Nickel-base superalloys can withstand hot and tough conditions, but are difficult to machine. With the right approach, machinists can keep their cool when cutting them.
Metal components used high in the sky and deep in the ground experience high-temperature, high-stress environments. For those applications, part designers often call on heat-resistant superalloys (HRSA), which are classified into nickel-, iron- and cobalt-base groups.
According to Pat Schuur, owner of metal distributor Schuur Metals Inc., San Clemente, Calif., the primary applications for nickel- and cobalt-base superalloys are for the aerospace, oil and gas and petrochemical industries. “That covers about 90 percent of HRSAs,” he said.
Superalloys provide high mechanical strength and resistance to surface degradation at temperatures of 1,200° F and above. That’s because HRSAs have high tensile, creep-rupture and fatigue strength; good ductility and toughness; and enhanced resistance to oxidation and hot corrosion, stated Rick Frank, metallurgist for metals producer Carpenter Technology Corp., Wyomissing, Pa.
Compared to other superalloys, iron-base superalloys cost less but are less tolerant of alloying additions and have less favorable mechanical properties and lower temperature limits. Cobalt-base superalloys cost significantly more than the others and typically cannot be age hardened to high strength levels. However, cobalt is an important alloying addition to nickel-base superalloys because it extends the maximum temperature they can be used at by reducing the solubility of the age-hardening phase.
Nickel-base metals represent at least half of the market for superalloys, with 718 Inconel, Waspaloy and Udimet 720 being the most prominent members of that group, according to Sean Holt, aerospace applications manager for Sandvik Coromant Co., Fair Lawn, N.J. He added that aerospace applications account for 60 percent of that group’s usage. Nickel-base superalloys represent about half of the weight of a typical aircraft engine, which has two hot areas: combustion and turbine.
This article covers applications for nickel-base superalloys, the properties of nickel and elements alloyed with it to produce the metals, tools and techniques for effectively cutting them and cost considerations when selecting the appropriate workpiece material.
Application Areas
In addition to aerospace engines, other common applications for nickel-base superalloys include power-generation-turbine parts, aerospace fasteners, automotive manifold bolts, diesel-engine exhaust valves and hot-working tools and dies, according to Carpenter Technology.
Paul Dickinson, new product engineer for Winsert Inc., Marinette, Wis., noted that the foundry is involved in numerous exhaust-gas recirculation applications using nickel alloys. “Basically, it’s making sure customers have a material that they can use to make their equipment, such as an engine running on diesel, EPA compliant,” he said. In addition to producing superalloys, the company also machines them based on customer requirements.
When copper is a major alloying element, the nickel-base superalloys are used to make electronic components, such as fuses and shunts, noted Gregory Zahm, quality and safety manager for Vista Metals Inc., Bristol, R.I., a warehouse distributor of bar, rod, wire and strip metals. One frequently used metal the company offers is Niclal 37 and 38, copper-manganese-nickel alloys that Vista sells in coil form or cuts to length. “For shunt applications, it takes high energy through a piece of equipment without any surges that may short out the equipment,” he said.
Zahm added that cobalt-nickel alloys provide magnetic shielding, so component-shielding shells and canisters are often made of the material, and copper-nickel alloys’ corrosion-resistance properties make them suitable for parts found in fumigation spraying equipment.
Because of their combination of strength, toughness and environmental resistance, some of the alloys are also suitable for other lower-temperature applications, such as medical implants.
Nickel and Alloying Elements
Although most superalloys contain more than 50 percent nickel, some do not. For example, Carpenter Technology reports its Pyromet A-286 alloy is still considered a superalloy with only 25 percent nickel.
In some applications, Zahm pointed out that the superalloy’s hardness and electrical properties increase as the percentage of nickel increases, which is beneficial for fuse or shunt applications.
Commercially pure (99.6 percent) nickel 200 is ductile and has good mechanical properties, high electrical and thermal conductivity and a low hardness, stated Ulbrich Stainless Steels and Special Metals Inc., North Haven, Conn., in a white paper about nickel-base superalloys. Although it has a relatively low workhardening rate, nickel strip can be cold worked to moderately higher strength levels while maintaining ductility.
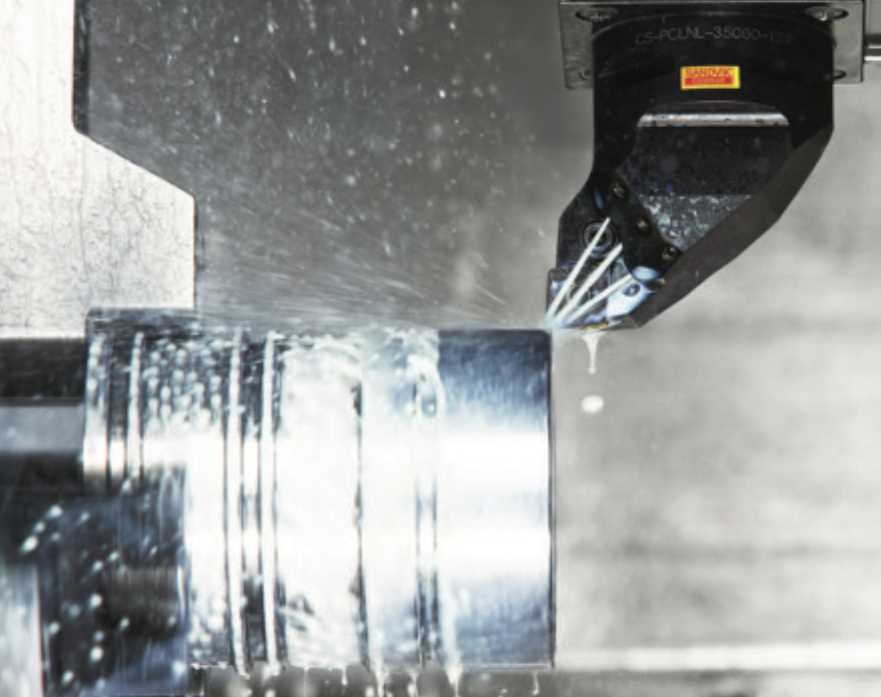

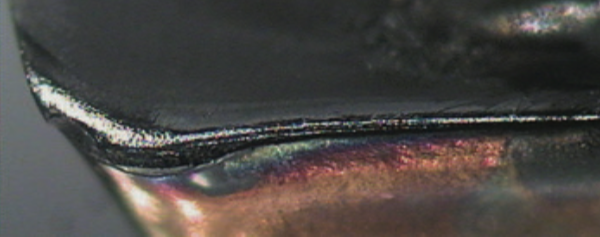
Courtesy of Sandvik Coromant
When turning heat-resistant superalloys, accurately targeted high-pressure coolant provides chip control while enhancing cooling at the tool/workpiece interface and enables higher cutting speeds.
The paper also stated that nickel 200 is best at resisting corrosion in reducing environments, which have little or no free oxygen, but can also be used under oxidizing conditions and in caustic environments that develop a passive oxide film on the alloy surface. Nickel also can withstand sulfuric acid at low or moderate temperatures, anhydrous hydrofluoric acid at elevated temperatures, organic acids of all concentrations (if aeration is not high), caustic soda and other alkalis and nonoxidizing halides.
Nickel 201, the low-carbon version of nickel 200, is similar in terms of corrosion resistance, according to the Ulbrich paper. It is preferred for applications involving exposure to temperatures higher than 600° F.
For most applications, alloying elements help to impart and maintain the desired properties at elevated temperatures, according to Carpenter’s Frank. In addition to nickel, superalloys contain various combinations of iron, cobalt and chromium, with smaller amounts of other elements, including molybdenum, niobium, titanium, aluminum and minor additions of beneficial elements such as boron and zirconium.
Refractory elements such as molybdenum, tungsten and niobium, with their large atomic diameters, increase high-temperature strength and stiffness by straining the nickel/iron base matrix, according to Frank. Larger additions of molybdenum increase this solid-solution strengthening effect. Other alloying additions, such as chromium and aluminum, also contribute to solid-solution strengthening, but to a lesser extent.
Frank added that titanium, aluminum and niobium are added to the nickel or nickel/iron matrix to form an intermetallic Ni3 (Al, Ti, Nb) phase during age-hardening heat treatments. The resultant gamma prime or gamma double-prime phases are the main strengthening agents in superalloys. Although other elements, such as boron, zirconium and magnesium, may be added at less than 0.1 weight percent, the beneficial effects are quite potent. These elements segregate to and stabilize grain boundaries, significantly improving hot workability, high-temperature strength and ductility. Small additions of carbon may be made to form carbides that restrict grain growth and grain boundary sliding during high-temperature exposure.
Numerous other elements, including silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, oxygen, nitrogen and a larger number of tramp elements (like lead, bismuth and selenium) must be tightly controlled in superalloys to avoid detrimental effects on high-temperature properties, Frank stated. These minor and tramp elements are controlled during raw material selection prior to melting, as well as during the melting and remelting processes.
Machining Guidelines
A number of wear mechanisms occur when machining HRSA. According to Sandvik Coromant’s Holt, the two major ones that have a detrimental effect on chip formation are built-up edge and, because the surface is prone to workhardening, notch wear.
The latter effect, also called notching, is found on the main and secondary cutting edges and is more prominent when cutting nickel- and cobalt-based alloys, the toolmaker reports. On the main edge, notching is seen as chipping at the DOC and is mainly mechanical wear. Notching occurs on the secondary edge where an insert exits the workpiece and negatively impacts the surface finish. Notching on the secondary edge is caused mainly by chemical wear; aluminum-oxide and PVD tool coatings are recommended to minimize it.
BUE and notching on the main and secondary edges can be minimized by applying round inserts with positive, reinforced geometries. “Round inserts are the strongest inserts available, and with a round insert you’re getting out of the area of notch wear by varying the entering/lead angle, depending on the depth of cut selected,” Holt said. “You should never be using a typical CNMG insert to machine superalloys as this creates a 95° entering angle, thus increasing notch wear on the insert.”
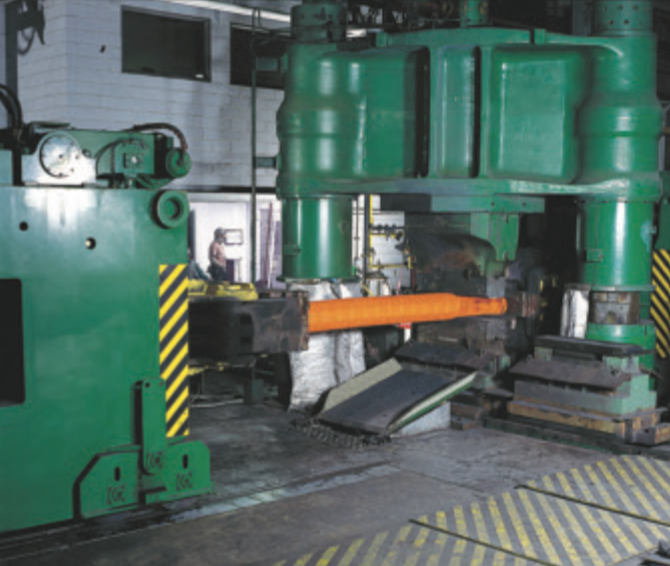

Courtesy of Carpenter Technology
Carpenter Technology’s vacuum arc remelting furnaces remove impurities from ingots produced in primary melting.
Although machining hardened materials tends to cause the most notching and increases the cutting temperature, it’s easier to effectively break a chip in harder nickel-base alloys because the material has less elasticity, Holt noted. “By fixing the coolant nozzle in the correct position, a parallel laminar coolant jet is created with high velocity to segment the chip in harder materials.”
He added that a heat-treated HRSA part with a hardness of 44 to 52 HRC is usually finish-machined, whereas the part is roughed in a softer state with a hardness of about 26 HRC. Softer materials are much gummier, he added.
Other wear mechanisms when cutting HRSA include plastic deformation, chip hammering and top slice, which is only found in ceramic tools. According to Sandvik Coromant, plastic deformation is thermal wear caused by high temperature and high pressure on the cutting edge.
An insert that resists flank wear and has high hot hardness helps reduce plastic deformation. “Wear on the insert should never exceed 0.008 " because that’s when you start to create plastic deformation in the insert and create negative residual stress in the part,” Holt said.
Chip hammering is a form of mechanical wear created when chips hit the edge line outside the cutting zone and mainly occurs when machining softer, more ductile nickel alloys. It can occur at the top and bottom of an insert, and changing the feed rate and DOC may redirect chips to reduce wear. Because they have a higher edge-line toughness, PVD-coated inserts rather than CVD-coated ones are recommended for nickel alloys, especially when roughing, according to Holt.
Top slice is caused by high cutting pressure and vibration and must be controlled when surface quality and burr minimization are important. To minimize top slice, Sandvik Coromant recommends lowering the cutting pressure by reducing the chip area in stable conditions, and reducing the engagement angle with programming techniques in vibration-generating unstable conditions.
Holt pointed out that when cutting nickel-base superalloys, trochoidal milling and trochoidal turning can be effective because they eliminate the high level of contact between the insert and workpiece and prevent wraparound. (Wraparound occurs when plunging or profiling corners with round inserts because of the high angular engagement, creating high cutting pressures. Therefore, the feed must be reduced.)
“A trochoidal toolpath is almost like a swinging toolpath,” he said. “You’re not plunging in. The insert is not under sudden shock and you get a nice, smooth, optimized toolpath. Especially when taking a smaller DOC, you can increase the feed rate and that helps with chip breaking as well.”
For controlling wear, in general, Holt recommends an entry angle of 45°, with a maximum of 60°.
According to Winsert’s Dickinson, getting through the surface layer, or forged skin, is the most difficult aspect of cutting nickel-base superalloys because that layer can have shrink porosity, slag inclusions and hairline cracks. “There are a whole lot of issues,” he said.
To get under the forged skin, also called “elephant scale,” Holt recommends a DOC up to 0.400 " with an insert having a sharp, positive rake angle to avoid high notch wear. That contrasts with a 0.020 " DOC for finishing.
Tooling and Cooling
In contrast to roughing titanium, where HSS tools are often applied, carbide and ceramic tools are suitable for roughing—and finishing—nickel-base superalloys, according to Holt. He noted that HSS tools would experience excessive notch wear and easily break down.
Holt explained that two basic types of ceramic inserts are available: whisker reinforced, which is for machining forged components with rough scale and ovality, and sialon, which is a mixture of silicon, aluminum oxygen and nitrogen. Examples of sialon use include Sandvik Coromant’s CC6060 sialon grade, for long cutting lengths in clean material and for profiling and pocketing with optimized programming techniques, and CC6065, for heavy roughing, plunging and machining directly into a corner.
When applying ceramic tools, the toolmaker recommends balancing the cutting speed to create enough heat in the cutting zone but not too much, which would unbalance the ceramic because not enough heat is generated. “You do not create a highly plasticized and sheared chip, unbalancing the material and creating top slice,” Holt said.
“Whisker is a much tougher ceramic than sialon ceramics and has increased bulk strength, allowing for tougher applications,” he added. “With sialon, you can run at about a 20 percent elevated speed. Regarding metal removal, sialon is quite a step change compared to whisker-reinforced inserts for the industry and more people are adopting it.”
When applying carbide inserts, Holt indicated that the cutting speed should never be higher than 220 sfm for finishing critical parts. “It’s not about maximizing productivity when you get to that last stage,” he said. “It’s about getting good surface quality and a predictable tool life with an optimized toolpath.” In addition, a maximum chip thickness from 0.08mm to 0.15mm is optimal.
Although some feel flood coolant promotes thermal fracturing of the workpiece when cutting nickel alloys, Holt recommends applying coolant because of the high amount of heat generated, with the exception being milling with ceramic tools. That’s because ceramic requires heat to shear the material and milling is an intermittent process. “To create enough heat when milling with ceramics, you should never use coolant,” he said.

Courtesy of Carpenter Technology
Carpenter Technology produces nickel-base superalloys in a variety of product forms to meet stringent customer specifications.
It is best to use accurately targeted high-pressure coolant—up to 1,200 psi—from an optimized nozzle to produce a high-velocity, parallel laminar jet, Holt noted. Benefits of high-pressure coolant include extending tool life, enabling higher cutting speeds and enhancing chip breaking and control by providing a hydraulic wedge between the tool and chip to lift the chip.
In a laboratory test, Sandvik Coromant compared the application of high- and low-pressure coolant when machining 718 Inconel. The high-pressure coolant increased tool life, increased metal removal 50 percent when using a CNMX insert at a cutting speed of 164 sfm, allowed a 20 percent increase in cutting speed with the same or better tool life and improved chip control during finishing.
Cost Considerations
Along with being able to withstand extreme environments better than steel, nickel-base steel superalloys are slightly more expensive. Nickel, cobalt, molybdenum and other superalloy elements are significantly more costly than iron, the major component of steel, according to Carpenter Technology. However, the cost can often be justified based on service life in demanding applications and other factors, such as engine efficiency.
In previous years, the price of the alloying elements also fluctuated, primarily because of global competition. “The market is constantly changing due to the volatility of supply and demand from countries like China,” said Zahm of Vista Metals. “At one time the price of nickel went as high as $21 per lb. Unfortunately, metal prices haven’t been very stable for the past 5 or 6 years as compared to the prior 10 to 20 years.”

Images courtesy of Sandvik Coromant
Typical insert wear mechanisms when machining heat-resistant superalloys include notch wear on the main cutting edge at the DOC (left), chip hammering (right) created by chips hitting the cutting edge line outside the cutting zone, and plastic deformation (below) caused by a combination of high temperature and high pressure on the cutting edge.
Zahm noted that some customers have been ordering peeled bar or rod, where the outer layer is removed. A shop can reduce material costs by purchasing hot-finished redraw stock instead of costlier bars that are cold-drawn to size. “You may waste a bit more processing time, but you’re not buying the more-expensive drawn bar,” he said.
When the application is appropriate, part manufacturers can save money by switching to a lower-cost alternative alloy. For example, in addition to its commercial alloy offerings, Winsert produces proprietary wear- and corrosion-resistant alloys to replace cobalt- and nickel-base superalloys. “If somebody wants something that will compete against a wrought material, we definitely have a cast alternative,” Dickinson said. “We can make an alloy that will work as good if not better.” The cost savings for a cast material can be as much as 25 to 50 percent, he added.
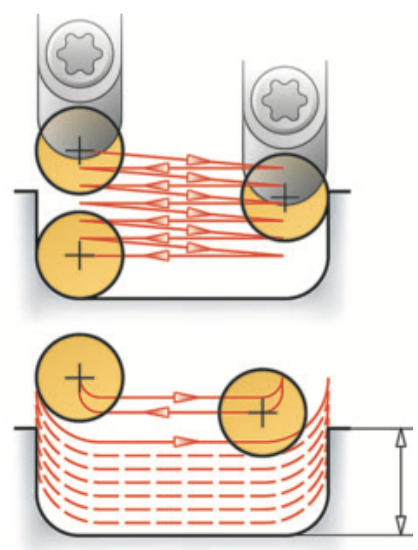
Courtesy of Sandvik Coromant
Compared to conventional profiling/pocketing with a round insert (top), trochoidal turning rolls the insert into and out of the cut with a reduced feed rate and increases the feed rate to the maximum fn for linear cuts.
However, if a nickel-base superalloy is required for the job, it requires disciplined machining—and that includes repeatable, rigid setups. “Doing the basics can’t be underestimated,” Dickinson said. “If you’re a little sloppy at times and used to cutting materials where alignments and things like that aren’t critical, you’re going to be in for a shock.”
Because nickel-base superalloys retain their strength at high temperatures and provide a high dynamic shear strength, high cutting forces are required. In addition, the material’s poor thermal conductivity generates high cutting temperatures, and hard carbides in its structure create abrasive wear during machining. As a result, “people tend to shy away once they hear Inconel and nickel alloys are involved,” Holt said. “But if you get the right recipe for nickel alloys, they’re very easy to machine.”
That recipe includes a rigid machine setup, high-pressure coolant delivery, positive-rake inserts, a suitable entry angle and achieving the optimal chip thickness. “It is a shock if you’re moving from aluminum and cast iron to nickel alloys,” Holt said. “If you’re getting into these materials, concentrate on the five key success factors and you should be OK.” CTE
About the Author: Alan Richter is editor of CTE, having joined the publication in 2000. Contact him at (847) 714-0175 or [email protected].
Contributors
Carpenter Technology Corp.
(610) 208-2000
www.cartech.com
Sandvik Coromant Co.
(800) SANDVIK
www.sandvik.coromant.com/us
Schuur Metals Inc.
(949) 498-3185
www.schuurmetals.com
Ulbrich Stainless Steels and Specialty Metals Inc.
(800) 243-1676
www.ulbrich.com
Vista Metals Inc.
(401) 253-1772
www.vismet.com
Winsert Inc.
(715) 732-1703
www.winsert.com
Related Glossary Terms
- abrasive
abrasive
Substance used for grinding, honing, lapping, superfinishing and polishing. Examples include garnet, emery, corundum, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride and diamond in various grit sizes.
- alloying element
alloying element
Element added to a metal to change its mechanical and/or physical properties.
- alloys
alloys
Substances having metallic properties and being composed of two or more chemical elements of which at least one is a metal.
- built-up edge ( BUE)
built-up edge ( BUE)
1. Permanently damaging a metal by heating to cause either incipient melting or intergranular oxidation. 2. In grinding, getting the workpiece hot enough to cause discoloration or to change the microstructure by tempering or hardening.
- built-up edge ( BUE)2
built-up edge ( BUE)
1. Permanently damaging a metal by heating to cause either incipient melting or intergranular oxidation. 2. In grinding, getting the workpiece hot enough to cause discoloration or to change the microstructure by tempering or hardening.
- burr
burr
Stringy portions of material formed on workpiece edges during machining. Often sharp. Can be removed with hand files, abrasive wheels or belts, wire wheels, abrasive-fiber brushes, waterjet equipment or other methods.
- ceramics
ceramics
Cutting tool materials based on aluminum oxide and silicon nitride. Ceramic tools can withstand higher cutting speeds than cemented carbide tools when machining hardened steels, cast irons and high-temperature alloys.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- corrosion resistance
corrosion resistance
Ability of an alloy or material to withstand rust and corrosion. These are properties fostered by nickel and chromium in alloys such as stainless steel.
- cutting speed
cutting speed
Tangential velocity on the surface of the tool or workpiece at the cutting interface. The formula for cutting speed (sfm) is tool diameter 5 0.26 5 spindle speed (rpm). The formula for feed per tooth (fpt) is table feed (ipm)/number of flutes/spindle speed (rpm). The formula for spindle speed (rpm) is cutting speed (sfm) 5 3.82/tool diameter. The formula for table feed (ipm) is feed per tooth (ftp) 5 number of tool flutes 5 spindle speed (rpm).
- depth of cut
depth of cut
Distance between the bottom of the cut and the uncut surface of the workpiece, measured in a direction at right angles to the machined surface of the workpiece.
- ductility
ductility
Ability of a material to be bent, formed or stretched without rupturing. Measured by elongation or reduction of area in a tensile test or by other means.
- fatigue
fatigue
Phenomenon leading to fracture under repeated or fluctuating stresses having a maximum value less than the tensile strength of the material. Fatigue fractures are progressive, beginning as minute cracks that grow under the action of the fluctuating stress.
- feed
feed
Rate of change of position of the tool as a whole, relative to the workpiece while cutting.
- flank wear
flank wear
Reduction in clearance on the tool’s flank caused by contact with the workpiece. Ultimately causes tool failure.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- hardness
hardness
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to surface indentation or abrasion. There is no absolute scale for hardness. In order to express hardness quantitatively, each type of test has its own scale, which defines hardness. Indentation hardness obtained through static methods is measured by Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop tests. Hardness without indentation is measured by a dynamic method, known as the Scleroscope test.
- high-speed steels ( HSS)
high-speed steels ( HSS)
Available in two major types: tungsten high-speed steels (designated by letter T having tungsten as the principal alloying element) and molybdenum high-speed steels (designated by letter M having molybdenum as the principal alloying element). The type T high-speed steels containing cobalt have higher wear resistance and greater red (hot) hardness, withstanding cutting temperature up to 1,100º F (590º C). The type T steels are used to fabricate metalcutting tools (milling cutters, drills, reamers and taps), woodworking tools, various types of punches and dies, ball and roller bearings. The type M steels are used for cutting tools and various types of dies.
- mechanical properties
mechanical properties
Properties of a material that reveal its elastic and inelastic behavior when force is applied, thereby indicating its suitability for mechanical applications; for example, modulus of elasticity, tensile strength, elongation, hardness and fatigue limit.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- parallel
parallel
Strip or block of precision-ground stock used to elevate a workpiece, while keeping it parallel to the worktable, to prevent cutter/table contact.
- physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
Tool-coating process performed at low temperature (500° C), compared to chemical vapor deposition (1,000° C). Employs electric field to generate necessary heat for depositing coating on a tool’s surface. See CVD, chemical vapor deposition.
- plastic deformation
plastic deformation
Permanent (inelastic) distortion of metals under applied stresses that strain the material beyond its elastic limit.
- profiling
profiling
Machining vertical edges of workpieces having irregular contours; normally performed with an endmill in a vertical spindle on a milling machine or with a profiler, following a pattern. See mill, milling machine.
- rake
rake
Angle of inclination between the face of the cutting tool and the workpiece. If the face of the tool lies in a plane through the axis of the workpiece, the tool is said to have a neutral, or zero, rake. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge more acute than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is positive. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge less acute or more blunt than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is negative.
- residual stress
residual stress
Stress present in a body that is free of external forces or thermal gradients.
- shear strength
shear strength
Stress required to produce fracture in the plane of cross section, the conditions of loading being such that the directions of force and of resistance are parallel and opposite although their paths are offset a specified minimum amount. The maximum load divided by the original cross-sectional area of a section separated by shear.
- stainless steels
stainless steels
Stainless steels possess high strength, heat resistance, excellent workability and erosion resistance. Four general classes have been developed to cover a range of mechanical and physical properties for particular applications. The four classes are: the austenitic types of the chromium-nickel-manganese 200 series and the chromium-nickel 300 series; the martensitic types of the chromium, hardenable 400 series; the chromium, nonhardenable 400-series ferritic types; and the precipitation-hardening type of chromium-nickel alloys with additional elements that are hardenable by solution treating and aging.
- stiffness
stiffness
1. Ability of a material or part to resist elastic deflection. 2. The rate of stress with respect to strain; the greater the stress required to produce a given strain, the stiffer the material is said to be. See dynamic stiffness; static stiffness.
- superalloys
superalloys
Tough, difficult-to-machine alloys; includes Hastelloy, Inconel and Monel. Many are nickel-base metals.
- toolpath( cutter path)
toolpath( cutter path)
2-D or 3-D path generated by program code or a CAM system and followed by tool when machining a part.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.
- workhardening
workhardening
Tendency of all metals to become harder when they are machined or subjected to other stresses and strains. This trait is particularly pronounced in soft, low-carbon steel or alloys containing nickel and manganese—nonmagnetic stainless steel, high-manganese steel and the superalloys Inconel and Monel.








