
SILICON-NITRIDE INSERTS.
Greenleaf Corp.’s GSN100 silicon-nitride inserts are for machining cast iron parts, such as cylinder blocks and heads, gear cases and housings, and brake drums and rotors. Blended with proprietary toughening agents, the inserts can achieve cutting speeds up to 5,000 sfm (1,525 m/min.) when single-point turning, grooving or milling, according to the company. The inserts can be ordered with special geometries and edge preparations for specific applications. (800) 458-1850.
Greenleaf Corp. www.greenleafcorporation.com

BLIND-HOLE TAP.
The Walter Prototyp Paradur Short Chip HT blind-hole tap from Walter USA LLC reportedly increases process reliability and quality when tapping long-chipping, high-tensile-strength steel. The tap prevents the coiled swarf, or “bird’s nest,” from forming when threading, according to the company. The tool has a 15° helix angle for enhanced chip evacuation. This reduces to a 9° helix angle in the lower section of the tool, which creates short chips when combined with a ground rake in the chamfer. The tool is also suitable for tapping low-tensile-strength materials. (800) 945-5554.
Walter USA LLC www.walter-tools.com/us
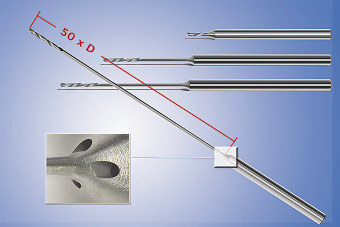
MINIATURE DRILLS.
Mikron Corp. Monroe’s CrazyDrill Flex solid-carbide drills have a flexible center between the drill section and the clamping shank, which provides elasticity. The through-coolant drills start at 0.3mm (0.012 ") in diameter, increasing in 0.05mm (0.002 ") increments for standard tools and 0.01mm (0.0004 ") increments for specials, and are for drilling up to 50 diameters deep. In addition to conventional cutting fluid, users can apply a lubricant that combines air, oil and mist. (203) 261-3100.
Mikron Corp. Monroe www.mikron.com

PVD COATING FACILITY.
Eifeler-Coating Services, the in-house PVD coating facility for PCT/GW Cutting Tools USA Inc. (Precision Cutting Tools USA Inc./Günther Wirth), received a certificate of registration for ISO 9001:2008 on March 6, 2013, from QAS International. The certificate is No. 3597US. The industries the companies serve include aerospace, automotive and medical. (800) 334-9373.
PCT/GW Cutting Tools USA Inc. www.pctcutters.com

DRILL.
Nachi America Inc.’s Aqua Drill EX Flat is for drilling inclined and curved workpiece surfaces. The tool is made from submicron-grain carbide and is available in through-coolant and non-through-coolant styles for drilling 3 and 5 diameters deep. Extended-length drills are also available. The drill is suitable for flat-bottom applications, such as those found in the automotive and oil and gas industries. To improve heat and wear resistance, the company offers its Aqua EX TiAlN and AlTiCR coatings. (888) 340-8665.
Nachi America Inc. www.nachiamerica.com

CYLINDRICAL GRINDER.
United Grinding Technologies Inc.’s Studer S33 CNC universal ID/OD cylindrical grinder has a modular design and digital control and drive systems. The center height is 175mm (6.9 "), between-centers grinding length is 650mm (25.6 ") or 1,000mm (39.4 "), chuck capacity between centers is 80 to 120 kg (176.4 to 264.6 lbs.) and OD wheel size is 500mm × 63mm × 203mm (19.7 "×2.5 "×8.0 "). The machine offers grinding speeds up to 120,000 rpm. The basic wheelhead can be indexed at 0° or 30° for straight and angular plunge grinding. (937) 859-1975.
United Grinding Technologies Inc. www.grinding.com

WHEEL, NOZZLE CHANGER.
Rollomatic Inc. offers an optional six-station wheel and nozzle changer for its GrindSmart series 5-axis 528 and 6-axis 628 CNC grinding machines. The changer is suited for grinders that make specialty and custom rotary cutting tools, and perform continuous production grinding and tool modification and regrinding. The changer can replace wheel packs while an automatic loader places a new blank into the machine without increasing cycle time, according to the company. (866) 713-6398.
Rollomatic Inc. www.rollomaticusa.com

TAILSTOCK FORCE GAGE.
For precision jobs using face drivers, Riten Industries Inc. says its tailstock force gage, in conjunction with the tailstock’s hydraulic cylinder pressure reading, accurately calibrates a lathe or grinder to deliver the precise load for fast setup and repeatable, scrap-free production. The antivibration analog gage displays force from 200 to 6,000 lbs. (90.7 to 2,721.6 kg). It features dual indicators: The black needle shows actual force in real time, while the red needle becomes permanently set at the highest reading recorded during the procedure. (800) 338-0027.
Riten Industries Inc. www.riten.com

SOLID-CERAMIC ENDMILLS.
Beyond KYS40-grade solid-ceramic endmills from Kennametal Inc. rough nickel-base alloys at up to 3,300 sfm (1,000 m/min.) and last two to three times longer than comparable solid-carbide tools, according to the company. The tools have an enlarged core to enhance rigidity and reduce deflection at high cutting speeds and a 40° helix to increase shearing action and chip evacuation. Two types of endmills are available: a 6-flute version for facemilling and profiling and a 4-flute, necked version for slot milling and pocketing. (800) 446-7738.
Kennametal Inc. www.kennametal.com

COLLET CHUCK.
Based on the ER collet standard, the FAHRION Centro P collet chuck from HORN USA Inc. provides a total indicator runout of less than 3µm at 3 times diameter and is balanced for speeds up to 30,000 rpm. The system’s rigid construction dramatically reduces vibration to impart high-quality surface finishes and extend tool life and, compared to the ER standard, is six times more precise and increases clamping forces 100 percent, according to the company. (888) 818-4676.
HORN USA Inc. www.hornusa.com

CARBIDE, P/M ENDMILLS.
YG-1 Tool Co. offers high-performance carbide and P/M endmills specifically designed for milling titanium, stainless steel and aluminum alloys. A 61-page catalog about the tools is available on the company’s Web site (see below) or from distributors. (800) 765-8665.
YG-1 Tool Co. www.yg1usa.com

VERTICAL LATHES.
SMTCL USA Inc. reports that it introduced two vertical lathes to its vertical turning center line after recognizing that a niche needed to be filled in the vertical turning function of the machining industry. According to the company, the machines are built in an ISO-certified factory environment using the latest casting technology. (626) 667-1192.
SMTCL USA Inc. www.smtcl-americas.com

CB-STYLE BORING HEADS.
Criterion Allied Inc.’s CB-style boring heads (shown is a CB-202B head with a CHB-80B/DI bar) are for use in CNC machine tools and provide a direct reading adjustment of 0.001 " (0.025mm) on diameter. The large mounting surface maximizes rigidity and stability, according to the company. The boring range is from 0.050 " to 21.500 " (1.27mm to 546.1mm). Criterion Allied was recently formed when Allied Machine & Engineering Corp. acquired Criterion Machine Works. (800) 321-5537.
Allied Machine & Engineering Corp. www.alliedmachine.com
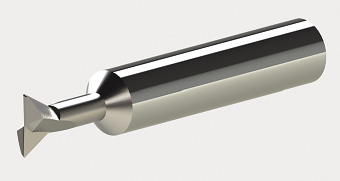
DOVETAIL CUTTERS.
Micro 100 Tool Corp.’s solid-carbide dovetail cutters are available with 30°, 60° and 90° included angles, uncoated or with an AlTiN coating and in diameters up to 0.500 " (12.7mm). According to the company, it makes the tools with a proprietary carbide process that eliminates chipping and breakage under normal machining conditions, which extends tool life. (800) 421-8065.
Micro 100 Tool Corp. www.micro100.com

TOP JAWS.
Dillon Manufacturing Inc. has expanded its line of full-grip jaws to 24 " (609.6mm) in diameter. The cast aluminum, wraparound-type top jaws minimize jaw force for thin-walled parts and distribute the gripping pressure over more of the workpiece surface to help maintain repetitive accuracy, according to the company. This type of jaw reportedly reduces distortion and allows users to achieve close tolerances and concentricity. (800) 428-1133.
Dillon Manufacturing Inc. www.dillonmfg.com
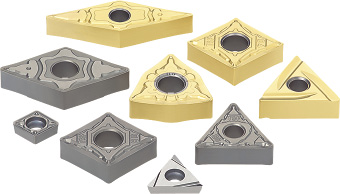
CERMET INSERTS.
Tungaloy Corp.’s uncoated NS9530 and coated GT9530 cermet insert grades are for turning carbon and alloy steels. According to the company, its R&D team developed the grades to enhance fracture resistance and tool life and impart fine surface finishes. The grades are used to produce a vast array of insert styles to suit numerous turning applications. (888) 554-8394.
Tungaloy Corp. www.tungaloyamerica.com

MILLING TOOL.
Mil-Tec Inc.’s HV11 is a high-velocity, high-performance milling tool for machining nonferrous alloys. The tool’s ground and polished insert has positive axial and radial rakes and a razor sharp cutting edge, allowing it to shear the workpiece material, according to the company. The long insert length is reportedly ideal for deep axial cuts and generates a 90° shoulder. A two-screw design enhances holding strength between the insert and tool body. (800) 564-5832.
Mil-Tec Inc. www.miltecusa.com

MULTITASK MACHINE.
The Nakamura-Tome NTJ-100 multitask machine from Methods Machine Tools Inc. is suitable for low- to high-volume production. The machine offers up to 54 tool stations for turning operations and 24 tool stations for milling. According to the company, an upper turret swiveling B-axis with a range of 182° is ideal for producing angular features, eliminating the need for angle milling heads. The machine provides X-axis and Z-axis speeds of 787 ipm (20 m/min.) and 1,574 ipm (40 m/min.), respectively. (877) MMT-4CNC.
Methods Machine Tools Inc. www.methodsmachine.com

FACE GROOVING HEADS.
Sandvik Coromant Co. offers its CoroBore 825 SL face grooving heads as an alternative to groove milling. The rotating axial face grooving tool accepts a standard SL32 blade and CoroCut 1-2 inserts and has through-coolant capability for enhanced chip control, which is critical when grooving because chips are more prone to becoming trapped inside a groove and being recut. The heads offer radial fine adjustment for presetting purposes and are available in diameters from 47mm to 1,275mm (1.85 " to 50.20 "). (800) SANDVIK.
Sandvik Coromant Co. www.sandvik.coromant.com/us

WHEEL TRUING AND DRESSING MACHINES.
Rush Machinery Inc.’s wheel truing and dressing machines are for truing and dressing flats, angles and radii on individual diamond and CBN wheels and multiple wheel packs. The machines are simple to operate, accurate and cost effective, according to the company. The customized, easy-to-use vision software reportedly makes it easy to achieve tight-tolerance truing and dressing. Fully enclosed machines with a 3-axis PLC and machines with diameter capacities to 42 " (1.07m) are available. (800) 929-3070.
Rush Machinery Inc. www.rushmachinery.com
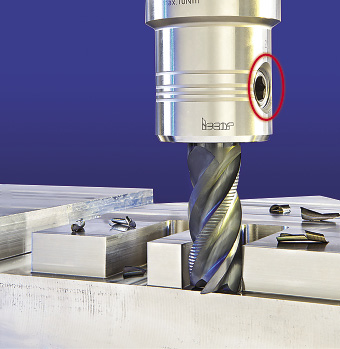
COMBINATION CHUCKS.
Iscar Metals Inc.’s HYDRO-SURE chucks combine hydraulic clamping with side-screw clamping for Weldon-type shank tools. Because the HYDRO-SURE adapters can be used for standard Weldon shank tools, there is no need for special tools and adapters to prevent tool pullout, according to the company. The chucks provide high-torque transmission when applying standard Weldon shank tools and have 0.003mm concentricity. They are available for tool diameters from 16mm to 32mm. (877) BY-ISCAR.
Iscar Metals Inc. www.iscarmetals.com

DIGITAL BORING HEADS.
BIG Kaiser Precision Tooling Inc.’s Kaiser family of digital boring heads provide a digital readout with 0.00005 " (1.27µm) resolution on diameter. This represents the actual movement of the tool carrier, which eliminates the backlash factor, according to the company. Users can swap existing Kaiser analog boring heads with the digital ones. (888) TOOL-PRO.
BIG Kaiser Precision Tool Inc. www.bigkaiser.com

MICROENDMILLS.
Tungsten Toolworks offers seven microendmill geometries in a virtually unlimited variety of diameters, lengths, end conditions and coatings, including diamond. The geometries are based on customer input. The company can configure cutting diameters as small as 0.005 " (0.127mm) from fractional-inch or metric carbide blanks. The company also offers carbide drills, step drills, routers, reamers, tapered tools and other cutting tools. (800) 854-2431.
Tungsten Toolworks www.tungstentoolworks.com

DEEP-HOLE DRILL.
KOMET of America Inc.’s KUB Centron Powerline drill is for drilling up to 9 diameters deep. The drill offers modularity, is available in an extended-diameter range up to 65mm (2.6 ") and is suitable for a variety of applications, including those for the oil and gas, heavy machinery and automotive industries. (800) 656-6381.
KOMET of America Inc. www.komet.com

FILTER ELEMENTS.
Filter Technology Engineered Systems offers replacement filter flex tubes for filtering systems from various manufacturers. Compatible, high-performance replacement flex tubes are available for Coopermatics, Chem-San, CSI, Belmont, National Standard and other brands. A long-life 304 stainless steel spring and polyester felt gasket come standard with the super-polymer filter flex tube. (734) 744-6446.
Filter Technology Engineered Systems www.filtertechno.com

COATING SYSTEM.
Platit Inc.’s PI411 coating system deposits the new QuadCoatings4 PVD coatings. The coating system is the company’s largest in its “11” series and is for companies that want to productively coat tools around the clock, according to Platit. The system enables easy tool loading and the ability to coat 504 10mm-dia. cutters in 3.5 hours. The system’s LGD etching procedure provides a strong adhesion of the coating to the substrate and tolerates cleaning errors. (847) 680-5270.
Platit Inc. www.platit.com

CARBIDE ENDMILLS.
Dura-Mill Inc.’s WhisperKut Plus solid-carbide endmills with Dura Shield are an enhanced version of the WhisperKut series. By incorporating several design features, the endmills provide a long tool life and enable roughing and finishing in peripheral and slotting operations when milling all types of ferrous materials, according to the company. (800) 444-6455.
Dura-Mill Inc. www.duramill.com
Related Glossary Terms
- alloy steels
alloy steels
Steel containing specified quantities of alloying elements (other than carbon and the commonly accepted amounts of manganese, sulfur and phosphorus) added to cause changes in the metal’s mechanical and/or physical properties. Principal alloying elements are nickel, chromium, molybdenum and silicon. Some grades of alloy steels contain one or more of these elements: vanadium, boron, lead and copper.
- alloys
alloys
Substances having metallic properties and being composed of two or more chemical elements of which at least one is a metal.
- aluminum alloys
aluminum alloys
Aluminum containing specified quantities of alloying elements added to obtain the necessary mechanical and physical properties. Aluminum alloys are divided into two categories: wrought compositions and casting compositions. Some compositions may contain up to 10 alloying elements, but only one or two are the main alloying elements, such as copper, manganese, silicon, magnesium, zinc or tin.
- backlash
backlash
Reaction in dynamic motion systems where potential energy that was created while the object was in motion is released when the object stops. Release of this potential energy or inertia causes the device to quickly snap backward relative to the last direction of motion. Backlash can cause a system’s final resting position to be different from what was intended and from where the control system intended to stop the device.
- blind-hole
blind-hole
Hole or cavity cut in a solid shape that does not connect with other holes or exit through the workpiece.
- boring
boring
Enlarging a hole that already has been drilled or cored. Generally, it is an operation of truing the previously drilled hole with a single-point, lathe-type tool. Boring is essentially internal turning, in that usually a single-point cutting tool forms the internal shape. Some tools are available with two cutting edges to balance cutting forces.
- centers
centers
Cone-shaped pins that support a workpiece by one or two ends during machining. The centers fit into holes drilled in the workpiece ends. Centers that turn with the workpiece are called “live” centers; those that do not are called “dead” centers.
- chuck
chuck
Workholding device that affixes to a mill, lathe or drill-press spindle. It holds a tool or workpiece by one end, allowing it to be rotated. May also be fitted to the machine table to hold a workpiece. Two or more adjustable jaws actually hold the tool or part. May be actuated manually, pneumatically, hydraulically or electrically. See collet.
- collet
collet
Flexible-sided device that secures a tool or workpiece. Similar in function to a chuck, but can accommodate only a narrow size range. Typically provides greater gripping force and precision than a chuck. See chuck.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- cubic boron nitride ( CBN)
cubic boron nitride ( CBN)
Crystal manufactured from boron nitride under high pressure and temperature. Used to cut hard-to-machine ferrous and nickel-base materials up to 70 HRC. Second hardest material after diamond. See superabrasive tools.
- cutting fluid
cutting fluid
Liquid used to improve workpiece machinability, enhance tool life, flush out chips and machining debris, and cool the workpiece and tool. Three basic types are: straight oils; soluble oils, which emulsify in water; and synthetic fluids, which are water-based chemical solutions having no oil. See coolant; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- dressing
dressing
Removal of undesirable materials from “loaded” grinding wheels using a single- or multi-point diamond or other tool. The process also exposes unused, sharp abrasive points. See loading; truing.
- facemilling
facemilling
Form of milling that produces a flat surface generally at right angles to the rotating axis of a cutter having teeth or inserts both on its periphery and on its end face.
- flat ( screw flat)
flat ( screw flat)
Flat surface machined into the shank of a cutting tool for enhanced holding of the tool.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- grinding
grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by a powered abrasive wheel, stone, belt, paste, sheet, compound, slurry, etc. Takes various forms: surface grinding (creates flat and/or squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (for external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding with extremely fine grits to create ultrasmooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding.
- grooving
grooving
Machining grooves and shallow channels. Example: grooving ball-bearing raceways. Typically performed by tools that are capable of light cuts at high feed rates. Imparts high-quality finish.
- helix angle
helix angle
Angle that the tool’s leading edge makes with the plane of its centerline.
- inches per minute ( ipm)
inches per minute ( ipm)
Value that refers to how far the workpiece or cutter advances linearly in 1 minute, defined as: ipm = ipt 5 number of effective teeth 5 rpm. Also known as the table feed or machine feed.
- lathe
lathe
Turning machine capable of sawing, milling, grinding, gear-cutting, drilling, reaming, boring, threading, facing, chamfering, grooving, knurling, spinning, parting, necking, taper-cutting, and cam- and eccentric-cutting, as well as step- and straight-turning. Comes in a variety of forms, ranging from manual to semiautomatic to fully automatic, with major types being engine lathes, turning and contouring lathes, turret lathes and numerical-control lathes. The engine lathe consists of a headstock and spindle, tailstock, bed, carriage (complete with apron) and cross slides. Features include gear- (speed) and feed-selector levers, toolpost, compound rest, lead screw and reversing lead screw, threading dial and rapid-traverse lever. Special lathe types include through-the-spindle, camshaft and crankshaft, brake drum and rotor, spinning and gun-barrel machines. Toolroom and bench lathes are used for precision work; the former for tool-and-die work and similar tasks, the latter for small workpieces (instruments, watches), normally without a power feed. Models are typically designated according to their “swing,” or the largest-diameter workpiece that can be rotated; bed length, or the distance between centers; and horsepower generated. See turning machine.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- modular design ( modular construction)
modular design ( modular construction)
Manufacturing of a product in subassemblies that permits fast and simple replacement of defective assemblies and tailoring of the product for different purposes. See interchangeable parts.
- outer diameter ( OD)
outer diameter ( OD)
Dimension that defines the exterior diameter of a cylindrical or round part. See ID, inner diameter.
- physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
Tool-coating process performed at low temperature (500° C), compared to chemical vapor deposition (1,000° C). Employs electric field to generate necessary heat for depositing coating on a tool’s surface. See CVD, chemical vapor deposition.
- profiling
profiling
Machining vertical edges of workpieces having irregular contours; normally performed with an endmill in a vertical spindle on a milling machine or with a profiler, following a pattern. See mill, milling machine.
- rake
rake
Angle of inclination between the face of the cutting tool and the workpiece. If the face of the tool lies in a plane through the axis of the workpiece, the tool is said to have a neutral, or zero, rake. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge more acute than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is positive. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge less acute or more blunt than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is negative.
- shank
shank
Main body of a tool; the portion of a drill or similar end-held tool that fits into a collet, chuck or similar mounting device.
- slotting
slotting
Machining, normally milling, that creates slots, grooves and similar recesses in workpieces, including T-slots and dovetails.
- swarf
swarf
Metal fines and grinding wheel particles generated during grinding.
- tap
tap
Cylindrical tool that cuts internal threads and has flutes to remove chips and carry tapping fluid to the point of cut. Normally used on a drill press or tapping machine but also may be operated manually. See tapping.
- tapping
tapping
Machining operation in which a tap, with teeth on its periphery, cuts internal threads in a predrilled hole having a smaller diameter than the tap diameter. Threads are formed by a combined rotary and axial-relative motion between tap and workpiece. See tap.
- threading
threading
Process of both external (e.g., thread milling) and internal (e.g., tapping, thread milling) cutting, turning and rolling of threads into particular material. Standardized specifications are available to determine the desired results of the threading process. Numerous thread-series designations are written for specific applications. Threading often is performed on a lathe. Specifications such as thread height are critical in determining the strength of the threads. The material used is taken into consideration in determining the expected results of any particular application for that threaded piece. In external threading, a calculated depth is required as well as a particular angle to the cut. To perform internal threading, the exact diameter to bore the hole is critical before threading. The threads are distinguished from one another by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance that is specified. See turning.
- titanium aluminum nitride ( TiAlN)
titanium aluminum nitride ( TiAlN)
Often used as a tool coating. AlTiN indicates the aluminum content is greater than the titanium. See coated tools.
- total indicator runout ( TIR)
total indicator runout ( TIR)
Combined variations of all dimensions of a workpiece, measured with an indicator, determined by rotating the part 360°.
- truing
truing
Using a diamond or other dressing tool to ensure that a grinding wheel is round and concentric and will not vibrate at required speeds. Weights also are used to balance the wheel. Also performed to impart a contour to the wheel’s face. See dressing.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.
- wear resistance
wear resistance
Ability of the tool to withstand stresses that cause it to wear during cutting; an attribute linked to alloy composition, base material, thermal conditions, type of tooling and operation and other variables.
- web
web
On a rotating tool, the portion of the tool body that joins the lands. Web is thicker at the shank end, relative to the point end, providing maximum torsional strength.







