ESPRIT CAM Software Delivers Solutions for Industry 4.0
ESPRIT CAM Software Delivers Solutions for Industry 4.0
To prepare factories for an increasingly digital future, and to better support Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing initiatives, DP Technology is focusing on a range of solutions to drive automation in manufacturing. The ESPRIT CAM system enables manufacturers to streamline their workflows, prevent silos from forming during the manufacturing process, increase tool life and machine utilization, and create greater access to practical knowledge for process improvement.
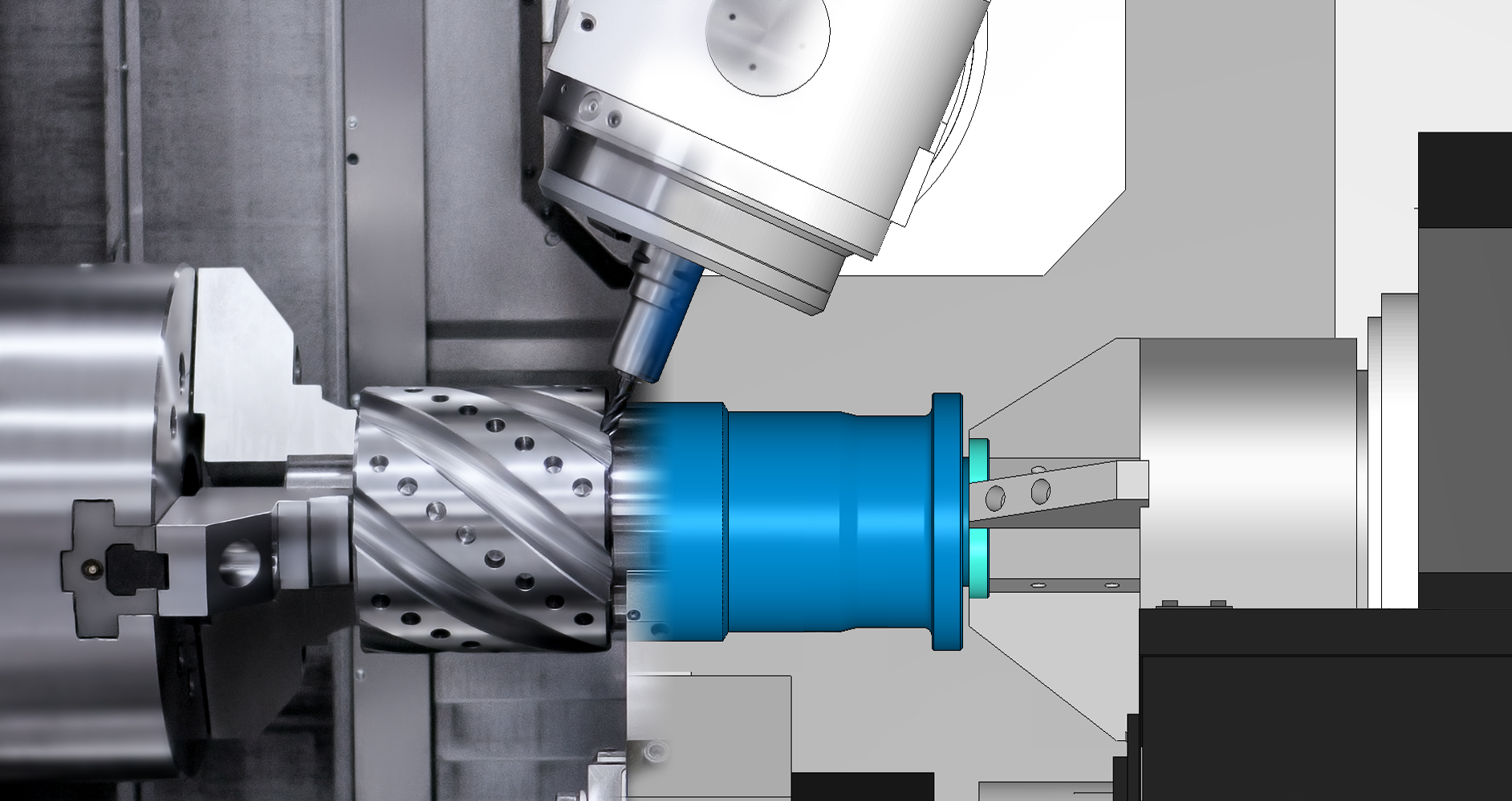
To prepare factories for an increasingly digital future, and to better support Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing initiatives, DP Technology is focusing on a range of solutions to drive automation in manufacturing. The ESPRIT CAM system enables manufacturers to streamline their workflows, prevent silos from forming during the manufacturing process, increase tool life and machine utilization, and create greater access to practical knowledge for process improvement.
ESPRIT allows users to create a digital twin of their machine tools for programming, optimization and simulation. This virtual machine ensures that whatever happens on screen will also occur on the shop floor. Workpieces and cutting tools are set up virtually, resulting in exacting simulations, greater productivity and better toolpaths for higher quality parts.
With ESPRIT, a digital thread ties together each step of the workflow from CAD design to finished part, ensuring that none of the manufacturing process is siloed. ESPRIT reads part data from CAD software and creates machine-optimized G-code and setup sheets, which it then passes on to shop floor management, tool data management and enterprise resource planning software.
ESPRIT provides machine-aware CAM programming to increase tool life and reduce cycle times. The CAM system's ProfitMilling and ProfitTurning apps reportedly represent a fundamental change in the way toolpath in created: most CAM software works from the shape of the part first and considers the machine last, if at all. ESPRIT machine-aware solutions first consider the machine tool – its axes positions and their limits, acceleration, and attainable and requested cutting speeds, allowing users to run machines faster, get a better surface finish on their parts and significantly increase their tool life. As a result, with machine-aware CAM, programmers make better choices regarding toolpath, without asking the machine tool or cutting tool to exceed their own abilities.
Knowledge-based machining, the term for artificial intelligence built directly into a CAM system, makes it possible to significantly cut programming time by capturing best practices, including machining processes and cutting conditions—leaving more time to focus on strategic process improvements and reducing time spent on repetitive tasks. ESPRIT's KnowledgeBase solution streamlines part programming by automatically selecting the optimum processes—machining cycles, tools and conditions—for part features based on proven best practices. Recording practical knowledge via KnowledgeBase is more reliable than leaving it to memory and allows for higher levels of automation
through repeatable steps. Because programming is more predictable and consistent, programmers encounter fewer problems and produce higher quality parts.
As shops move to data-driven manufacturing, integration with cloud-based databases, such as MachiningCloud Inc., further facilitates access to knowledge, product data, resources and process controls for machines, cutting tools and work holding. These cloud-enabled databases suggest factory-recommended feeds and speeds for a given cut, let users quickly find the tools they need, and provide continuously updated manufacturer product data, including drawings and models of tools and cutting tool assemblies for simulation. Because information is stored in the cloud, it is always up to date, available on demand and can be accessed anywhere.





