Metalworking fluids market resurgent as regulations mandate safe disposal
Metalworking fluids market resurgent as regulations mandate safe disposal
The primary focus of metalworking applications revolves around maximizing efficiency of machinery and operations. Thus it is preferable to use metalworking fluids that are multifunctional in nature. Significant growth in metalworking processes worldwide have propelled demand for metalworking fluids. However, metalworking fluids used for machineries have undergone intense regulatory scrutiny in last two decades.
Article from Fact.MR
The primary focus of metalworking applications revolves around maximizing efficiency of machinery and operations. Thus it is preferable to use metalworking fluids that are multifunctional in nature. Significant growth in metalworking processes worldwide have propelled demand for metalworking fluids. However, metalworking fluids used for machineries have undergone intense regulatory scrutiny in last two decades.
Nevertheless, regulations regarding safe disposal of these fluids have been constantly revised to meet several different formulations and blends introduced by industrial manufacturers. Furthermore, new metalworking processes, such as flow forming, hydro forming and low carbon manufacturing, are gaining traction, which is fostering demand for metalworking fluids. As per recently concluded report on global metalworking fluid market, study analyzes that the global market for metalworking fluid is projected to grow at a modest CAGR of just over 4% till 2027.
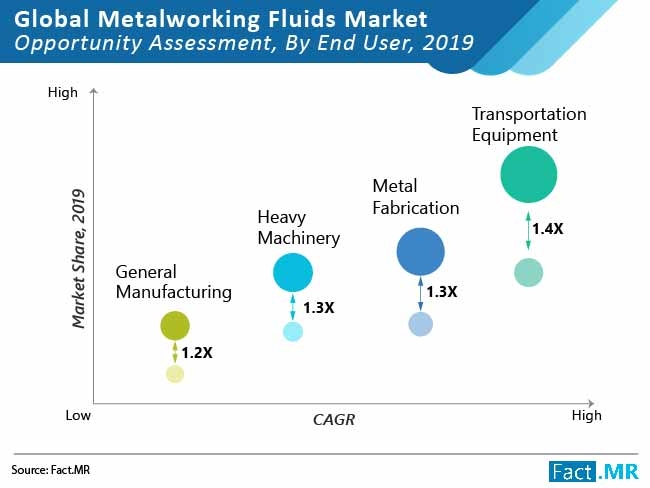
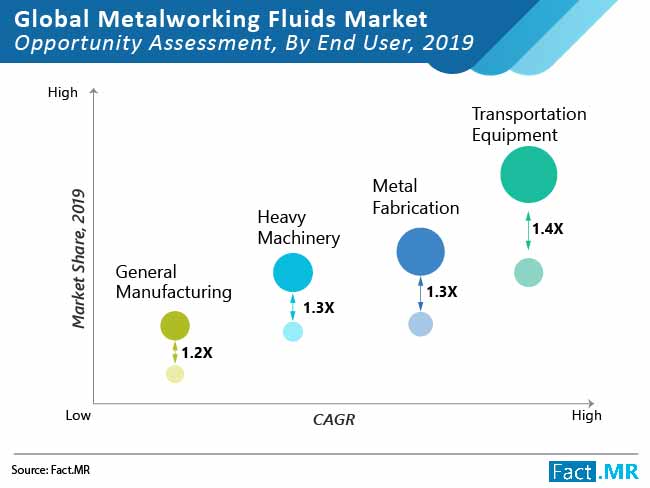
Key Takeaways of Global Metalworking Fluids Market
- Global metalworking fluids market is forecast to surpass US$13 Bn by 2027 end, adding 1.4 times more value than 2019
- Semisynthetic metalworking fluids are projected to hold nearly half of the market share by 2027 end, which can be attributed to relatively low price in comparison with synthetic metalworking fluids
- The recent past has witnessed a resurgence in consumption of synthetic metalworking fluids, as it is more stable than any other metalworking fluids and can be applied in complex processes such as fine grinding
- Removal fluids are emerging as the most innovative technique in the metalworking fluid market growing at the fastest CAGR throughout the forecast period as it facilitates the easy removal of unwanted metal chips, produced during milling, drilling and other machining operations.
- Demand for metalworking fluids for transportation equipment is expected to gain 177 BPS by 2027 as high rate of metalworking fluid is employed an additive to achieve desirable results
- USA accounted for around a third of market share in 2019, demand backed by mature end use industries such as automotive and aerospace
- Significant increase in manufacturing facilities, aerospace industries, marine and automotive industries in China are expected to create lucrative growth opportunities for China metalworking fluids market participants during the forecast period
"Users of metalworking fluids in machining and fabrication have to invest in expensive and effluent treatment facilities in order to meet environmental and waste treatment regulations. As a result, metalworking fluid producers are making a seismic shift to bio-based metalworking fluids to obtain regulatory clearance." says a report analyst.
Market Players Targeting Growth Opportunities in Emerging Countries
Global metalworking fluid market being slightly fragmented in nature, leaves limited scope of expansion for manufacturers. Key market players such ExxonMobil Corp., Houghton International, Fuchs Petrolub SE, Idemitsu Kosan Co. Ltd., Quaker Chemical Corp. and Yushiro Chemical Industry Co. Ltd. have been quite active toward establishing supply contracts with end-use industries. Manufacturers are also investing huge sums in expanding their presence in emerging countries and regions such as India, China and the Middle East.





