MVR-5X Machining Center
MVR-5X Machining Center
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. has developed a new 5-face plano miller type machining center, the "MVR-5X," suitable for machining of free-form curved surfaces such as aircraft parts and metallic molds.
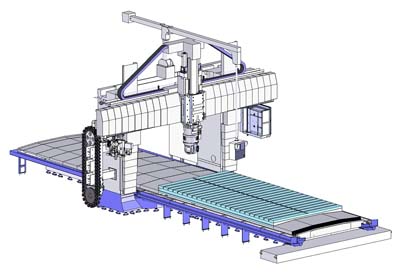
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (MHI) has developed a new 5-face plano miller type machining center, the "MVR-5X," suitable for machining of free-form curved surfaces such as aircraft parts and metallic molds. Plano miller type machining centers form the mainstream among large-size machine tools. Through adoption of an optional 2-spindle device attachable to the main spindle, the MVR-5X enables users to select either simultaneously controlled 5-face machining or regular 3-face machining according to the work desired, thereby offering users a broader range of potential applications.
The MVR-5X is the newest model in the "MVR Series," a lineup MHI introduced to the market in 2003 whose product portfolio has undergone progressive expansion. The adoption of an attachment device with two spindles — one slant-angled to the main spindle (B-axis) and the other right-angled to the main spindle at the spindle head (C-axis) — set to the main spindle enables simultaneous control of 5-axes, in addition to regular X-, Y- and Z-axis control. With the attachment, the MVR-5X is capable of performing arbitrary angle machining that enables machining of any desired angle at any desired spot, besides regular machining by the main spindle.
The two axes of the 2-spindle attachment deliver a maximum spindle speed of 15,000 revolutions per minute (rpm) and a rated spindle motor power output of 15 kilowatts (kW); maximum motor power output is 22 kW with a duty factor of 25 percent ED. The unit is designed to provide a wide range of spindle axis angles, enabling machining work at the desired face angle. The slant angle of the B-axis can be set within a range of plus or minus 92 degrees against the main spindle axis, while the C-axis's swivel angle can be set within a plus or minus 200 degree range. By minimizing the size of the attachment, an easy-to-operate structure has been achieved. Independent automatic changers for the attachments and tools enable quick changeover, thus contributing to enhanced productivity. The machine is also equipped with a scale feedback function, for high-precision positioning.
While demand for 5-face machining centers has been increasing, especially in the aircraft manufacturing industry, the number of users who use a 5-face machining as their core system in actual operation is still limited. Meanwhile, the number of users who look to expand their high-value-added machining work requiring 5-face machining, in addition to regular machining, is rising. Also, users who do not need 5-face machining but require arbitrary angle machining are increasing. The MVR-5X has been newly developed to respond to the desires of all these users.
The first MVR-5X unit will be delivered to Akaba Seisakusho in Nagano Prefecture, Japan, a company that undertakes precision machining of machine parts.





