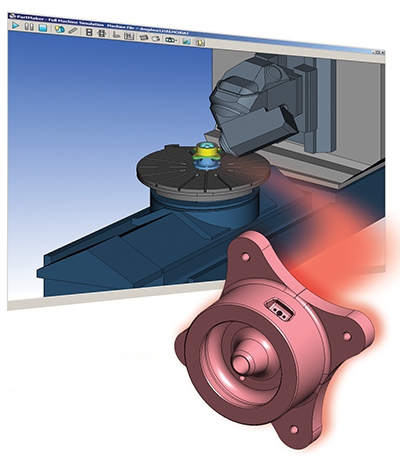
Delcam has released the latest version of its PartMaker software for programming CNC mills, lathes, wWire EDMs, turn/mill centers and Swiss-type lathes, PartMaker Version 2015. Major highlights of PartMaker Version 2015 include improved support for today's latest breed of multi-tasking machine tools, such as vertical mill/turns, more powerful milling and turning functionality, and a unique approach to post processing for multi-axis turn/mill centers and Swiss-type lathes among other productivity enhancements.
"The innovations in PartMaker Version 2015 include a unique blend of productivity enhancements that both new and existing users of the software are going to love along with a host of utterly unique and innovative technology you just won't find anywhere else," says PartMaker Inc. President, Hanan Fishman. "PartMaker 2015 extends support of the product's patented approach to programming multi-tasking machine tools to support today's latest breed of multi-function machines, allowing our customers to stay on the leading edge of multi-tasking."
PartMaker 2015 includes specialist support for a new breed of machine tools that has been growing steadily in popularity in recent years called vertical mill/turns (VMT). These machine tools are unique because they provide the turning functionality typically found on a VTL (Vertical Turret Lathe) with that of a 5-axis VMC (Vertical Machining Center). PartMaker 2015 also offers support for turret-based Swiss lathes with programmable B-axis live tooling attachments as well as more intuitive handing of angled live tooling attachments.
Also headlining PartMaker Version 2015 is a unique approach to post processing for multi-tasking machine tools. This new approach includes a variety of improvements to the software's post processing technology and new software functionality to help guide users on how to best take advantage of their specific multi-tasking machine tool's unique capabilities.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- centers
centers
Cone-shaped pins that support a workpiece by one or two ends during machining. The centers fit into holes drilled in the workpiece ends. Centers that turn with the workpiece are called “live” centers; those that do not are called “dead” centers.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.







