CAMplete Solutions Inc. partners with Doosan Machine Tools America
CAMplete Solutions Inc. partners with Doosan Machine Tools America
Kitchener, On— August 24th, 2018 — CAMplete Solutions Inc. and Doosan Machine Tools America have joined forces to offer CAMplete TruePath to their new and existing customers.
Kitchener, On— August 24th, 2018 — CAMplete Solutions Inc. and Doosan Machine Tools America have joined forces to offer CAMplete TruePath to their new and existing customers.
Doosan Machine Tools America offers a complete lineup of turning and machining centers for small to large sized parts. The high-speed, high-precision 5-axis machining centers enable ultra-high-precision, simultaneous 5-axis control for aviation and medical parts, and five-sided machining centers offer economically feasible multi-facet/complex shape machining, depending on customer needs.
CAMplete TruePath will be available for purchase for all Doosan Machine Tools America milling machines. Equipping Doosan's CNC machines with CAMplete's verification, postprocessing and simulation software will save users time and money.
Those interested in seeing the software in action can preview TruePath within the Doosan Machine Tools America Booth at IMTS 2018.
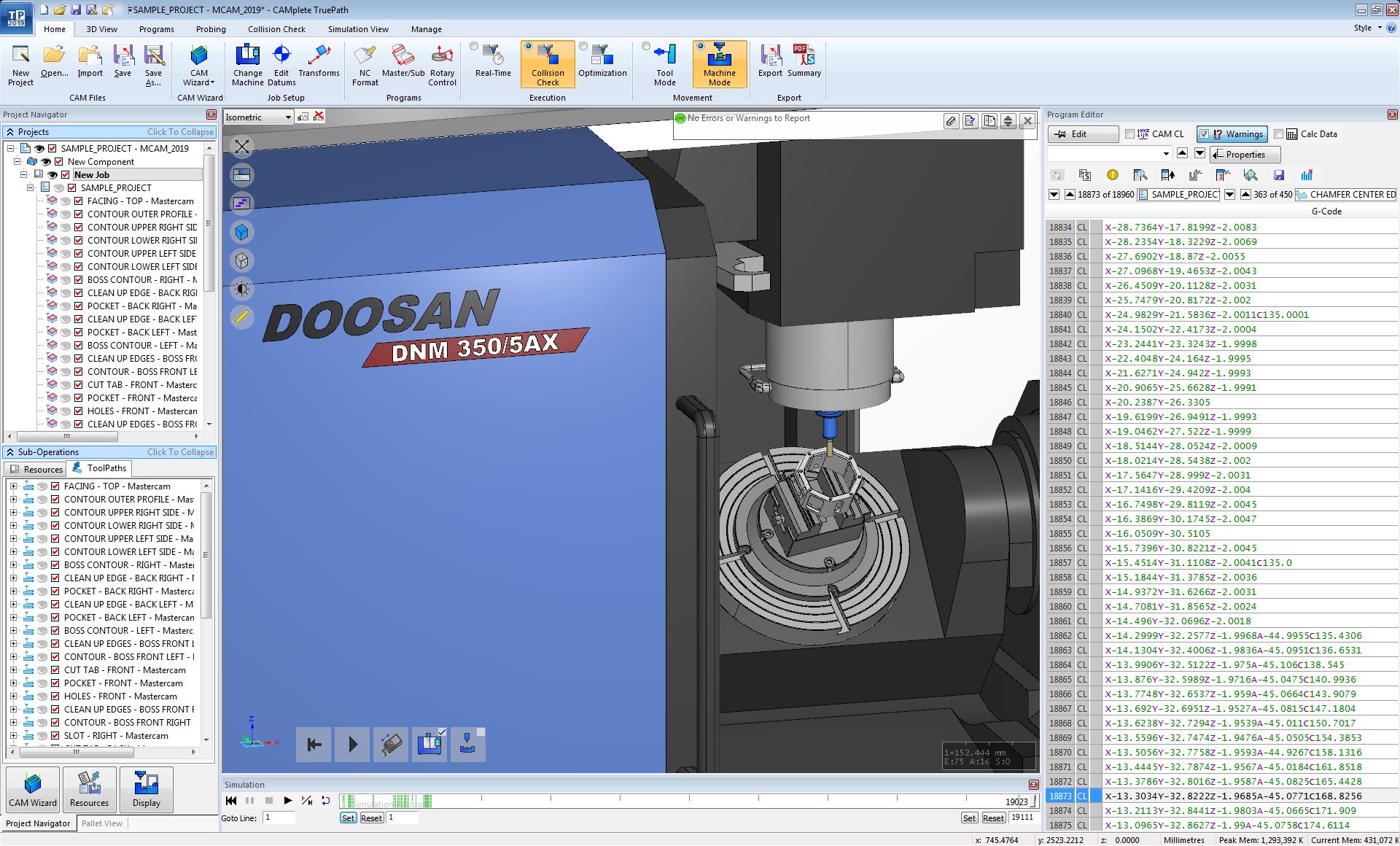
What is CAMplete TruePath?
CAMplete TruePath is an easy-to-use application that takes you from your CAM System to your 5-Axis machine efficiently and safely. Using toolpath data from all industry leading CAM Systems, TruePath's customizable post-processor allows you to output your NC programs the way you need, with no on-machine editing required. 5-axis simulation, visualization and verification tools give you the confidence of knowing how your machine will behave before you run a single line of G-code.
Post Processing
• Factory approved, proven post-processor for your machine developed in partnership with Doosan Machine Tools America
• Easily edit your post to get the G-Code you need
• Switch between and combine tool paths from all major CAM Systems
Verification
• Models built from original design data to show you the real machine motion of your Doosan Machine Tool
• Full G-Code Verification gives you complete confidence in your programs
Quote from Doosan Machine Tools America:
"Offering CAMplete's TruePath software allows us to provide a proven, universal postprocessor that also includes verification and optimization for the most efficient use of our customers' Doosan 5-axis and 5-sided milling machines. The collision detection offered with TruePath brings peace-of-mind, lowers the learning curve for those new to 5-axis machining, and truly helps save time and money. Given all the benefits of TruePath, partnering with CAMplete for our 5-axis and 5-sided product offerings was an easy choice."
- Jim Shiner, Director of Sales and Marketing
Quote from CAMplete:
"We are excited to be partnering with an industry leader in Machine Tool Manufacturing like Doosan Machine Tools America. As one of the world's largest CNC Machine Tool Builders, this partnership will provide our mutual customers with a rock solid "out of the box" solution. This is a tremendous added value for any new and existing Doosan customer, especially as both machines and software get more complex every year. Customers are noticing and invest heavily into 5 axis machines, and this new partnership is here to ensure they get the most out of their machine. We are honored to be part of Doosan Machine Tools America's growth and look forward to helping people transition safely and easily to 5-axis machining."
- Jeff Fritsch, VP Sales and Marketing





