SmartCAM v2017
SmartCAM v2017
SmartCAMcnc has announced the release of SmartCAM v2017. SmartCAM v2017 delivers new verification technology, as well as expanded rotary axis and code generation support, and improvements to the user interface and rough milling functionality. The SmartCAM CAM software family consists of toolpath creation applications for CNC milling, turning, fabrication and wire EDM.
SmartCAMcnc has announced the release of SmartCAM v2017. SmartCAM v2017 delivers new verification technology, as well as expanded rotary axis and code generation support, and improvements to the user interface and rough milling functionality. The SmartCAM CAM software family consists of toolpath creation applications for CNC milling, turning, fabrication and wire EDM.
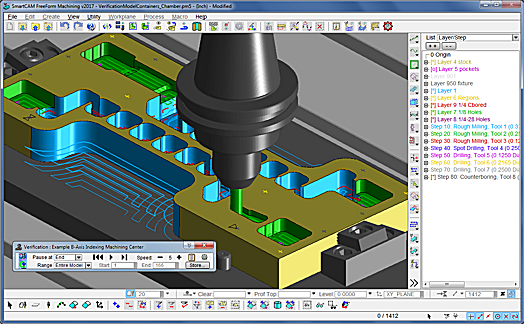
SmartCAM v2017 introduces a new integrated Verify module that replaces the separate ShowPath and ShowCut toolpath and material-removal verification functions of previous products. All verification is now performed in the main SmartCAM graphics window. Dynamic viewing and standard system display functionality is fully supported. Toolpath animation and back-plotting can be simultaneously viewed during material removal simulation.
The new SmartCAM verification uses the proven ModuleWorks simulation technology, and offers improved model accuracy and collision checking capabilities.
"Over the years we've had many customer requests to improve our material removal verification, in particular the ability to change the view while simulating. The new Verify module with its full dynamic viewing and tremendously improved capabilities, really delivers on those requests." said Doug Oliver, senior product manager at SmartCAMcnc.
"The new compact and simplified user interface provides much improved control. Users can now step through verification while automatically pausing after each move, element, or step." Douglas added. "Additionally, it's now possible to store the in-process stock model at any point during verification so it can be exported in standard STL format, or used as input to subsequent verification."
SmartCAM milling users will benefit from an updated Open Profile process, which uses new regioning technology to handle a wider set of geometric situations, and now includes lead in/out and cutter comp support, allowing it to be used for semifinishing and finishing applications. Rotary axis support has been enhanced and now includes features for specifying angle limits, and Euler angles for tilted plane commands, to name a few.
Numerous core improvements like drag and drop of the insert position or elements and nodes in the hierarchical list view, and enhanced code generation with new debugging and error checking capabilities, benefit all SmartCAM users. Additionally, SmartCAM v2017 incorporates the latest ACIS 2017 kernel with updated CAD data translators for SolidWorks and Inventor 2017, and Solid Edge ST9.
"SmartCAM v2017 marks the start of what we hope will be a long, productive relationship with ModuleWorks. We are excited by all the technology available to us, and think our customers will be as well when they receive more frequent and significant improvements to their SmartCAM products," said Oliver.





