Coated HSS cutting tools account for 70 percent of overall sales
Coated HSS cutting tools account for 70 percent of overall sales
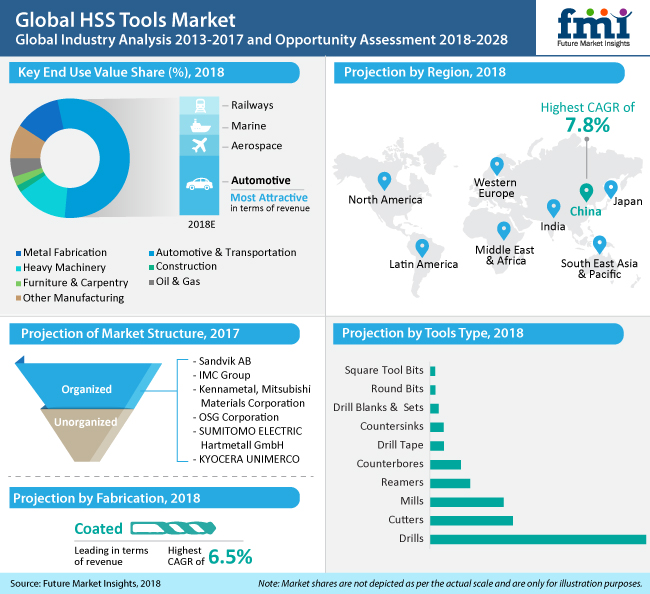
According to a new study, sales of high-speed steel (HSS) tools in 2019 are estimated at nearly 218,000 thousand units, projected to register a Y-o-Y growth at 4.8 percent over 2018. HSS tools sales have witnessed sheer proliferation, despite intense competition from solid-carbide tools, as these are best suited for shop production environments, wherein tool cost and versatility are of paramount importance.
Article from Future Market Insights
According to a new study, sales of high-speed steel (HSS) tools in 2019 are estimated at nearly 218,000 thousand units, projected to register a Y-o-Y growth at 4.8 percent over 2018. HSS tools sales have witnessed sheer proliferation, despite intense competition from solid-carbide tools, as these are best suited for shop production environments, wherein tool cost and versatility are of paramount importance.
The study opines that coated HSS tools will retain their supremacy, with nearly 70 percent share in the market. Although HSS tools have gained widespread acceptance in the metalworking and machining industries globally, additives such as powder metallurgy provide higher alloy-content, which imparts a combination of attributes including hardness, toughness and wear resistance. Coated HSS tools have been deemed effective in light of their performance in high feed and speed rates, and productivity, as well as in complex machining processes and dry machining operations.
HSS tools continue to gain ground, adapting with new coating technologies and adjusting their composition accordingly, thereby retaining their position as vital materials in machining and metalcutting industries. Additionally, coated HSS tools remain the fabrication of choice in metal cutting and machining operations, despite the intense competitive nature of the cutting tool industry.
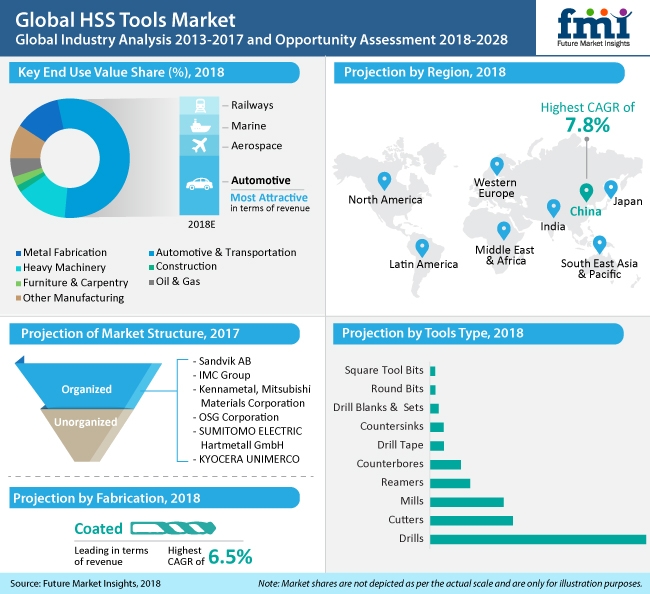
Drills Account for 4 in 10 Sales of HSS Tools Sales
Sensing varied requirements of tools for machining and metalworking operations, manufacturers of HSS tools have introduced myriad products, which range from drills and mills to cutters and reamers. The study estimates sales of drills will relatively larger from all the other variants, and are estimated to account for nearly four in 10 sales in 2019. However, mills, cutters and reamers are also expected to remain lucrative in the HSS tools market.
To uphold growing demand for HSS tools, manufacturers are committing extensive resources to drill design and development efforts. Investment by HSS tool manufacturers have resulted in significant optimization in reliability, quality, cost of production and lead times, and addition of enhanced substrates continues to remain instrumental in enhancement of HSS tool performance.
Shifting Demand within Customer Base Driving Adoption
Automotive and fabrication industries continue to remain largest adopters of HSS cutting tools, accounting for over half volume share of the market in 2018. Approximately 121,000 thousand units of HSS tools are expected to be sold in automotive and fabrication industries in 2019. Shifting customer demand toward application-specific and indexable tools with removable cutting tips, in light of their simplified repair procedures and cost-effectiveness, has been influencing the growth of the HSS tools market.
Growth of the HSS tools market is also expected to be affected from significant demand in the cyclical industries, which oscillate between contraction and expansion. Vendors who seek protection from economic turmoil are expected to benefit from the orthopedic and surgical HSS tools in the long run.
"Local distributors possess a vast experience in diverse catalogs, providing first-line input on selection and utility-related aspects of HSS tools with respect to their application. This factors have been discouraging customer purchases through online channels, as customers consider advertisements and referrals for cutting tools while choosing vendors, which is relatively less prevalent in online sales platforms," articulates a lead analyst.
Key players operating in the HSS tools market are focusing on strengthening their distribution footprint to keep pace with growing demand and gain coverage in lucrative locations. As distributor recommendations continue to play a pivotal role in HSS tool sales for vendors, long-term partnerships and strategic agreements with these distributors continues to remain a key growth strategy for players in the HSS tools market.
The HSS tools market is foreseen to record a CAGR of 5.5 percent through 2028.





