Are grinding machine safety guards overdesigned?
Are grinding wheel or other abrasive tool for the purpose of removing metal and finishing workpieces to close tolerances. Provides smooth, square, parallel and accurate workpi…" title="Powers a grinding wheel or other abrasive tool for the purpose of removing metal and finishing workpieces to close tolerances. Provides smooth, square, parallel and accurate workpi…" aria-label="Glossary: grinding machine">grinding machine safety guards overdesigned?
Guards on grinding machines are particularly important for ensuring operator safety. Grinding wheels seldom burst, but when they do, there is a great risk of serious injury to the machine operator. Recent studies suggest, however, that the enclosures commonly used in gear grinding machines, for example, could be overdesigned at present. Investigations conducted by the VDW (Verein Deutscher Werkzeugmaschinenfabriken – German Machine Tool Builders' Association) and the Institute of Machine Tools and Factory Management (IWF) at TU Berlin reveal that it is possible to use safety guards which are up to 70% thinner, depending on the width of the grinding wheel. These findings are leading to changes in ISO standardization.

Article from VDW German Machine Tool Builders' Association
Guards on grinding machines are particularly important for ensuring operator safety. Grinding wheels seldom burst, but when they do, there is a great risk of serious injury to the machine operator. Recent studies suggest, however, that the enclosures commonly used in gear grinding machines, for example, could be overdesigned at present. Investigations conducted by the VDW (Verein Deutscher Werkzeugmaschinenfabriken – German Machine Tool Builders' Association) and the Institute of Machine Tools and Factory Management (IWF) at TU Berlin reveal that it is possible to use safety guards which are up to 70% thinner, depending on the width of the grinding wheel. These findings are leading to changes in ISO standardization.

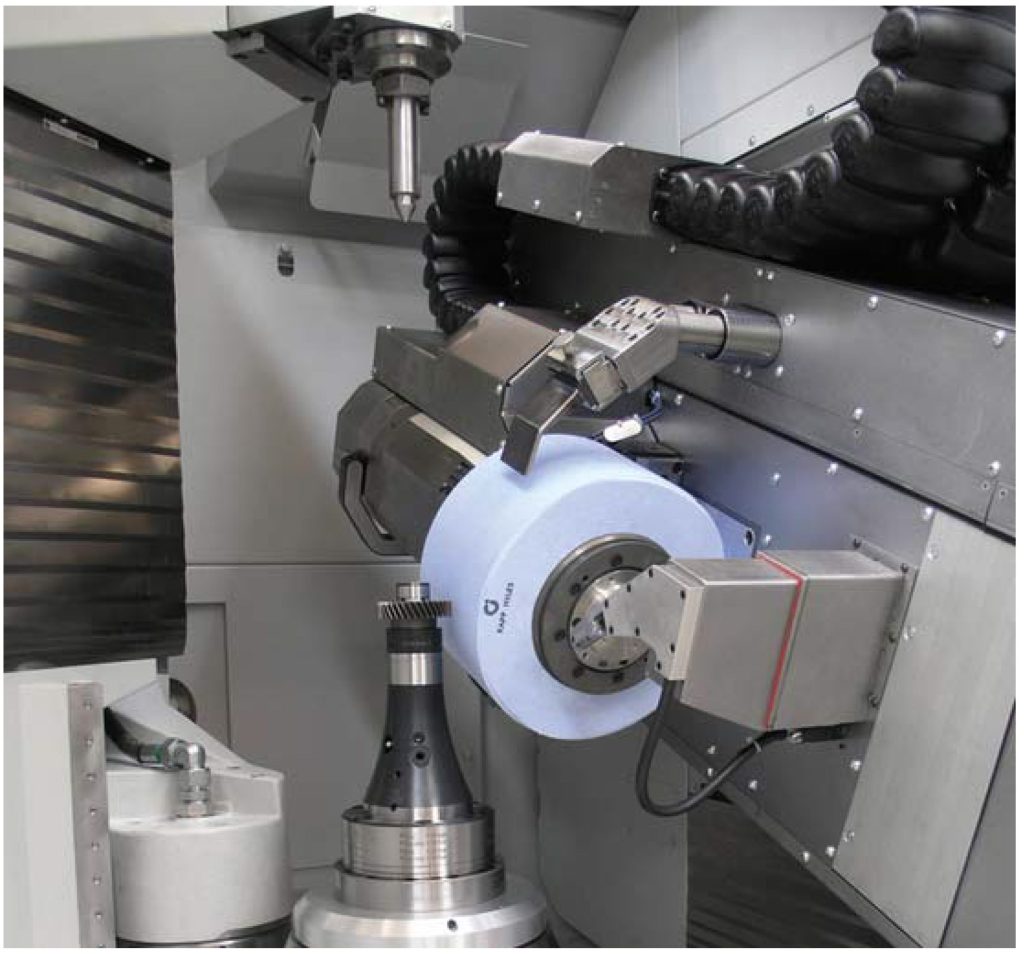
Workspace of a gear grinding machine. High rotational energy levels can arise in large grinding tools, such as those used for generation grinding. If a grinding wheel does burst, it can cause serious injury to the machine operator. Source: Kapp
Overdesigned safety guards soon a thing of the past?
The minimum wall thicknesses for safety guards are specified in ISO Standard 16089 "Machine tools - Safety - Stationary grinding machines." For example, there is a directly proportionate link between the requirements concerning primary protective covers for gear grinding machines and those for the full enclosures located further away. The reason for this is that no specific safety precautions were initially specified for the safety guards of gear grinding machines, which do not normally have a primary protective cover. This is because the preceding standard, EN 13218 "Safety of machine tools - Stationary grinding machines," did not explicitly include gear grinding machines. But this proportionate scaling has been repeatedly questioned, including by the Japanese association JMTBA, because it results in overdesigned polycarbonate safety guards and screens.
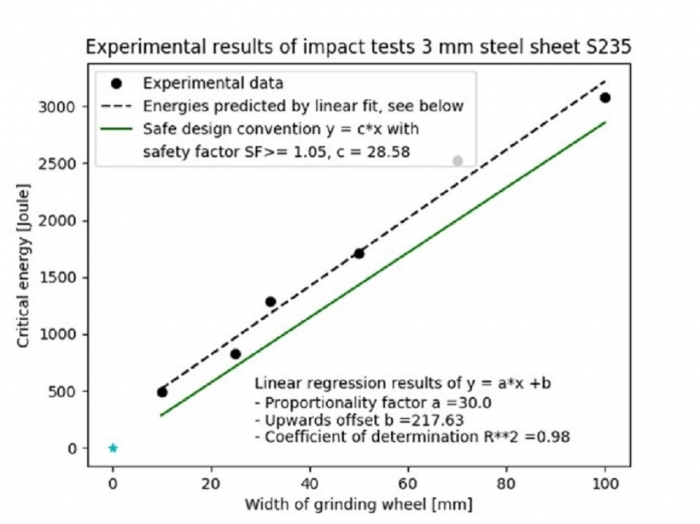
Figure 2. Safe design convention for 3 mm sheet steel. Source: BGHM/VDW
Major simplifications are possible
The member companies of VDW Working Group 5, which is responsible for machine tool component safety, therefore concluded that new specification tables were required for the full enclosures of stationary grinding machines. A two-year project was thus launched by the IWF (TU Berlin) in 2012 to develop the necessary test equipment.
"The ensuing burst and impact tests showed that the thickness of the enclosure wall can be reduced by up to 70%, depending on the width of the grinding wheel," explained Simon Thom, group leader for machine tool technology at IWF (TU Berlin). "This is very good news for the machine tool manufacturers, who are keen to avoid excess weight in their machines. Reducing the thickness of a sheet steel housing by half a millimeter, for example, will save 4 kg/m2 in weight." This also yields indirect savings because the motors for opening and closing correspondingly lighter steel gates can be less powerful or are rendered entirely superfluous.
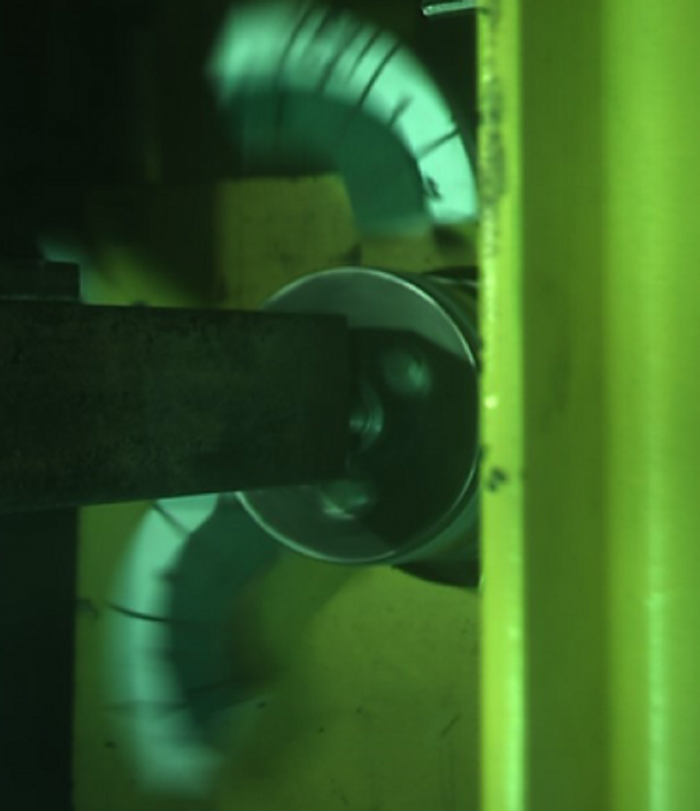

Burst scenario. Source: IWF TU Berlin
Unity among the partners
It is not only the industrial companies and the scientists who agree that guards are overdesigned in such machines. The DGVU (German Statutory Accident Insurance System) based in St. Augustin, Germany, and the BGHM trade association in Hanover, Germany, also carried out similar tests on a burst test stand – with comparable results. The burst tests were conducted over eight years. Then, at the end of 2019, the BGHM presented its report covering a total of over 400 burst grinding wheels and more than 800 usable impact events. Based on this, a safe design convention stipulating 3 mm for sheet steel with different grinding wheel widths was drawn up in conjunction with the VDW (see Figure 2).
The consolidation of the results in Germany was motivated not least by comparable studies abroad. The Japanese JMTBA association carried out tests that found that some of the previous standard specifications set out in ISO 16089 could be reduced by up to 30%.
Finally, in January 2020, a standardization meeting was held in Tokyo, where the Japanese and German findings were compared. The experts agreed that the Japanese results for adapting the specification tables for the primary protective cover, and the German results for the design of the full enclosure should be incorporated into the ISO standard. A consolidated working paper will soon be prepared by the ISO Secretariat at DIN in Berlin and submitted to the relevant public as a so-called "committee draft" for comments. This is scheduled for completion by October 2020.
Further investigations ongoing
Nevertheless, the existing results of the study on full enclosures in Project 20438 "Safely dimensioned machine enclosures" of the IGF (Industrielle Gemein-schaftsforschung) are being corroborated empirically and theoretically.
"We're also using simulations to highlight the worst-case scenario. As our burst tests have shown, this occurs when the outer edge of the fragment hits the guard. We can reproduce this type of impact in models with different materials, grinding wheel widths and safety guard thicknesses. In this way we've succeeded in simplifying the extremely complex burst tests," reported Thom. "Our plan for this year is to propose even simpler dimensioning procedures."
The reduced minimum wall thicknesses that are now to be specified in the ISO standard could therefore be made even thinner on the basis of the further test results.





