P6006 Indexable Inserts
P6006 Indexable Inserts
Ideal for holemaking without a pilot drill up to 10×Dc, the inserts provide time savings that boost productivity. The inserts were designed to achieve maximum tool life in stable machining conditions thanks to the wear resistant WPP25 grade with HIPIMS technology. The grade has a particularly hard and robust substrate to extend tool life.
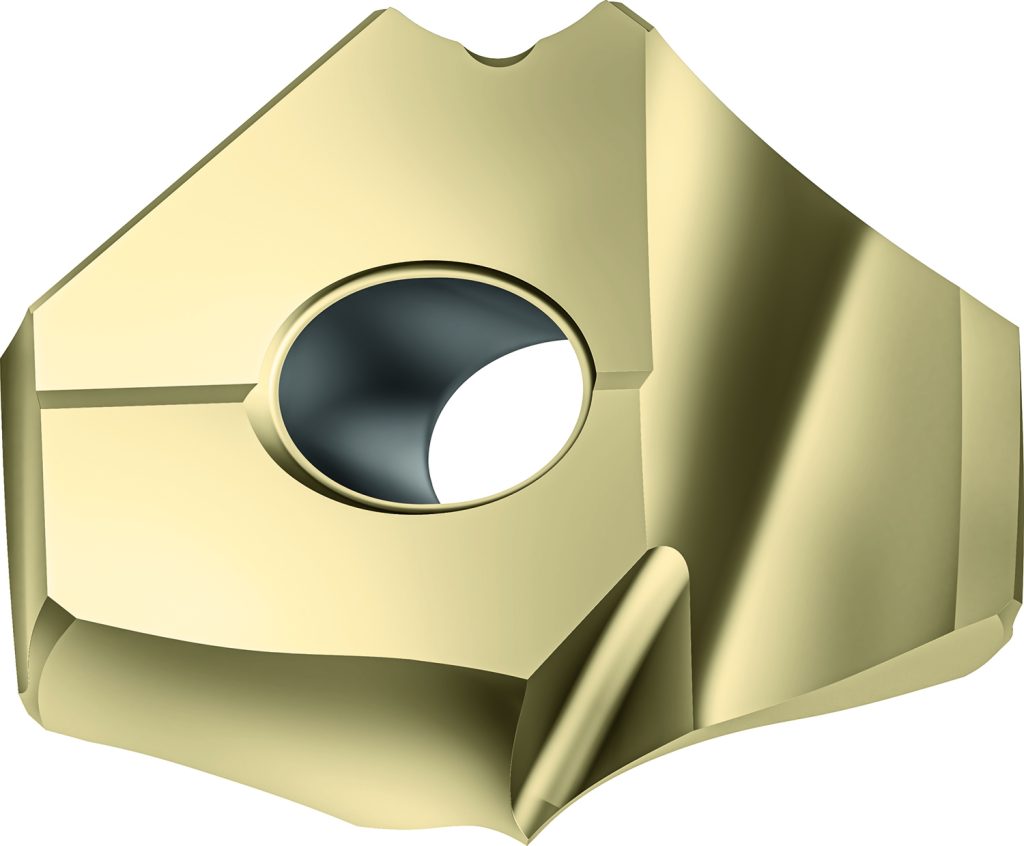
Walter has announced an expansion of the range for its P6006 indexable inserts for exchangeable-tip drills. The P6006 can be used in all exchangeable-tip drills D4140, D4240, and D4340. Drilling from solid material and stacked plate (laminate) drilling is possible with the D4140 indexable drill insert.
The primary application for the inserts is drilling low carbon, or unalloyed steels (ISO P workpiece group), specifically with low hardness range of 300HB or lower. The secondary application is for drilling non-ferrous metals (ISO N workpiece group). Areas of use include the general mechanical engineering, energy, automotive and aerospace industries.
Ideal for holemaking without a pilot drill up to 10×Dc, the inserts provide time savings that boost productivity. The inserts were designed to achieve maximum tool life in stable machining conditions thanks to the wear resistant WPP25 grade with HIPIMS technology. The grade has a particularly hard and robust substrate to extend tool life. The inserts provide maximum process reliability because of efficient chip breaking, a high level of centering accuracy and the ability to impart the finest surface quality and the best wear detection because of the exceptionally smooth gold-colored top layer.
The inserts feature a new type of geometry with a 140°point angle. The sharp cutting edge in connection with a positive rake angle reduces cutting forces. The tools also feature the signature 100° prismatic base for the contact point in the body and a corner-protection chamfer. Walter offers the P6006 indexable drill inserts for diameters of 12.00-37.99 mm (0.472-1.496 in.).





