Cutting tool inserts to see ballooning sales
Cutting tool inserts to see ballooning sales
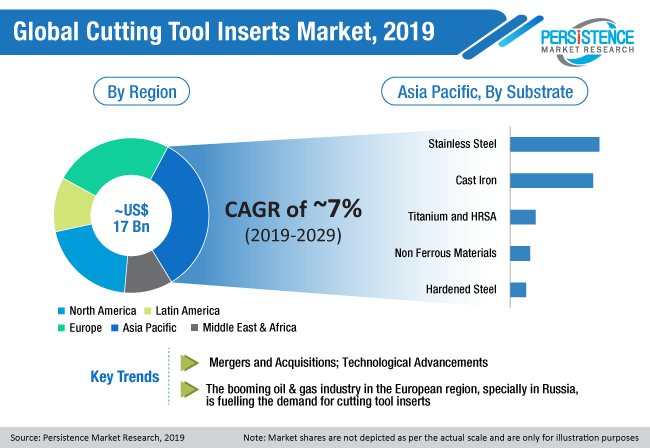
The global cutting tool inserts market is likely to account for ~US$ 18.1 Bn by the end of the assessment year 2019, and is estimated to expand at a CAGR of ~7.0% during the forecast period of 2019-2029. Among the type of material, the carbides segment is anticipated to grow at a noteworthy rate, owing to their cost effectiveness and durability, thereby contributing to the relatively high growth rate of the carbides segment over the forecast period.
Article from Persistence Market Research
The global cutting tool inserts market is likely to account for ~US$ 18.1 Bn by the end of the assessment year 2019, and is estimated to expand at a CAGR of ~7.0% during the forecast period of 2019-2029. Among the type of material, the carbides segment is anticipated to grow at a noteworthy rate, owing to their cost effectiveness and durability, thereby contributing to the relatively high growth rate of the carbides segment over the forecast period.
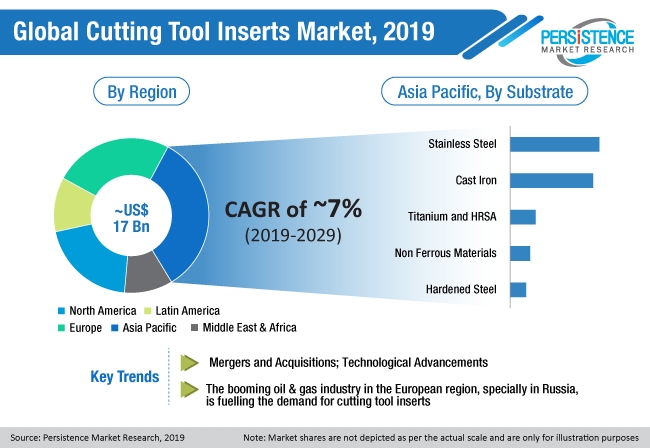
Key applications of cutting tool inserts, such as threading, milling and shearing, parting and grooving, and drilling and boring, are expected to drive the cutting tool inserts market growth at a significant rate. The stainless steel segment is estimated to retain its market share over the forecast period. According to the report, the demand for cutting tool inserts is expected to be driven primarily by the rise of automotive industry, oil and gas sector, construction industry, urbanization, and the increasing demand from other end use industries. Furthermore, massive demand from automotive OEMs, automotive refinishing service companies, construction companies, general industrial manufacturers and maintenance service providers, marine service companies, manufacturers of cans, coils, and wood and transport industries will contribute to the demand for cutting tool equipment, which, in turn, will augment the demand for cutting tool inserts.
For instance, wood working industry in Latin America is at a boom and this has facilitated the increase in the number of sales of cutting tool inserts. Cutting tool inserts are used to draw grooves in wooden furniture and artifacts. The most common type of cutting tool insert used to machine wood is carbide. In addition, with rising competition in the field of aerospace and marine, the requirement of jet engines, turbines, transmission parts and other vital components of aircraft or submarine has significantly increased the need for machining these components thereby increasing the scope of cutting tool inserts market.
Europe's Increasing Investments in Asian Markets Fueling Market Growth
European investments in Asia are motivated by the need to reduce costs, to exploit benefits of the local supply chains and to be close to an untapped customer base, which enables them to better understand user needs and better serve their customers. European machine tool builders' investment strategies abroad vary from strategic alliances to joint ventures, from the acquisition of foreign companies to opening production facilities in third countries. Increasing investments of global car manufacturers in emerging countries, for instance, India, China and Brazil, along with large publicly funded energy and infrastructure projects in these countries, make them attractive enough for European investments from machine tool builders.
APAC and Europe to be the Top Revenue Pockets
Geographically, APAC and European markets are picking up pace in the global cutting tool inserts market, owing to expansion of industrial infrastructure and an upsurge in the automotive and oil and gas industry over the years. Europe being an automotive hub has a lot of scope for transportation industry including railways. Most of the metal used in this industry is machined with cutting tool inserts, thus accounting for better sales of the same. The transportation segment is anticipated to soar the cutting tool inserts market in Europe. The demand for cutting tool inserts is majorly driven by its applications in various sectors such as aerospace, automotive, marine, medical, woodworking, die and mold, driven by growth in global GDP. Moreover, stable economic growth in developing countries such as India, Brazil, China and ASEAN countries, and rising urbanization and expenditure in these regions, acts as the major growth factors that are propelling the growth of the cutting tool inserts market.
Furthermore, the APAC region is also expected to remain the most attractive region in terms of market attractiveness by market share index, on account of the largest volumes of cutting tool inserts consumptions expected by the region, over the forecast period, mainly driven by China. A high growth rate due to considerable industrial activity in the region is expected to contribute to the rising demand. Europe is expected to hold a significant market share in terms of both value and volume after APAC region, owing to growing automotive and other end use industries and infrastructural developments in the region.
Vendor Insights – Key Companies Focus on Global Footprint Expansion
The global cutting tool inserts market highlights some of the key market participants operating in the global cutting tool inserts market, such as Kennametal Inc., Sumitomo Electric Carbide Inc., Sandvik AB, Knight Carbide Inc., Compagnie de Saint-Gobain, Total Carbide Ltd., Asahi Diamond Industrial Co. Ltd., Tomei Diamond Co. Ltd., Kyocera Corp., Mitsubishi Materials Corp., Showa Denko K.K., YG-1 Co. Ltd., Element Six, Iscar Ltd. and NGK Spark Plugs Co. Ltd. (NTK Cutting Tools).
Key strategies are the expansion of production capacities and focus on mergers and acquisitions to increase their global and regional footprint in the cutting tool inserts market. For instance, in July 2017, Sumitomo Electric Carbide Inc., started operations at the Dayton Plant, which is operated by one of its subsidiaries named Sumiden Wire Products Corp. (SWPC) in the U.S. The plant is dedicated to the manufacturing of wires for automobile springs. In April 2017, Kyocera Corp. expanded its industrial ceramic manufacturing business in Washington, U.S. ILJIN Diamond Co. Ltd. is focused on developing human friendly technologies that can impart to better customer relations and long-term deeds.





