RoboGauge
RoboGauge
Perceptron Inc. has launched the AutoScan Collaborative RoboGauge that extends further its family of next generation industrial gauging products to include automated robotic 3D scanning for dimensional measurement and gauging applications on the manufacturing floor.
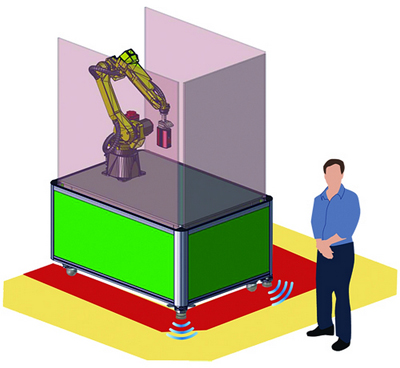
Perceptron Inc. has launched the AutoScan Collaborative RoboGauge that extends further its family of next generation industrial gauging products to include automated robotic 3D scanning for dimensional measurement and gauging applications on the manufacturing floor. AutoScan Collaborative RoboGauge, combines traditional industrial FANUC robot technology and Perceptron's revolutionary Helix smart scanning sensor, integrated with an innovative collaborative robot safety solution as a standardized gauging package.
Jeff Armstrong, president of Perceptron says, "The AutoScan Collaborative RoboGauge harnesses Perceptron's automated in-line and near-line measurement expertise in the automotive industry and is specifically targeted to automate a wide range of production gauging processes offering a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional "hard-gauges" utilizing proven industrial robot technology in a collaborative safety manner negating the need for traditional robot safety fences.
The RoboGauge Cell includes a rigid machine base for holding both Robot and part fixture with translucent side panels that light up to provide visual color status indication. The RoboGauge perimeter is monitored utilizing integrated Guardmaster SafeZone laser scanners, which use the diffused reflection of emitted infrared laser light to create a two-dimensional programmable detection safety field that determines intrusion within the defined programmable safety zone.
The Dual Check Safety Zone system provides:
• Programmable safety zone control
• Warning (amber) and protection (red) modes
• Reduced robot speed in the warning mode
• Robot reach restricted to the measurement volume
• Speed and separation monitoring
• Safety-rated robot stop monitoring Automatic recovery when the safety zone is cleared
The AutoScan Collaborative RoboGauge provides a highly-flexible automated shop-floor metrology solution capable of handling a wide variety of parts including sheet metal, fabrications, molded parts and castings, and can be used in comparative or absolute inspection mode. The Perceptron shop-hardened Vector software ensures no in-depth metrology expertise is required to operate the RoboGauge and provides real-time status monitoring, SPC reporting, Visual Fixturing alignment, and AutoSolve feature extraction comparison to CAD. RoboGauge is also available with temperature compensation.
The Helix 3D smart scanning sensor incorporates a state-of-the-art MEMS device allowing laser line quantity, density, length and orientation characteristics to be programmable and eliminates the need for the robot to physically move the Helix sensor over the part while scanning; its capabilities also allows scanning of multiple features in a single sensor position providing fast and precise measurement of complex part geometries.





