Version 2011’s Bar Fed Mills
Version 2011’s Bar Fed Mills
Aug. 2010 — PartMaker Inc.'s Vesion 2011 CAM software offers specialist functionality for the programming and simulation of Bar Fed Mills.
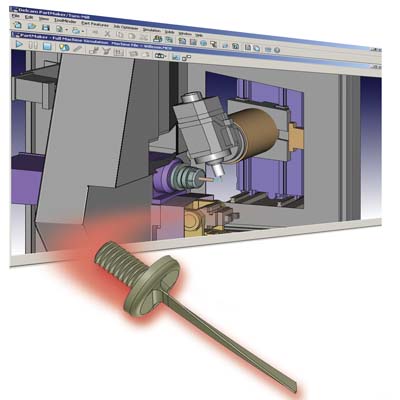
PartMaker Inc.'s Vesion 2011 CAM software offers specialist functionality for the programming and simulation of Bar Fed Mills. The new specialist software provides more realistic simulation of the machining processes carried out on Bar Fed Mills with unique architectures from such leading builders as Willemin-Macodel, Bumotec, Chiron, Mazak, Star, Tornos-Almac, Stama among others. Bar Fed Mills are a unique breed of mill/turn centers that combine the continuous production capability of traditional bar-fed turn/mill center with platform of a vertical machining center. PartMaker CAM software has an ability to automate the programming of Bar Fed Mills as a result of the blend of two unique technologies it employs. For parts with features requiring 2-axis, 2 ½; axis, 3-axis and 3+2 machining, the software employs a patented "Divide and Conquer" programming strategy to automate programming. PartMaker's Divide and Conquer technique makes programming the multi-axis operations found on a Bar Fed Mill easier by allowing the programmer to break the part down into a series of simpler operations. When a part requires simultaneous 5-axis programming, PartMaker is able to integrate the extraordinarily sophisticated 5-axis machining strategies found in PowerMILL.





