Eccentric positioning system determines tool position and angle
Eccentric positioning system determines tool position and angle
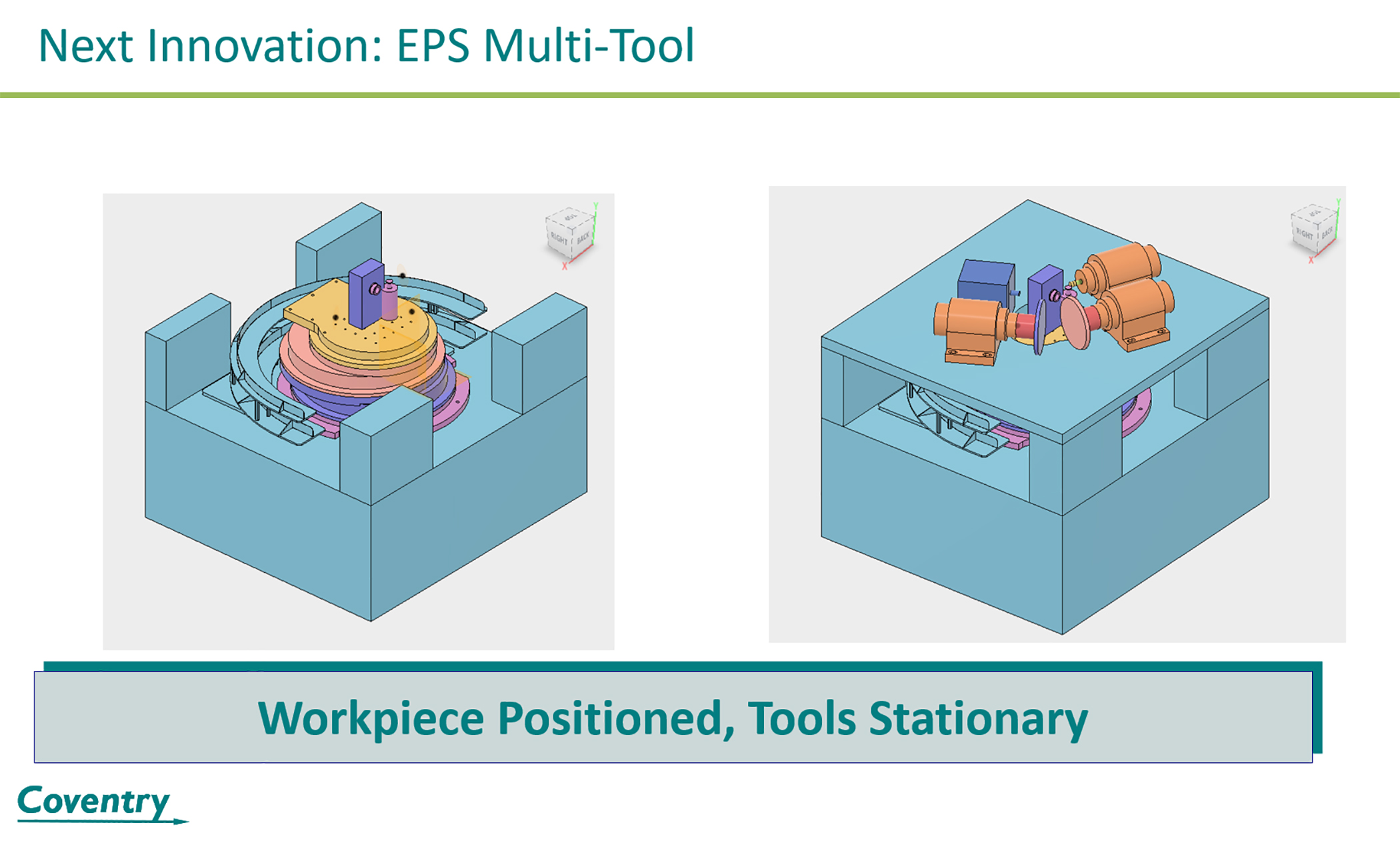
A breakthrough ultrahigh-precision robotic machine tool positions an object anywhere in a 215 mm circle with accuracy, speed and controlled force.
Coventry Associates in Shrewsbury, Mass., has developed a three-axis system for a variety of machining operations. Called the Eccentric Positioning System (EPS), the fully electric system, eliminates pneumatics and hydraulics, reduces setup and cycle time, uses less energy, and has a small footprint, said Craig Gardner, president of Coventry Associates.
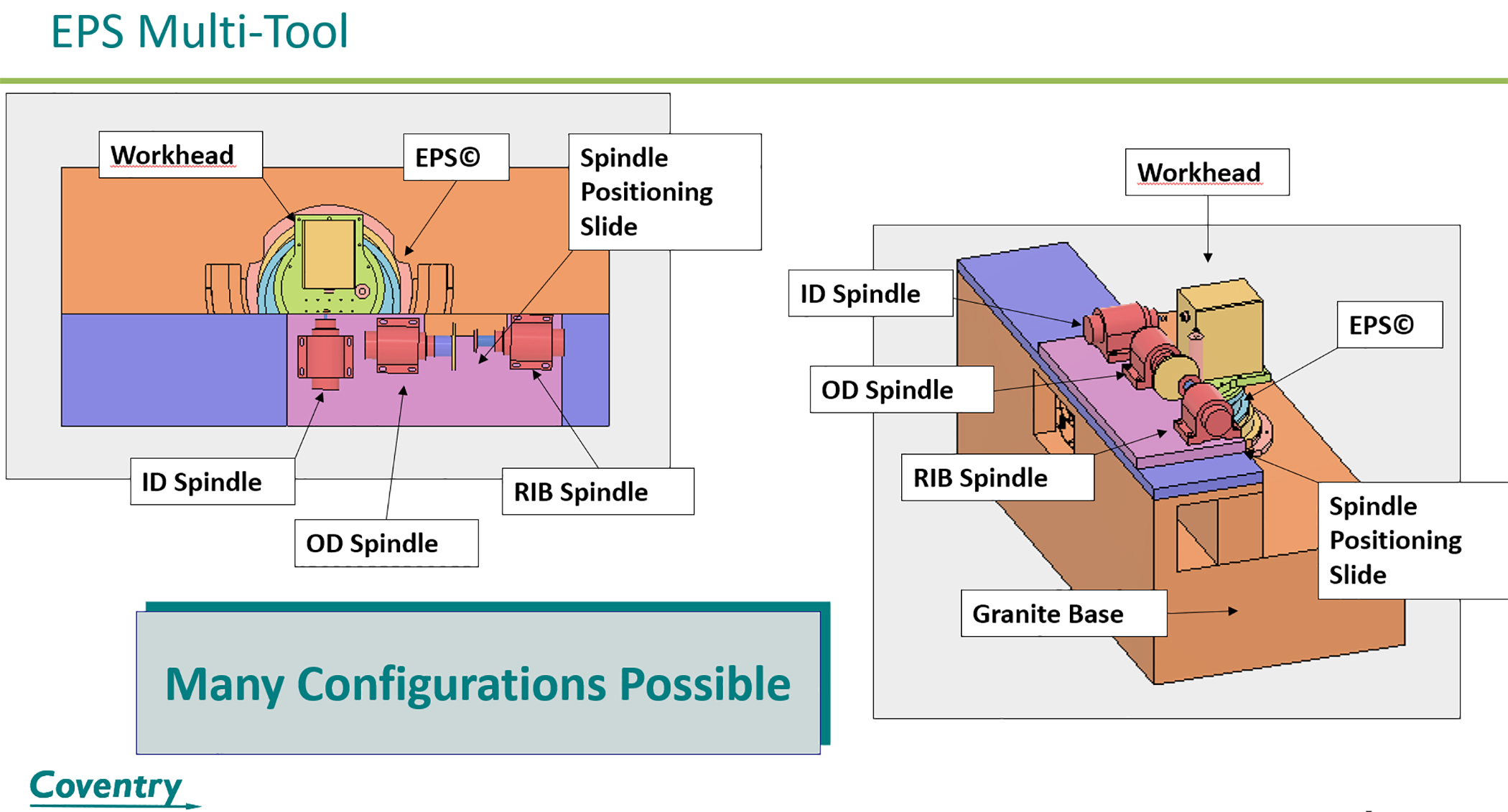
EPS is a mechatronic system that consists of a stack of three eccentric rotary tables. By controlling the rotation of each rotary table, the precise position and angle of a tool are achieved. The positioning accuracy and adaptive performance of the EPS system are enabled by the Siemens Sinumerik CNC, as seen in this video.
EPS has been incorporated into an ID grinding-machine/" data-glossary-id="141847" data-glossary-teaser="Powers a grinding wheel or other abrasive tool for the purpose of removing metal and finishing workpieces to close tolerances. Provides smooth, square, parallel and accurate workpi…" title="Powers a grinding wheel or other abrasive tool for the purpose of removing metal and finishing workpieces to close tolerances. Provides smooth, square, parallel and accurate workpi…" aria-label="Glossary: grinding machine">grinding machine where it has demonstrated three distinct advantages. It can dress or grind any shape without the use of diamond rolls or special dressing attachments. Secondly, it can grind by adaptively controlling the normal grinding force, rather than the feed rate, which dramatically improves material removal rates. Third, it compensates in real time for deflections that result in workpiece diameter and/or taper variation, improving both quality and throughput.
Gardner said that the EPS "has potential applications in all grinding and chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery…" title="Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery…" aria-label="Glossary: turning">turning operations for the machine tool industry." He added that the EPS will be made suitable for any machining operation that requires a combination of high positioning accuracy and controlled force.
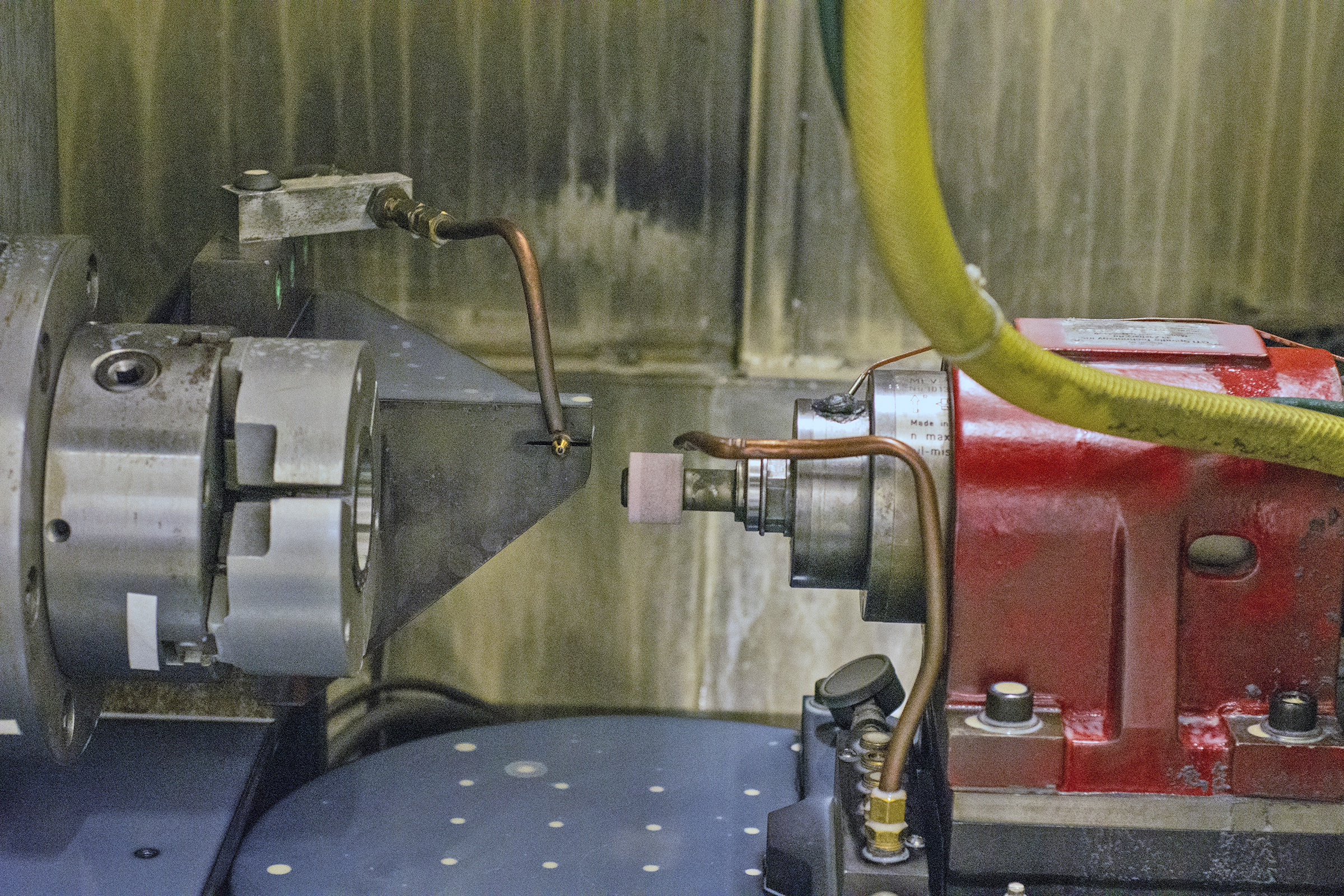
Coventry's launch product, EPS SingleTool, is designed for bearing ID grinding operations, using a single wheelhead. A shoe or chuck workhead can be used, with a single point or rotary dresser for shaping any contour. Power consumption is 10kW max. and the weight is 630 kg, with exterior dimensions of 305 mm x 660 mm x 560 mm.
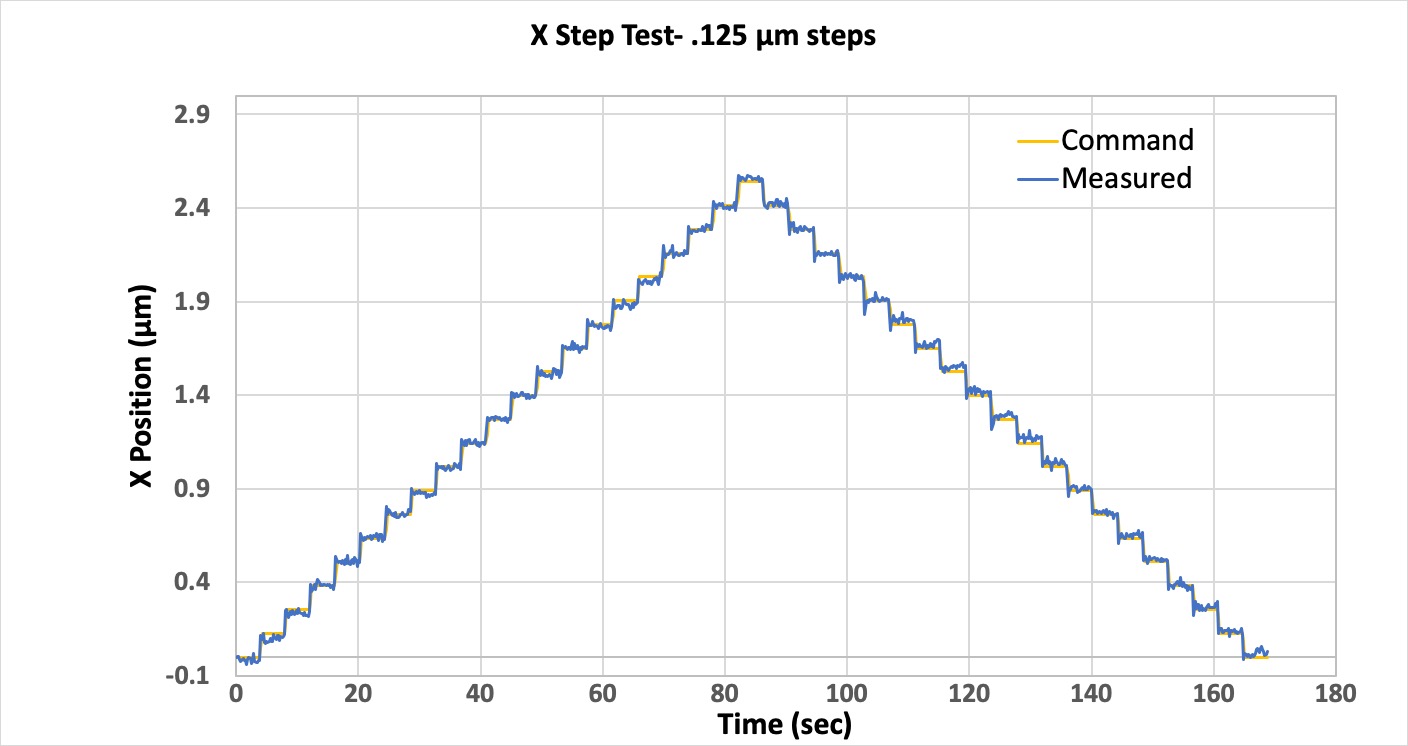
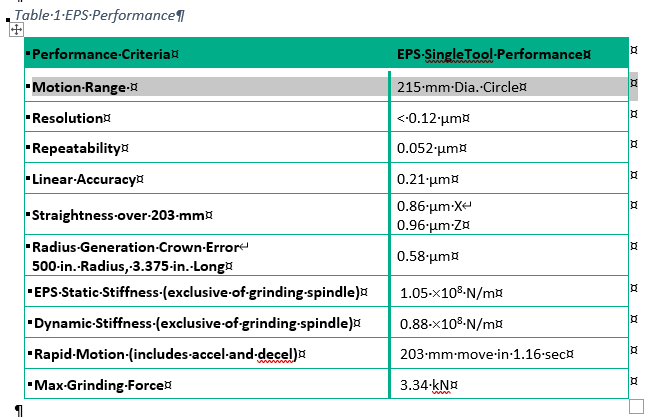
Coventry validated the positioning performance of the EPS SingleTool using a laser interferometer to measure its resolution, accuracy, repeatability, and straightness capability.
Because of the unique kinematics of the EPS, all motions are three-axis interpolated moves. The results of these measurements are shown in Table 1. These measurements show state-of-the-art positioning capability with a repeatability of 52 nanometers.
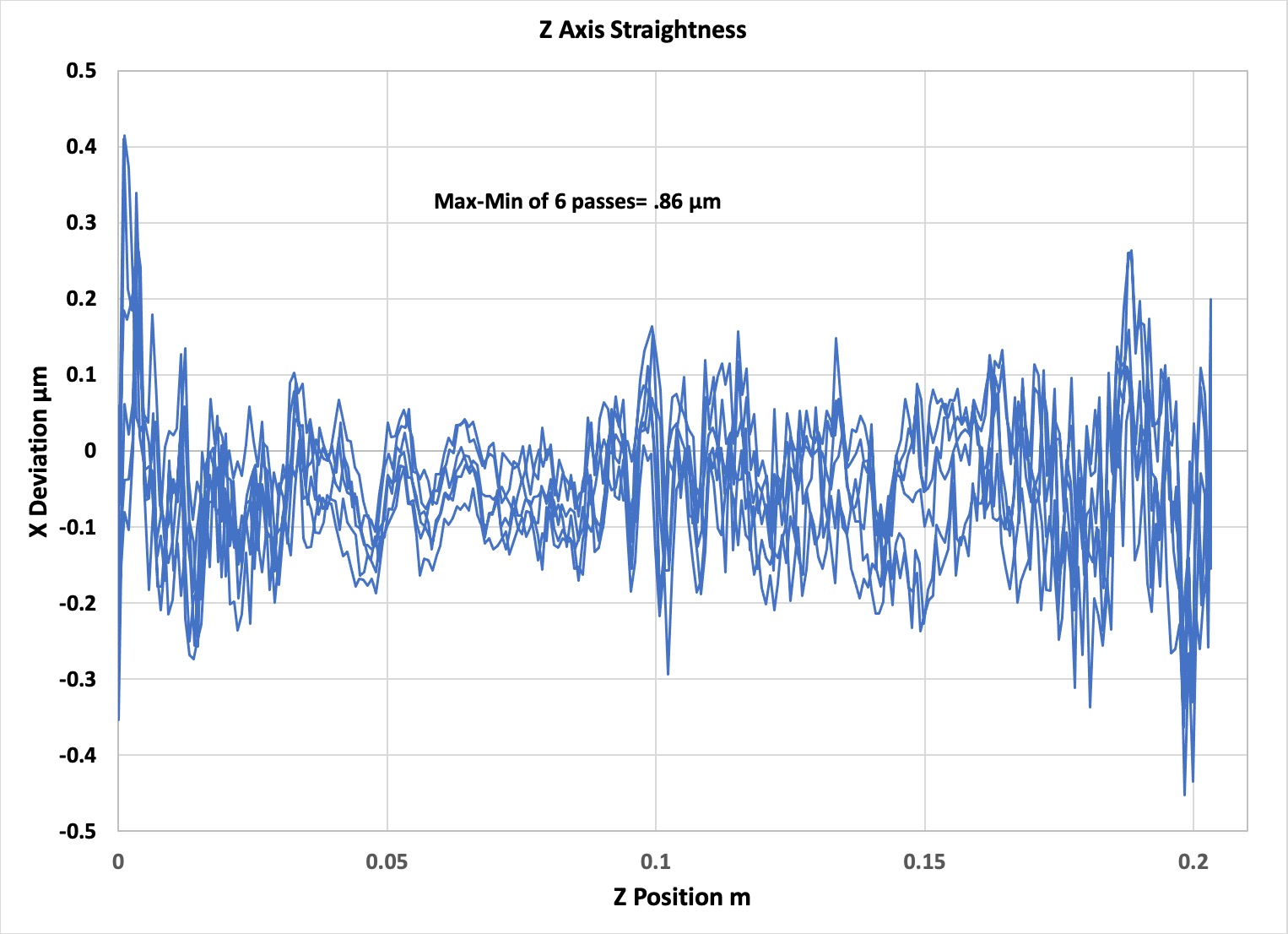
The system also has high static and stiffness/" data-glossary-id="141930" data-glossary-teaser="Measure of a machining system’s ability to dampen vibration from a forced input. If the stiffness/" data-glossary-id="141930" data-glossary-teaser="Measure of a machining system’s ability to dampen vibration from a forced input. If the dynamic stiffness of a system is not sufficient to dampen vibration, chatter occurs. See sta…" title="Measure of a machining system’s ability to dampen vibration from a forced input. If the dynamic stiffness of a system is not sufficient to dampen vibration, chatter occurs. See sta…" aria-label="Glossary: dynamic stiffness">dynamic stiffness of a system is not sufficient to dampen vibration, chatter occurs. See sta…" title="Measure of a machining system’s ability to dampen vibration from a forced input. If the dynamic stiffness of a system is not sufficient to dampen vibration, chatter occurs. See sta…" aria-label="Glossary: dynamic stiffness">dynamic stiffness as well as the ability to grind with large forces and make rapid motions to minimize the time required to make non-grinding motions.
The figure below (figure 4) shows the X deviation or "straightness" achieved during 3 back and forth (6 passes total) Z axis moves. This data shows that the difference between the maximum and minimum values for all 6 passes was less than a micron over 200 mm of travel.
Coventry worked closely with the Fraunhofer USA offices in Boston, Massachusetts, plus two key partners, Saint Gobain Abrasives and Siemens Industry, Inc., to develop the initial SingleTool ID grinding application.
As Gardner explained, "Our business strategy is to bring the EPS to market as a hardware and software solution, either as a complete machine to end users or as a platform for machine builders. Our solution features all-electric operation, using no pneumatics or hydraulics. We typically see resolution less than 0.12 microns with 0.05 microns repeatability, plus linear accuracy to 0.12 microns with consistent static and dynamic stiffness to a maximum grinding force of 3.34 kN. Rapid motion, including acceleration and deceleration, is tracking a 203 mm movement in 1.16 sec."