VERO-S Clamping System
VERO-S Clamping System
SCHUNK's VERO-S SPM-138 diaphragm clamping system allows users to machine the contour of their workpieces into the SPM unit.
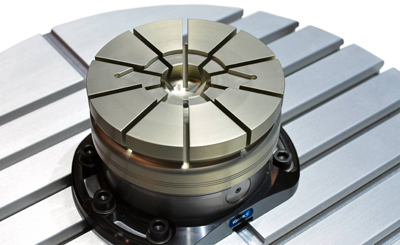
SCHUNK's VERO-S SPM-138 diaphragm clamping system allows users to machine the contour of their workpieces into the SPM unit. When the VERO-S module is engaged with the Turbo function the SPM-138 unit clamps evenly around the outside of the part.
The VERO-S SPM Plus 138 can clamp workpiece sizes: 36mm — 125mm in diameter, although the workpieces do not have to be round. The SPM unit generates clamping forces up to 50kN. The SCHUNK VERO-S is paving the way to more precision, efficiency, process reliability, and set up reduction in metal cutting and cmm inspection, according to the company.
The same VERO-S plus 138 module clamps small workpieces with the SPM Plus 138 top plate as well as pallets, clamping stations, existing fixtures, and tombstones with one or more clamping pins. The radial aligned clamping slides of the quick-change pallet system pulls in the clamping pin and locks it. This action retracts the Diaphragm top plate to hold the work piece with up to 50kN of force with a repeat accuracy of at least 5µm (0.0002"). The new VERO-S is completely compatible and interchangeable with SCHUNK's previous pallet system and the clamping pins work universally across the new line. Workpieces can be transferred from machine to machine or to a CMM accurately and seamlessly. Hardened Stainless Steel is used for all the functional components of the VERO-S, such as base body, clamping pin, and clamping slide. This increases the modules' life and reliability, and reduces maintenance.
The maintenance-free module is completely sealed and protected against the penetration of chips, dust, and coolant. Integrated into the standard module from SCHUNK is an air purge connection, which can also be used for part recognition. The position of the clamping slide can also be monitored via an air purge monitoring system. Each module is compatible for automated loading out of the box. Since the module is equipped with bottom and lateral air connections, it is completely flexible in its' mounting.





