Beyond Evolution GUP-V insert
Beyond Evolution GUP-V insert
All Beyond Evolution insert styles feature the Triple-V Seating: Tight grip on the back (1) and top & bottom (2) provides maximum stability, especially when operating multidirectional turning and profiling.
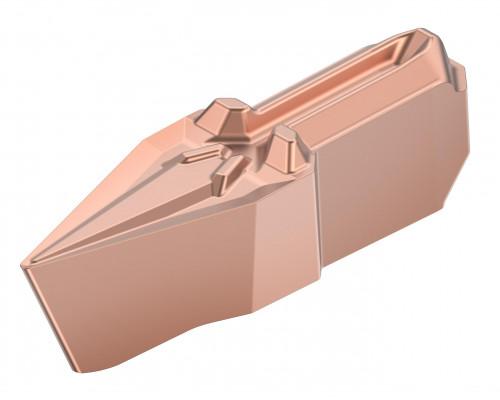
Kennametal has introduced the new Grooving Universal Positive Profiling geometry (GUP-V), expanding on its Beyond Evolution grooving & cut-off platform. With the addition of the new V- shaped single-sided insert, Beyond Evolution can cover now more applications than ever and helps to save tooling cost.
Expanding from grooving, cutoff, facing, and turning now also to profiling applications: the new Beyond Evolution GUP-V insert.
"Since the introduction of the Beyond Evolution platform, we have continued to focus on enhancing its versatility, and the new GUP-V multidirectional profiling insert is no exception says Robert Keilmann, Product Manager, Kennametal. "Together with the other insert geometries, users can now groove, cutoff, face, and turn a wide variety of materials with just a single tooling system. Simply put, when a customer adopts Beyond Evolution for their turning needs, they do not need anything else. It is that versatile."
All Beyond Evolution insert styles feature the Triple-V Seating: Tight grip on the back (1) and top & bottom (2) provides maximum stability, especially when operating multidirectional turning and profiling.
Like all other Beyond Evolution inserts, the GUP-V profiling insert leverages a proprietary Triple-V seating design that features contact on the top, bottom, and back of the insert, providing superior rigidity that results in excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy while delivering the highest metal removal rates.





