Diamond and CBN Superabrasives
Diamond and CBN Superabrasives
GMSi Group Inc. offers decades of experience in abrasive machining applications in metalworking, industrial sharpening and manufacturing. Proprietary formulations, aggressive stock-removal rates with product consistency while yielding the finish results your applications require, according to the company.
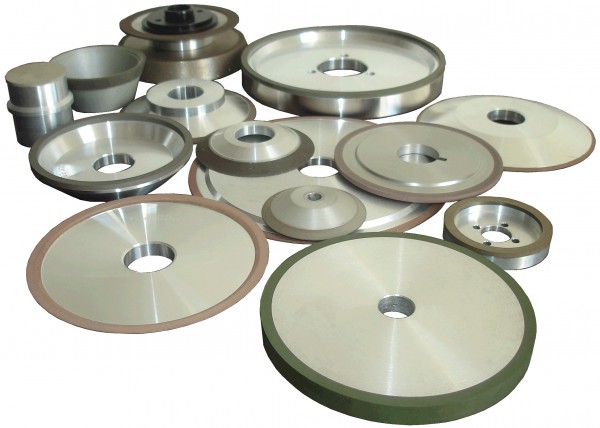

GMSi Group Inc. offers decades of experience in abrasive machining applications in metalworking, industrial sharpening and manufacturing. Proprietary formulations, aggressive stock-removal rates with product consistency while yielding the finish results your applications require, according to the company. Products are readily available and competitively priced.
- Resin Bonds for cool cuting in heat sensitive applications
- Vitrified bonds for longer tool life and aggressive stock removal rates
- Diamond and CBN saw and tool sharpening wheels
- Hand hones and dressing sticks