VERICUT 9.4
VERICUT 9.4
VERICUT 9.4 introduces a new module, CNC Machine Monitoring, which connects VERICUT directly to CNC machines and streams data to allow users to monitor what their machines are doing on the shop floor, live in real time. Users can see which NC program or subroutine is running, monitor machine motions and spindle activity, see if overrides have been applied to spindle or feedrates, identify when machining has been interrupted by Emergency stops or taken out of productive cycle mode, and much more, all within VERICUT.
CGTech is proud to announce the latest release of VERICUT, Version 9.4. VERICUT is the industry leader in machine simulation, verification, and optimization for all types of CNC machine processes, including metal cutting, additive and hybrid manufacturing, composites and more. VERICUT is an independent, standalone software that supports integrations with all leading CAM and tool management systems.
In addition to improvements within the core product, VERICUT 9.4 focuses on increased connectivity across the manufacturing workflow, enabling organizations to do more with the resources they already have.
"The release of 9.4 focuses on improving what makes VERICUT a powerful tool while enabling customers to connect both new and existing technologies across their manufacturing ecosystem," says Gene Granata, Director of Product Management. "The improvements and new capabilities within VERICUT enable teams involved across manufacturing to work more efficiently and intelligently, while simultaneously enabling higher competency levels for machinists and NC programmers."
VERICUT 9.4 introduces a new module, CNC Machine Monitoring, which connects VERICUT directly to CNC machines and streams data to allow users to monitor what their machines are doing on the shop floor, live in real time. Users can see which NC program or subroutine is running, monitor machine motions and spindle activity, see if overrides have been applied to spindle or feedrates, identify when machining has been interrupted by Emergency stops or taken out of productive cycle mode, and much more, all within VERICUT.
CNC Precheck is a new standalone application that allows machinists to ensure that key aspects of the machine setup match what was verified in VERICUT. This final precheck before machining enables differences to be identified such as NC programs that are the wrong version or contain edits, missing and/or different work or tool offsets, so these can be investigated and resolved before running the machine.
Streamlined Optimization
All VERICUT users, even those without the Force optimization module, benefit from streamlined optimization enhancements in setup and pre-determined Tool Data settings to quickly optimize NC programs. Starting optimization values for materials and other cutting data is available in VERICUT to give users more confidence in how their NC programs will be used in machining, or for use in optimization to create optimized NC programs that will perform better.
Improved VERICUT Reviewer Files
File sizes for the free, downloadable VERICUT Reviewer Application have been reduced by 50% or more for shorter load/save times, and easier transport to other departments. Machinists, engineers, and quality assurance teams can more easily review NC programs and measure part features.
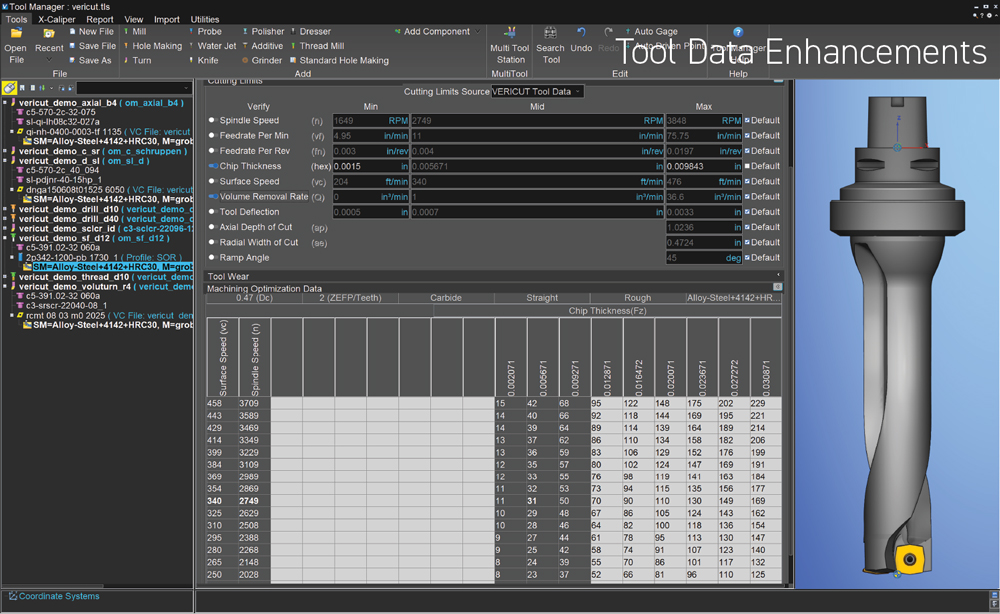
Tool Data Enhancements
VERICUT's Tool Data has been expanded to include more types of cutters, including Ceramic, HSS and serrated edge types, with even more on the way in coming releases. With just one-click, the "Provide New Default Tool Data" feature provides industry standard cutting data for all Cutters (or Inserts) for most common stock materials, allowing users to easily adjust tool data such as cutting limits and more, and verify that tools are being used within acceptable ranges.
New ToolsUnited Interface
Access tool and cutting data from over 40 tooling vendors using the new ToolsUnited interface. Directly read 3D tool assemblies and their cutting data for use in VERICUT simulation and optimization.





