Model RG Linear Drive Assemblies
Model RG Linear Drive Assemblies
Amacoil-Uhing Model RG linear drive assemblies feature an option for fine adjustment of travel distance.
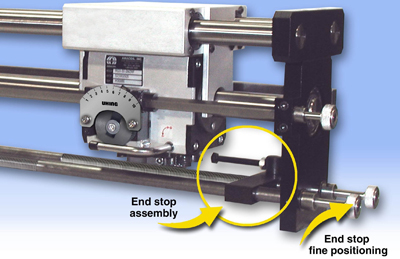
Amacoil-Uhing Model RG linear drive assemblies feature an option for fine adjustment of travel distance. The option enables more precise location of the drive unit reversal points. This is useful in linear motion applications where precision setting of the reversal points enhances process accuracy and integrity. The Model RG drive is used in various types of production equipment including converting/packaging machinery, CNC machinery, wire/cable spooling equipment and other automated machinery with a linear motion component.
In a standard Uhing linear drive assembly, the end stops determining stroke length are situated on hex rods held in place with set screws. Users loosen the set screws, slide the stops to set the travel distance, then re-tighten the set screw. The fine adjustment option has the end stops positioned on threaded rods. The rods extend through the pillow block end supports and a control knob is mounted on the end of each rod. Turning the control knobs rotates the threaded rods causing the end stops to move in very fine increments. This permits accurate location of the reversal points resulting in a higher degree of precision in applications such as level winding, spray coating, scanning, slitting and other reciprocating linear motion processes.
An additional benefit of the travel adjustment option is that operators may adjust travel distance while the drive is running, without placing hands near moving parts and risking injury. The control knobs are typically positioned on the end of the threaded rods opposite the drive end of the assembly. This assures clearance for connecting the shaft to the drive motor. Existing Uhing linear drive assemblies are readily retrofitted either in the field or at Amacoil's assembly shop.
Uhing Model RG drives are available in seventeen sizes with axial thrust from 7 to 800 pounds. A complex electronic control system is not needed because travel speed and direction are mechanically controlled, independent of the drive motor. Amacoil representatives can help with correct size selection for almost any application. Periodic light lubrication of the shaft is the only maintenance required.





