Disruptive megatrends affect manufacturing
Disruptive megatrends affect manufacturing
The Manufacturers Alliance for Productivity and Innovation published a report in January about megatrends that are reshaping manufacturing. Titled "Manufacturing Megatrends: The Impact of Megatrends on U.S. Manufacturers," the report was authored by MAPI Director of Councils and Business Research Jenn Callaway, and is based on surveys conducted with manufacturing executives.
 The Manufacturers Alliance for Productivity and Innovation published a report in January about megatrends that are reshaping manufacturing. Titled "Manufacturing Megatrends: The Impact of Megatrends on U.S. Manufacturers," the report was authored by MAPI Director of Councils and Business Research Jenn Callaway, and is based on surveys conducted with manufacturing executives.
The Manufacturers Alliance for Productivity and Innovation published a report in January about megatrends that are reshaping manufacturing. Titled "Manufacturing Megatrends: The Impact of Megatrends on U.S. Manufacturers," the report was authored by MAPI Director of Councils and Business Research Jenn Callaway, and is based on surveys conducted with manufacturing executives.
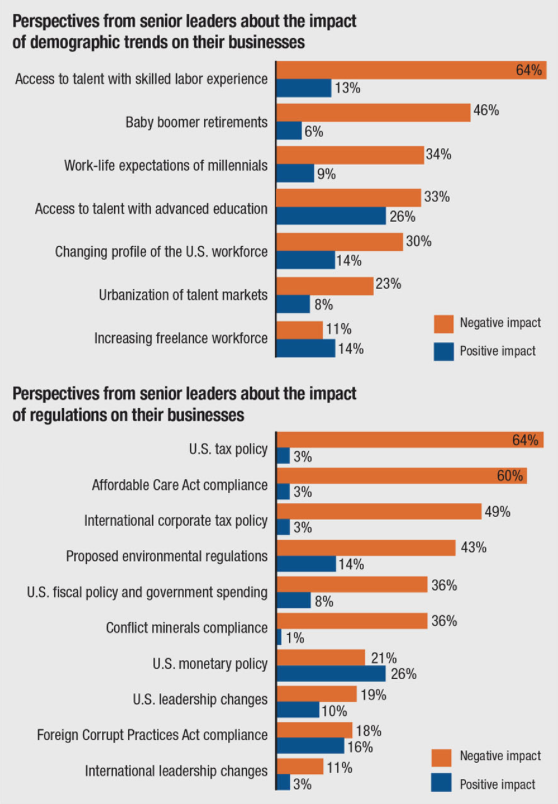
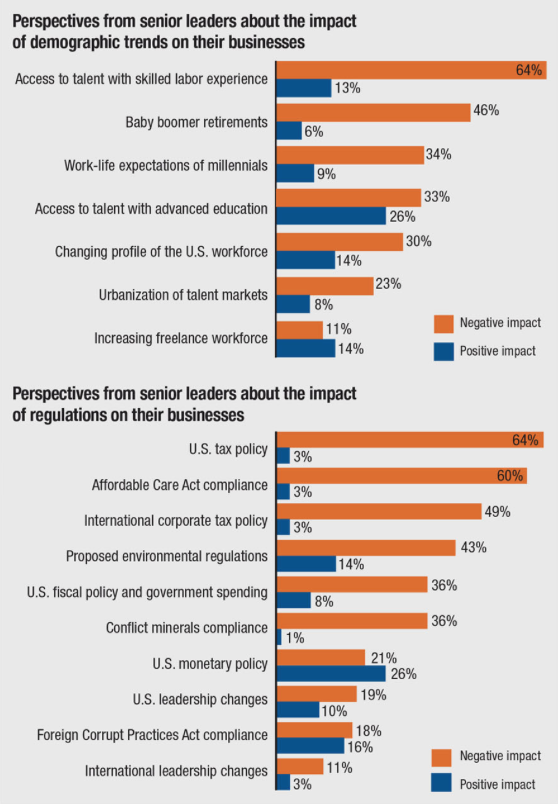
The MAPI report discusses five megatrends having the biggest impacts on the current manufacturing environment:
- The global economy and currency markets hindered business performance in 2015. "The executives we surveyed overwhelmingly pointed to economic factors as having the most significant negative impact on their businesses in 2015," the report stated. "Of the top 10 negative trends affecting businesses in 2015, all but one—the skills gap—concern economic or regulatory matters." In fact, economic and currency factors took four of the five spots on MAPI's list of factors negatively impacting businesses.
- The regulatory playing field isn't level. Company executives are the most critical of U.S. tax policy and point to the Affordable Care Act and conflict minerals compliance as examples of regulatory burdens that impede business performance.
- Tight labor markets continue to plague manufacturers. Although many baby boomers have delayed retirement to counterbalance the impact of the Great Recession on their savings, their unavoidable retirement compounds the challenge of finding skilled workers.
- Information transparency trends could be cause for optimism. Thanks to unparalleled access to information about pricing and profitability, 75 percent of surveyed executives report that understanding total cost of ownership had a positive impact on their business in 2015.
- Automation, robotics and remote monitoring are poised to offer companies a surge of opportunity in the future. Executives are overwhelmingly positive about the possibilities of these technologies.
The full report can be found here.





