Contact Details
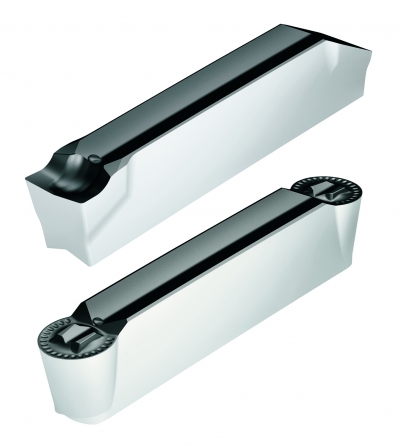

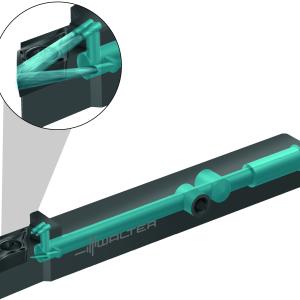
Walter has added PCD grooving inserts to its Walter Cut GX grooving system, the innovative tool technology for grooving and parting off. These new geometries, straight edge (F1) and full radius (M1) excel at grooving in aluminum and titanium alloys, bringing high cutting speed, longer tool life and fine surface quality to grooving, parting and recessing operations. These geometries work particularly well in aerospace, medical device and automotive applications.
The WDN10 is a new high-performance and wear-resistant polycrystalline diamond (PCD) grade that delivers outstanding hardness, a low coefficient of friction and minimum heat distortion. This helps result in maximum productivity and cost efficiency in the high-speed machining of nonferrous materials. These new Walter grooving inserts achieve excellent surface finish because of their exceptional cutting-edge sharpness. This sharpness is achieved by controlling the PCD grain size and through the Walter manufacturing process.
The GX24-WDN10 inserts boast chipbreaker geometry, are laser marked with grade designation along with ISO and ANSI corner-radius designation, and feature widths from 0.078 in. to 0.118 in. (2 to 8 mm).
Related Glossary Terms
- alloys
alloys
Substances having metallic properties and being composed of two or more chemical elements of which at least one is a metal.
- chipbreaker
chipbreaker
Groove or other tool geometry that breaks chips into small fragments as they come off the workpiece. Designed to prevent chips from becoming so long that they are difficult to control, catch in turning parts and cause safety problems.
- cutting speed
cutting speed
Tangential velocity on the surface of the tool or workpiece at the cutting interface. The formula for cutting speed (sfm) is tool diameter 5 0.26 5 spindle speed (rpm). The formula for feed per tooth (fpt) is table feed (ipm)/number of flutes/spindle speed (rpm). The formula for spindle speed (rpm) is cutting speed (sfm) 5 3.82/tool diameter. The formula for table feed (ipm) is feed per tooth (ftp) 5 number of tool flutes 5 spindle speed (rpm).
- grooving
grooving
Machining grooves and shallow channels. Example: grooving ball-bearing raceways. Typically performed by tools that are capable of light cuts at high feed rates. Imparts high-quality finish.
- hardness
hardness
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to surface indentation or abrasion. There is no absolute scale for hardness. In order to express hardness quantitatively, each type of test has its own scale, which defines hardness. Indentation hardness obtained through static methods is measured by Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop tests. Hardness without indentation is measured by a dynamic method, known as the Scleroscope test.
- parting
parting
When used in lathe or screw-machine operations, this process separates a completed part from chuck-held or collet-fed stock by means of a very narrow, flat-end cutting, or parting, tool.
- polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
Cutting tool material consisting of natural or synthetic diamond crystals bonded together under high pressure at elevated temperatures. PCD is available as a tip brazed to a carbide insert carrier. Used for machining nonferrous alloys and nonmetallic materials at high cutting speeds.
- polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)2
polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
Cutting tool material consisting of natural or synthetic diamond crystals bonded together under high pressure at elevated temperatures. PCD is available as a tip brazed to a carbide insert carrier. Used for machining nonferrous alloys and nonmetallic materials at high cutting speeds.
- recessing
recessing
A turning operation in which a groove is produced on the periphery or inside a hole of a workpiece. The grooving tool moves at right angles to the axis of rotation.










 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

