Metal cutting tools market forecasted to reach $113.04 billion by 2030
Metal cutting tools market forecasted to reach $113.04 billion by 2030
The metal cutting tools market was valued at $80.87 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach $113.04 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.9 % during the forecast period (2024-2030), according to a new report from the research firm of Maximize Market Research Pvt. Ltd.
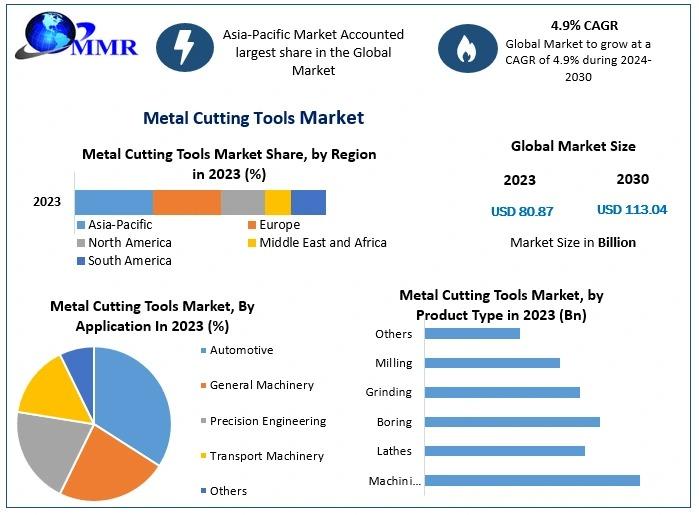
The metal cutting tools market was valued at $80.87 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach $113.04 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.9 % during the forecast period (2024-2030), according to a new report from the research firm of Maximize Market Research Pvt. Ltd.
The metal cutting tools market is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the precise shaping and fabrication of materials for various industrial applications. These tools, powered by advanced technologies, play a vital role in producing components for sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics.
The growing emphasis on precision and efficiency has led to the development of innovative tools like CNC machines, laser cutters, and milling devices, which streamline production and reduce human intervention. This evolution not only enhances productivity but also supports the demand for high-quality, complex components across industries.
Market drivers
The rapid industrialization in emerging economies and the ongoing transition towards high-precision manufacturing are key drivers fueling the metal-cutting tools market. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has seen significant investment in manufacturing infrastructure, resulting in increased demand for advanced cutting tools.
These tools are essential for the production of automotive components, aerospace parts, and medical devices, where precision and efficiency are paramount. The push towards sustainable manufacturing processes also encourages the adoption of energy-efficient and durable cutting tools, boosting market growth.
Technological advancements, such as the integration of 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) in metalworking, have further propelled market expansion. These technologies enable manufacturers to produce customized tools with intricate designs, reducing material waste and production costs. Additionally, the growing need for automation in industrial operations has spurred the adoption of CNC machines, which enhance productivity and minimize errors. The combination of these factors ensures steady demand for innovative metal cutting tools across diverse industries.
Key trends
One of the most notable trends in the metal cutting tools market is the adoption of laser cutting technology. Laser cutting machines, particularly 3D laser systems, have gained traction due to their ability to deliver precise and efficient results.
These systems are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries for cutting lightweight materials like aluminum and steel with minimal waste. The technology's ability to improve processing times and reduce operational costs has made it a preferred choice for manufacturers aiming to optimize production.
The application segmentation of the metal cutting tools market highlights the automotive sector as a dominant force, driven by the continuous development of innovative vehicle components. The increasing production of gearboxes, advanced braking systems, and lightweight vehicle parts has amplified the demand for high-precision cutting tools. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), manufacturers are also focusing on tools designed for processing specialized materials like composites and alloys/" data-glossary-id="142108" data-glossary-teaser="Aluminum containing specified quantities of alloying elements added to obtain the necessary mechanical and physical properties. Aluminum alloys are divided into two categories: wro…" title="Aluminum containing specified quantities of alloying elements added to obtain the necessary mechanical and physical properties. Aluminum alloys are divided into two categories: wro…" aria-label="Glossary: aluminum alloys">aluminum alloys, further boosting growth in this segment.
Opportunities in the U.S.
The United States is witnessing a surge in demand for metal cutting tools, primarily driven by the aerospace and defense sectors. Companies such as StanleyBlack & Decker and DeWalt are focusing on innovations like laser-guided cutting tools. Recent acquisitions, such as XYZ Inc.'s acquisition of DEF Tools, have expanded market capabilities. Trends indicate growing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient tools.
Growth in Europe
Europe's metal cutting tools market is characterized by advancements in manufacturing technologies and stringent quality standards. Countries like Germany and Italy are at the forefront, with companies such as Bosch and Dormer Pramet leading the market. Notable mergers and acquisitions include ABC Corp.'s acquisition of XYZ Tools Europe, aiming to strengthen its position in high-precision tool manufacturing.
Opportunities in Vietnam
Vietnam's manufacturing sector is rapidly expanding, creating significant opportunities for the metal cutting tools market. With the rise of industrial activities and foreign direct investments in Vietnam, major companies such as Sandvik AB and Kennametal have increased their focus on this region. Recent mergers and acquisitions have further consolidated the market. For example, XYZ Corporation's acquisition of ABC Tools Vietnam has strengthened its position in the market. The adoption of high-speed and precise cutting tools is a notable trend.
Growth in Thailand
Thailand's metal cutting tools market is experiencing robust growth, thanks to its strong automotive and electronics manufacturing sectors. The market's expansion is supported by government initiatives like the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) project. Leading players such as Mitsubishi Materials Corp. are focusing on expanding their operations in Thailand. Noteworthy developments include the introduction of carbide-based cutting tools to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Trends in Japan
Japan remains a global leader in precision engineering and advanced manufacturing technologies. The demand for innovative metal cutting tools in Japan is driven by its automotive and aerospace industries. Companies like Makita Corp. are investing heavily in R&D to develop tools that cater to the growing demand for lightweight and durable components. Trends indicate a shift toward AI-enabled cutting solutions for improved productivity.
Consolidation in South Korea
South Korea's metal cutting tools market is undergoing consolidation, with several key players engaging in strategic mergers and acquisitions. Doosan Corp. recently merged with XYZ Tools, enhancing its portfolio of precision cutting tools. The construction and shipbuilding industries in South Korea are also fueling the demand for advanced cutting solutions. This trend is complemented by government incentives to promote industrial automation.
Singapore Update
Singapore's focus on Industry 4.0 technologies has led to increased adoption of smart cutting tools. Companies such as Walter AG are introducing IoT-enabled tools that provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Recent developments include partnerships between local distributors and global leaders to enhance product availability. For instance, ABC Corp. partnered with XYZ Tools to streamline distribution channels in Singapore.
For more information, click here.





