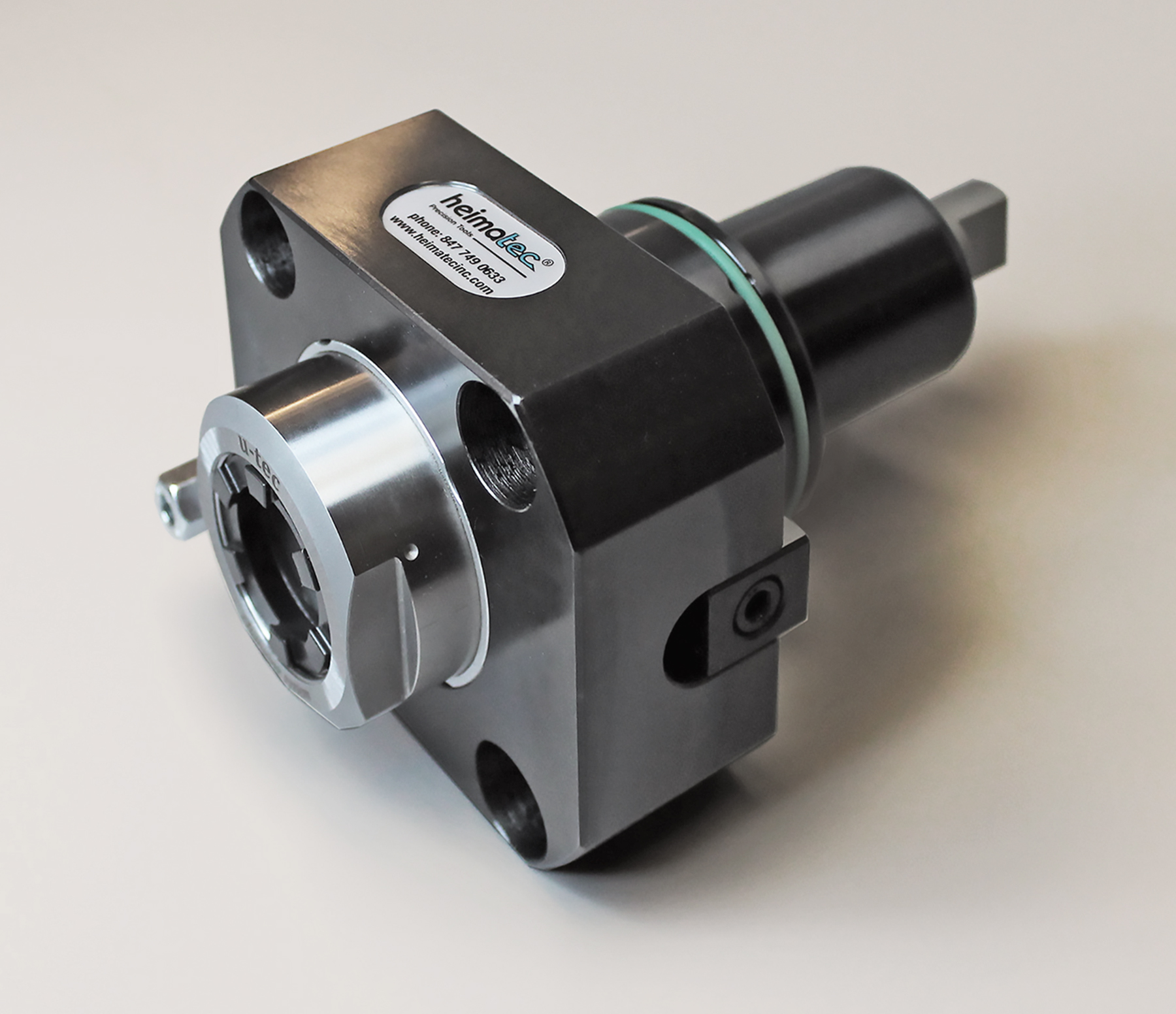

Live tooling, as a component on a lathe, is specifically manipulated by the CNC to perform various milling, drilling and other operations while the workpiece is being held in position by the main or sub-spindle.
These components, whether BMT or VDI, are also called driven tools, as opposed to static tools, that are used during chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery…" title="Workpiece is held in a lathe or drill-press spindle. It holds a tool or workpiece by one end, allowing it to be rotated. May also be fitted to the machine table…" title="Workholding device that affixes to a mill, lathe or drill-press spindle. It holds a tool or workpiece by one end, allowing it to be rotated. May also be fitted to the machine table…" aria-label="Glossary: chuck">chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery…" aria-label="Glossary: turning">turning operations. All live and static tools are built per the machine tool builder's specifications for each of the various models they produce. A key to running a successful job shop or production department is to partner with a supplier who can meet the tooling needs for all or most of the machines on your floor.
Most often, live tooling is offered in standard straight and 90-degree angle head configurations with a wide range of tool output clamping systems, including ER collet chuck, arbor, Weldon, Capto, whistle notch, hydraulic, HSK, CAT, ABS, and a variety of custom or proprietary systems developed by the many suppliers to the industry.
Need a new tool?
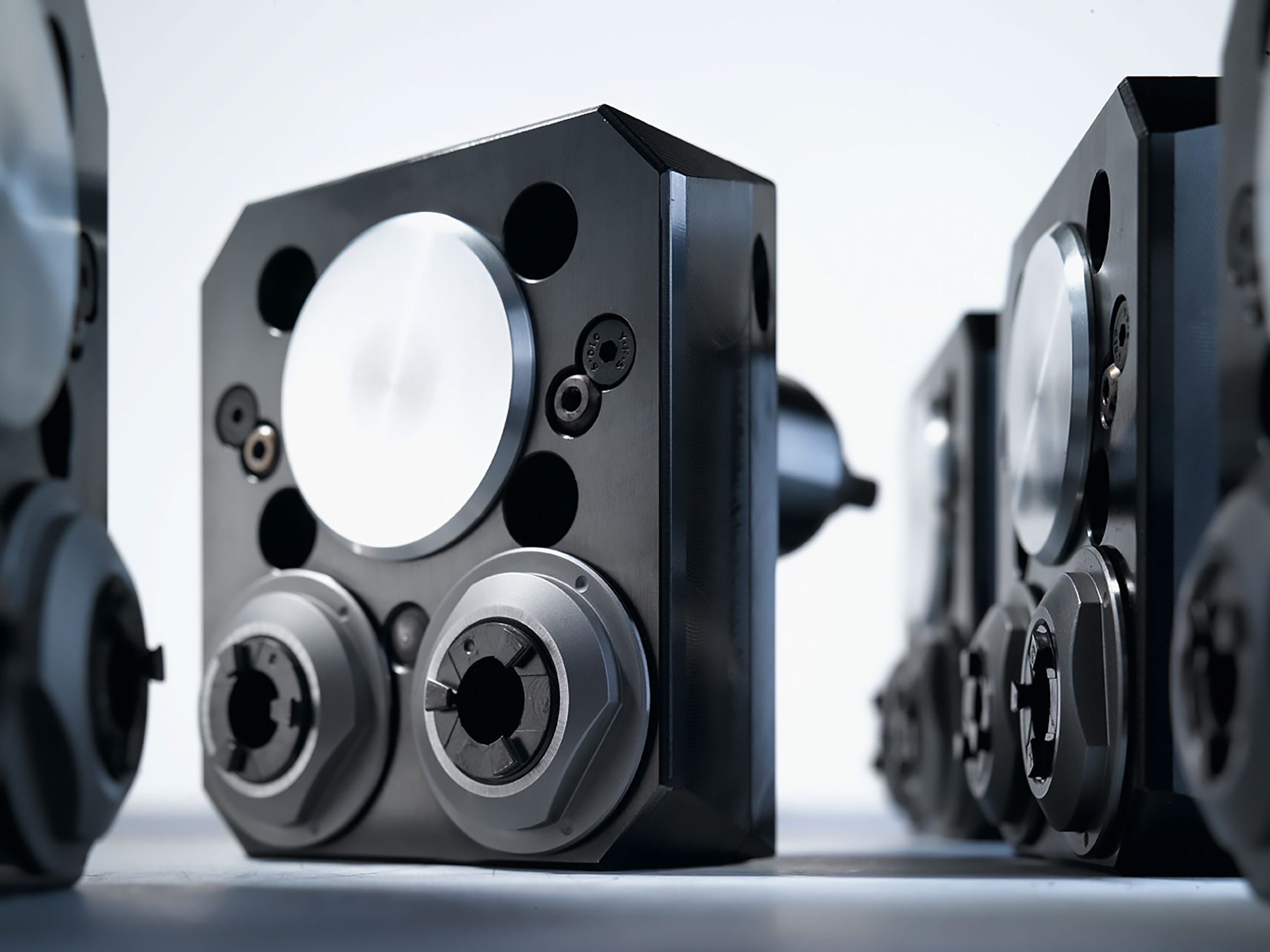

When the need arises for a new machine tool, careful consideration should be made to determine which live tools are appropriate for your application. While a standard machine tool package will help you get started, it is important to anticipate job and volume changes, as well unforeseen machining challenges from the beginning, in order to avoid machine downtime.
This short article is meant to give you a set of parameters to consider when evaluating the live and static tooling to use in your shop or production department. Simply stated, you need to do as much evaluation of your process, when determining the proper tooling to be used, as you did when you evaluated the various machines available for purchase. This fact is often overlooked and that can be a critical error, in the long run.
Your examination can range from the simple such as external vs. internal coolant, for example, to the sublime including adjustable or multi-spindle configurations, to the custom tool, which may be required and built to suit your special application. Finding a supplier who has an in-house machine shop for the preparation of special tools is a great value-add.
Tooling needs
Tool life is the product of cutting intensity, materials processed, machine stability and parts produced. Two seemingly identical job shops can have vastly different tooling needs because one is automotive and one is medical, or one specializes in the one-off and low-volume work, while the other has a greater occurrence of longer running jobs. The totality of your operation determines the best tooling for the machines being purchased.
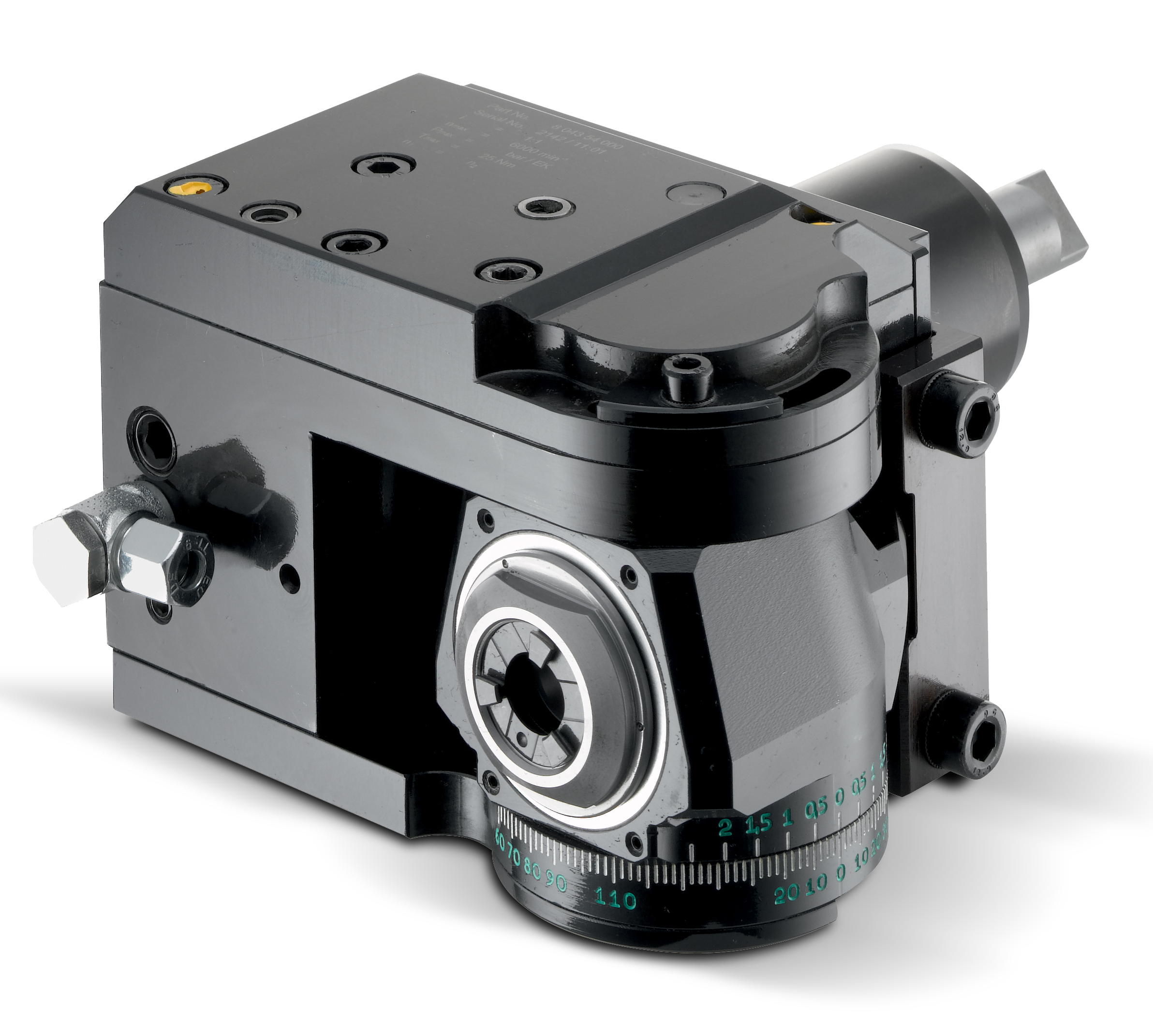

Bearing construction and the resulting spindle concentricity drive the life of any tool. You might find that just a 10-15% greater investment in a better design can yield both longer-lasting cutters and consistently superior finish on your products. Of course, the stability and rigidity of the machine tool are always critical factors. Bevel and spur gears that are hardened, ground and lapped in sets are best for smooth transition and maximum torque output.
Taper roller bearings are consistently superior to spindle bearings in live tool milling applications, so look for a combination system to get the highest rigidity possible. Also, look for an internal vs. external collet nut, so the cutting tool seats more deeply in the tool, as superior performance will result.
Likewise, high pressure internal coolant might be desirable. Look for 2000 psi capabilities in 90 degree tools and 1000 psi in straight tools.
You need to ask another question, namely, is the turret RPM sufficient to handle the work to be done?
It's possible that a live tool with a built-in speed increaser, often called a speed multiplier, would be helpful. Would it be beneficial to move secondary operations to your lathe? Gear hobbing can be accomplished in this manner, as can producing squares or flats, through the use of polygon machining.
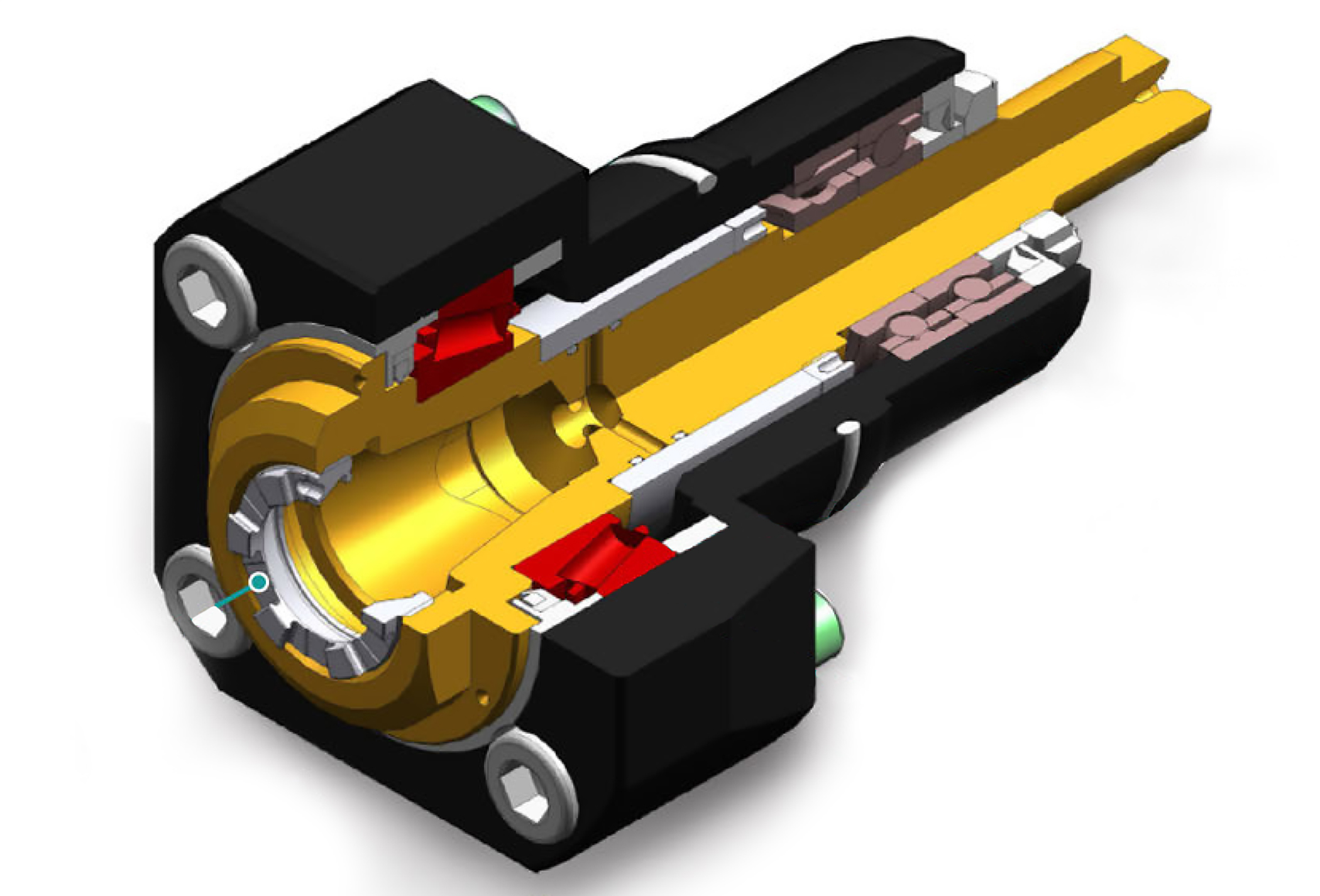
Standard live tooling most often is best suited to production work, where the finish, tolerances and cutter life are critical, while quick-change systems may be better suited to the shop producing families of products and other applications where the tool presetting offline is a key factor in keeping the shop at maximum productivity. It's a given in our industry that when the machine isn't running, the money isn't coming.
This opens the discussion of long-term flexibility and it's the most often overlooked consideration in buying live tools. You might ask, 'what work do you currently have in the shop and what work will be coming in the future?'
The overall economies of a changeable adapter system on your tooling may be a consideration not often made when your focus is centered on the machine being purchased. Dedicated tools for large families of products may often be desirable for some applications, but do consider whether a flexible changing system would be more appropriate. Talk to your tooling supplier for the various options, before making that determination.
If standard ER tooling is suitable for the work, there are many good suppliers. It is important though, to pay close attention to the construction aspects noted above. For a quick-change or changeable adapter system, there are fewer suppliers in the market, so seek them out and be sure they can supply the product styles you need for all your lathe brands.
Testing live tool performance
Now, an application example showing clear evidence of the value of testing live tool performance…
One company was performing a cross-milling application using an ER 32 output tool on a Eurotech lathe, running 10 ipm at 4000 rpm. They were making three passes with a cycle time of 262 seconds and were having difficulties with chatter on the finish, while producing 20,000 pieces per year.
The annual cost of the machining was over $130,000. By using an alternative live tool with an ER 32AX output, internal collet nut design, with the same parameters, they were able to produce the part in a single pass with a smooth finish and cycle time of just 172 seconds. Over the course of the year, this yielded a cost savings of $45,000, approximately 20x the cost of the tool. The bottom line is the bottom line, as the accountants tell us.
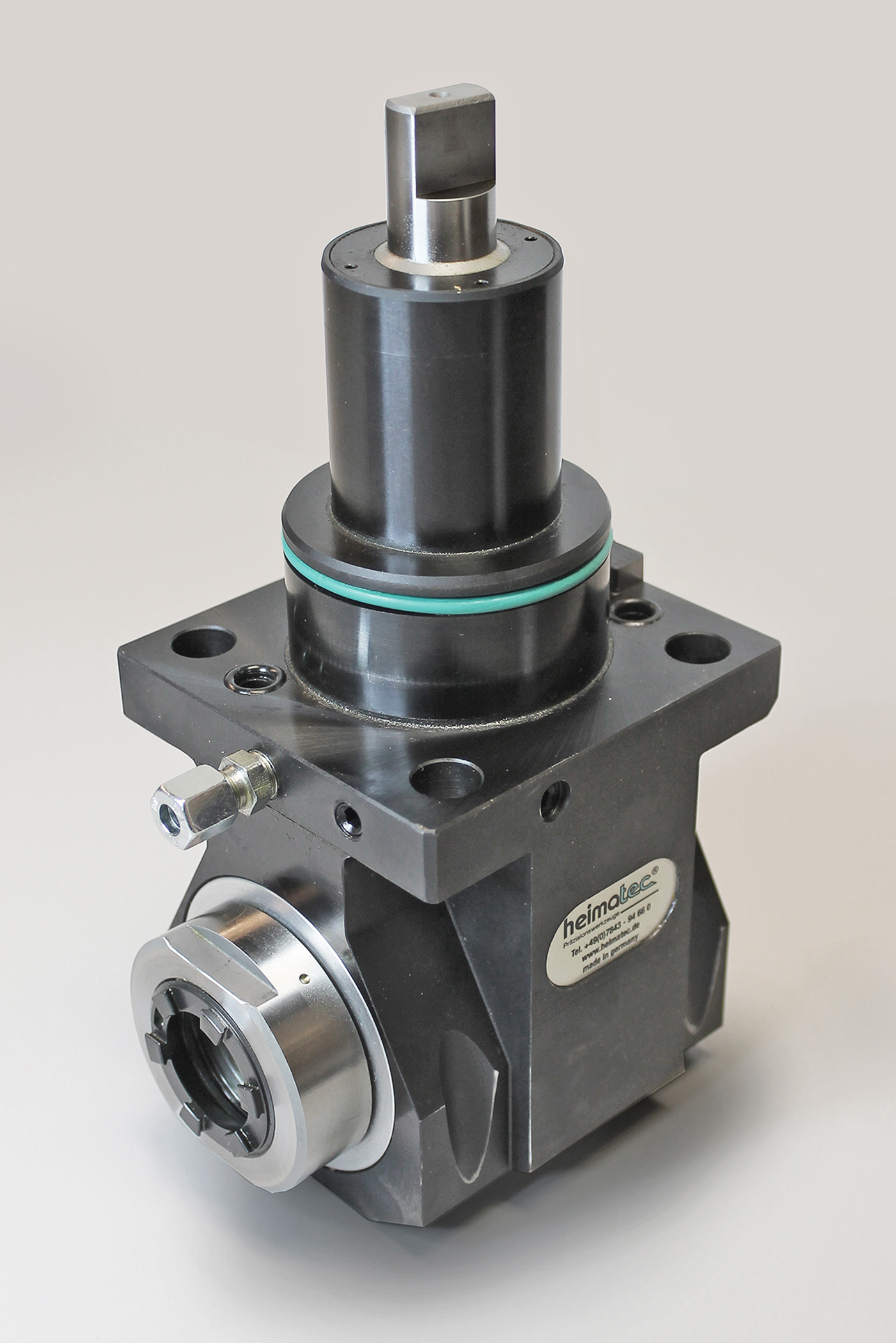

In the end, you may not need a universal adjustable tool or a multi-spindle live holder or even a quick-change adapter system, but do consider all these options. Talk to your machine builder and several tool suppliers, plus the most important people in this equation, your shop personnel, as their input is invaluable to keeping you up and running in a profitable, customer-satisfying scenario.
For more information, contact Preben Hansen at 847-749-0633 or [email protected].





