Tiger·tec Gold WSM35G Milling Grade
Tiger·tec Gold WSM35G Milling Grade
The new grade is Walter's response to the upwards trend towards milling steel with difficult machining properties and wear-resistant stainless steel, such as found in applications in the energy and aviation industries. WSM35G meets the most stringent requirement for process reliability, which is highly valued in the automotive sector, and is also suitable for general mechanical engineering applications.
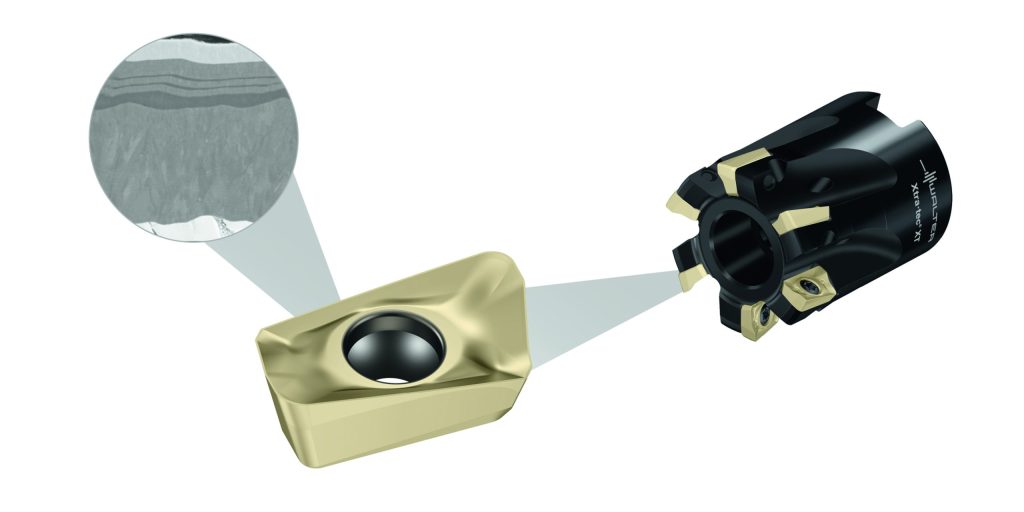
Walter is expanding its Tiger·tec® Gold range with the new WSM35G milling grade. The indexable insert is coated with the only PVD Al2O3 coating technology of its kind to date with a multi-layer structure on a carbide substrate. The structure consists of a bottom TiAlN layer for high wear resistance, a middle Al2O3 layer for high temperature resistance and a ZrN gold-colored top layer for minimized friction and the best wear detection.
The new coating ensures excellent cutting-edge stability and therefore a long tool life, as well as high process reliability, even in complex applications.
The grade WSM35G is for universal application even under abrasive and difficult conditions, such as interrupted cuts or during wet machining, when milling austenitic stainless steel or nickel-based superalloys (ISO M and S workpiece groups).
The new grade is Walter's response to the upwards trend towards milling steel with difficult machining properties and wear-resistant stainless steel, such as found in applications in the energy and aviation industries. WSM35G meets the most stringent requirement for process reliability, which is highly valued in the automotive sector, and is also suitable for general mechanical engineering applications.
Successful applications include milling aircraft engine components made of Inconel or titanium and machining high-temp automotive engine and turbocharger parts. In these applications, Walter's grade WSM35G increased tool life 30% or more compared to previously used cutting tool materials.
This new grade has been applied to inserts for all standard milling cutters in the Walter lineup, such as the Xtra·tec XT M5130 shoulder milling cutter, and many more.





