Contact Details
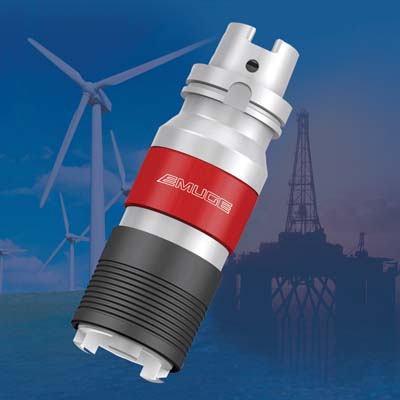

Emuge Corp. has introduced the KSN5 and KSN6 Softsynchro tap holders. The holders are designed for tapping operations in components used in oil, power generation and wind turbine applications and in the production of large diesel, locomotive and ship engines.
"We are seeing an increased need for larger tapping applications such as in the energy sector," said Mark Hatch, Product Director of Taps and Threads Mills at Emuge Corp. "The new KSN5 and KSN6 Softsynchro Series are ideal for work in energy and other large component applications."
The KSN5 series is for tap sizes M16 to M56 and ANSI sizes to 1 ¾". The KSN5 series uses the ER50GB collet and is available in both DIN and ANSI tap sizes. Tension and compression of 2mm is used in machines with rigid tapping cycles. Coolant-through capability is available up to 50 bar and the KSN5 series is also available with an integral shank CAT50 or HSK100A.
The KSN6 series is for sizes M24 to M76 and uses Emuge HE2 large QC Tap Adapters used currently on Emuge HF20 tap holders. Emuge HE2-IKZZ adapters are available in both DIN and ANSI tap sizes 1" through 2 ½". The KSN6 has 2mm of tension and 2mm of compression for rigid tapping cycles. The tool is coolant-through capable, to a maximum of 50 bar.
Related Glossary Terms
- collet
collet
Flexible-sided device that secures a tool or workpiece. Similar in function to a chuck, but can accommodate only a narrow size range. Typically provides greater gripping force and precision than a chuck. See chuck.
- shank
shank
Main body of a tool; the portion of a drill or similar end-held tool that fits into a collet, chuck or similar mounting device.
- tap
tap
Cylindrical tool that cuts internal threads and has flutes to remove chips and carry tapping fluid to the point of cut. Normally used on a drill press or tapping machine but also may be operated manually. See tapping.
- tapping
tapping
Machining operation in which a tap, with teeth on its periphery, cuts internal threads in a predrilled hole having a smaller diameter than the tap diameter. Threads are formed by a combined rotary and axial-relative motion between tap and workpiece. See tap.










 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

