GN 753.1 Guide Rollers
GN 753.1 Guide Rollers
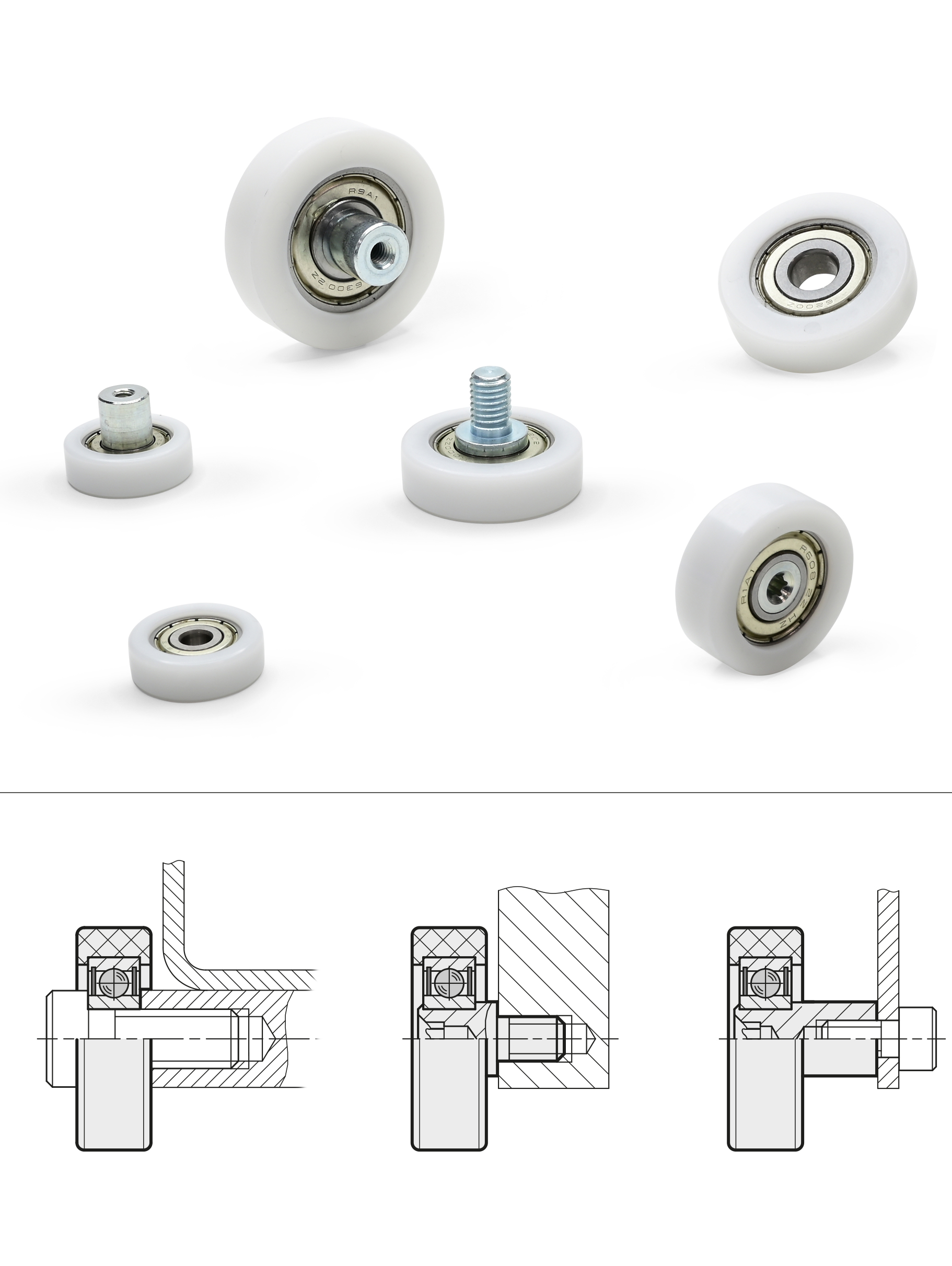
The outer race of the ball bearing is embedded in the POM plastic of the guide roller during the molding process. Each roller is machined to precise dimensions for an exact runout, which makes cylindrical and convex shaping of the running surface possible. Convex rolling surfaces compensate for alignment errors by preventing them from running on corners or edges.
They may appear unassuming, but their range of applications is enormous: guide rollers with ball bearings achieve smooth and dynamic movements. JW Winco is setting new standards with the guide roller generation GN 753.1.
Guide rollers may seem like simple, standard parts, but these rollers with ball bearings are in exceptionally high demand. Considering their central role in an extensive range of applications, JW Winco has expanded its guide roller offering to include the standard part GN 753.1. With its entirely new design, these guide rollers have a special deep groove ball bearing of hardened roller bearing steel. They are available in six sizes, from 0.866 to 1.969 inches (22 to 50 millimeters) outer diameter. The bearing features permanent lubrication and a typical 2Z seal to protect against dust and dirt. In other words, the bearing is covered on both sides by metal disks.
The outer race of the ball bearing is embedded in the POM plastic of the guide roller during the molding process. Each roller is machined to precise dimensions for an exact runout, which makes cylindrical and convex shaping of the running surface possible. Convex rolling surfaces compensate for alignment errors by preventing them from running on corners or edges.
The rollers can fasten via the smooth bore of the inner bearing race using a typical socket cap, shoulder screws, or through a permanently riveted bearing pin, designed either with male or female thread. Both types of bearing pins are fitted with Torx drives to ensure optimal transfer of the tightening torque.
The smallest roller option can accept dynamic radial loads of up to 400 newtons, while the largest roller rates for loads as high as 1,500 newtons. All rollers are designed for lifetime performance of 656,167 ft (200,000 meters) and speeds of 1.3 feet per second (0.4 meters per second).





