SmartCAM CAM Software
SmartCAM CAM Software
SmartCAMcnc has announced the release of SmartCAM v2018. The SmartCAM CAM software family consists of applications for CNC milling, turning, fabrication and wire EDM.
SmartCAMcnc has announced the release of SmartCAM v2018. The SmartCAM CAM software family consists of applications for CNC milling, turning, fabrication and wire EDM.
SmartCAM v2018 delivers new Adaptive Rough Milling technology in the Advanced Milling, SmartCAM FreeForm Machining and SmartCAM Advanced Turning applications; new Verification modules in SmartCAM Advanced Fabrication and SmartCAM Advanced Wire EDM; improved feed rate control and numerous other useful core additions found in all products.
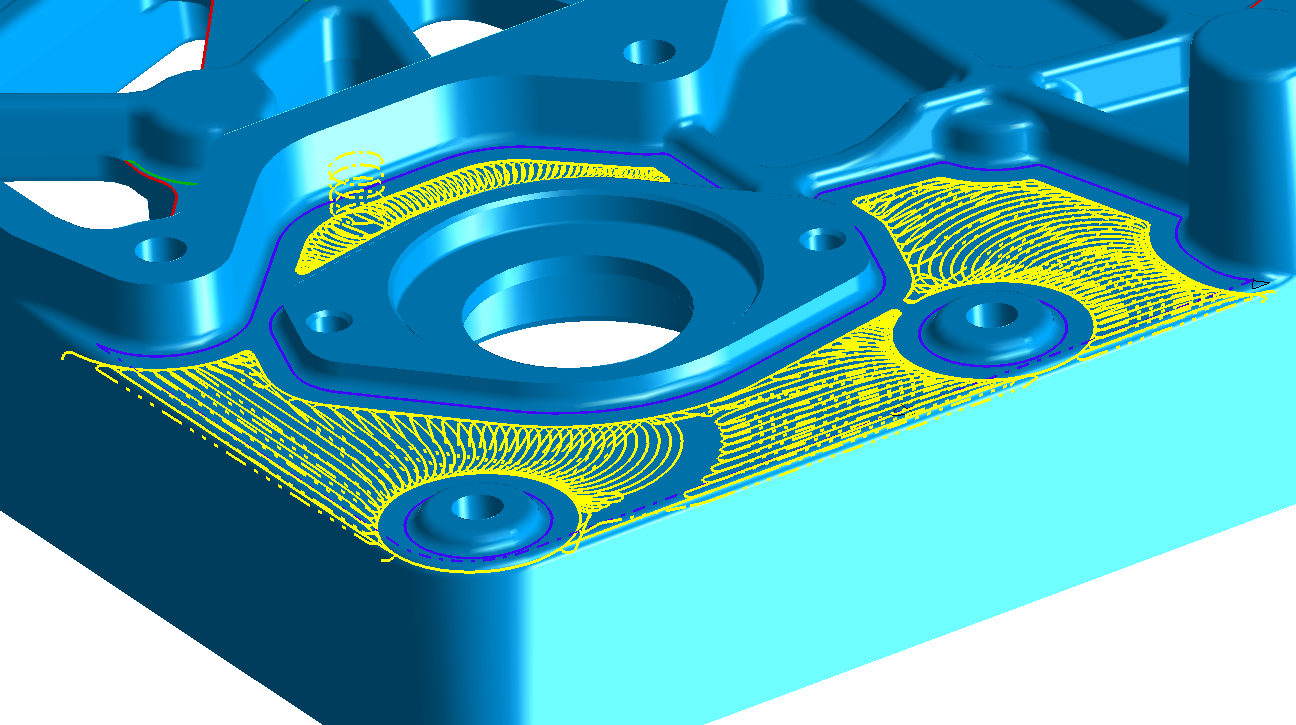
The SmartCAM Adaptive Roughing toolpath results in consistent cutting condition, elimination of full-width slotting cuts and automatically created adaptive feedrates, which provide end user benefits of increased tool life, reduced cycle time and reduced shock on their machine, according to the company.
"Traditional offset toolpaths present several problems such as sharp corners, sudden changes in cutting tool load and shock on the machine tool, all of which can lead to shortened tool and machine life, even breakage," said Doug Oliver, senior product manager at SmartCAMcnc.
"With the new SmartCAM Adaptive Roughing toolpath processes, the engagement volume of the cutter with stock is constantly monitored and maintained using in-process-stock algorithms. These algorithms handle the changing volume conditions encountered when creating toolpath for the infinite geometric possibilities," Oliver added.
Features of the SmartCAM Adaptive Roughing processes include:
- Near-constant cutting conditions throughout the toolpath
- Sharp corners are never generated
- Independent, user-controlled width of cut and feed rates for climb- and conventional-cut toolpath
- Auto-start position with smooth entry allows entry from open boundaries at full cut depth where possible
- Cuts can be linked with smooth connections that lift the tool off the floor while returning to the start of the next cut at fast-feed rate
- User controls for unidirectional with fast-feed returns or bi-directional adaptive passes
- Plunge, Ramp or Helical entry types can be specified under user control
- Options for Rest-Mill Uncut Regions creation
In May 2017, the new SmartCAM Verify Module was delivered in SmartCAM milling and turning applications; it is now included in the SmartCAM Advanced Fabrication and SmartCAM Advanced Wire EDM applications. The module uses the industry-leading ModuleWorks simulation technology, providing accurate material-removal verification and collision-checking capabilities.
Additional verification improvements:
- Creation of revolved stock in all applications using open- or closed-wireframe profiles. (Previously this ability was only found in SmartCAM turning applications.) With this change, the stock profile will be revolved around the X-axis of the workplane assigned to the profile geometry.
- Hide Small Pieces During Verification - Verification can now automatically remove separated stock pieces, or "chunks", such as when there is material remaining from inside a closed profile. This verification option allows the user to remove waste material during the simulation to better see the final results of the toolpath.
- Two new 'Pause At' Conditions for tool changes and/or collisions can be used to pause the simulation to allow closer examination of toolpath process Verification.
"In our previous release, we began a new and productive relationship with ModuleWorks. By Adding Adaptive Roughing in SmartCAM v2018, we extend that partnership, and remain excited by the various technology now available to us to implement going forward. Our customers have been uniformly pleased with the significant improvements resulting in their SmartCAM products," said Oliver.
SmartCAM Core Improvements Include:
- Feed Overrides and Feed Entity Type - feed rate capability and flexibility have been expanded with several changes that provide better and more complete control of toolpath feed rates
- New CAD/Process Plan List View - visually separates the CAD geometry from the CAM toolpath geometry
- Updated solid modeling kernel - SmartCAM v2018 includes the most-current ACIS 2018 Solid Modeling kernel
- Updated data translators - SmartCAM v2018 includes updated CAD data translators for Pro-E/Creo 4.0 and ACIS SAT/SAB R2018 data files





