Open Mind Technologies and Haimer machine a sleek panther
Open Mind Technologies and Haimer machine a sleek panther
Open Mind Technologies AG, a developer of CAD/CAM software solutions, teamed up with Haimer to perform 5-axis machining of a panther out of aluminum.
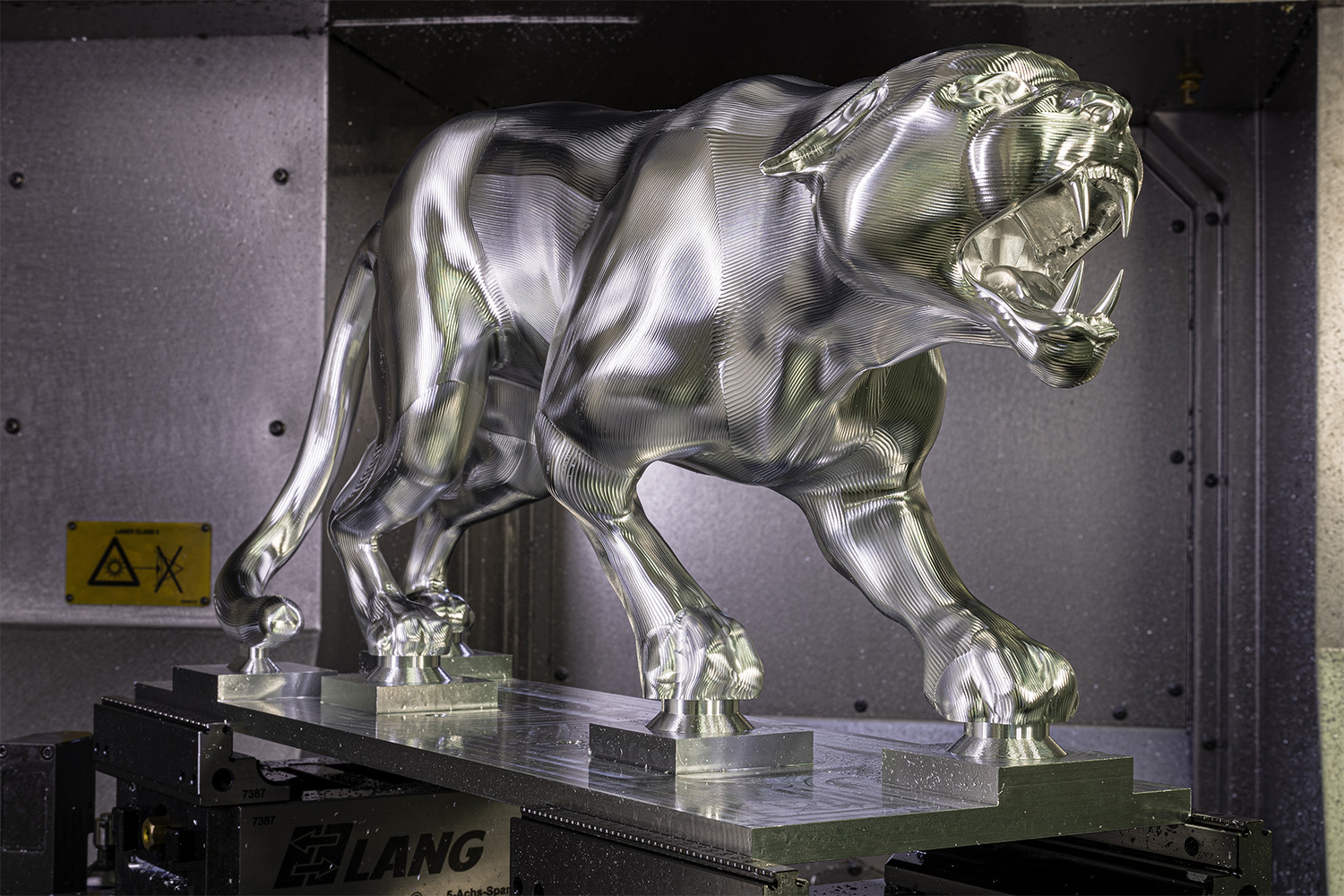

Open Mind Technologies AG, a developer of CAD/CAM software solutions, teamed up with Haimer in Igenhausen, Germany, to perform 5-axis machining of a panther figurine out of aluminum. Haimer is a partner of the German Hockey League's Augsburger Panther Professional Hockey Team.
Haimer had the tool ing aspect well covered, and turned to its longtime CAD/CAM software partner, Open MInd Technologies in Wessling, Germany, for its hyperMILL software suite and programming expertise to program the freely shaped contours required on the panther.
ing aspect well covered, and turned to its longtime CAD/CAM software partner, Open MInd Technologies in Wessling, Germany, for its hyperMILL software suite and programming expertise to program the freely shaped contours required on the panther.
It took the team approximately three intensive weeks to complete the first free-standing panther. Once the machining parameters were in place and optimized, the approximately 20" (500 mm) long panther was machined in just under 13 hours. In addition to being showcased by the Augsburger Panther hockey team, the panther model will be on display in Haimer and Open MInd trade show booths at future events.
"A model such as this one was a great opportunity to put the versatility and flexibility of our software to the test," said Christian Neuner, manager of global engineering services for Open Mind. "HyperMILL has a wide range of functions that allow CAM users to truly optimize a machine's capabilities to achieve the desired goal, including making intricate, challenging parts."
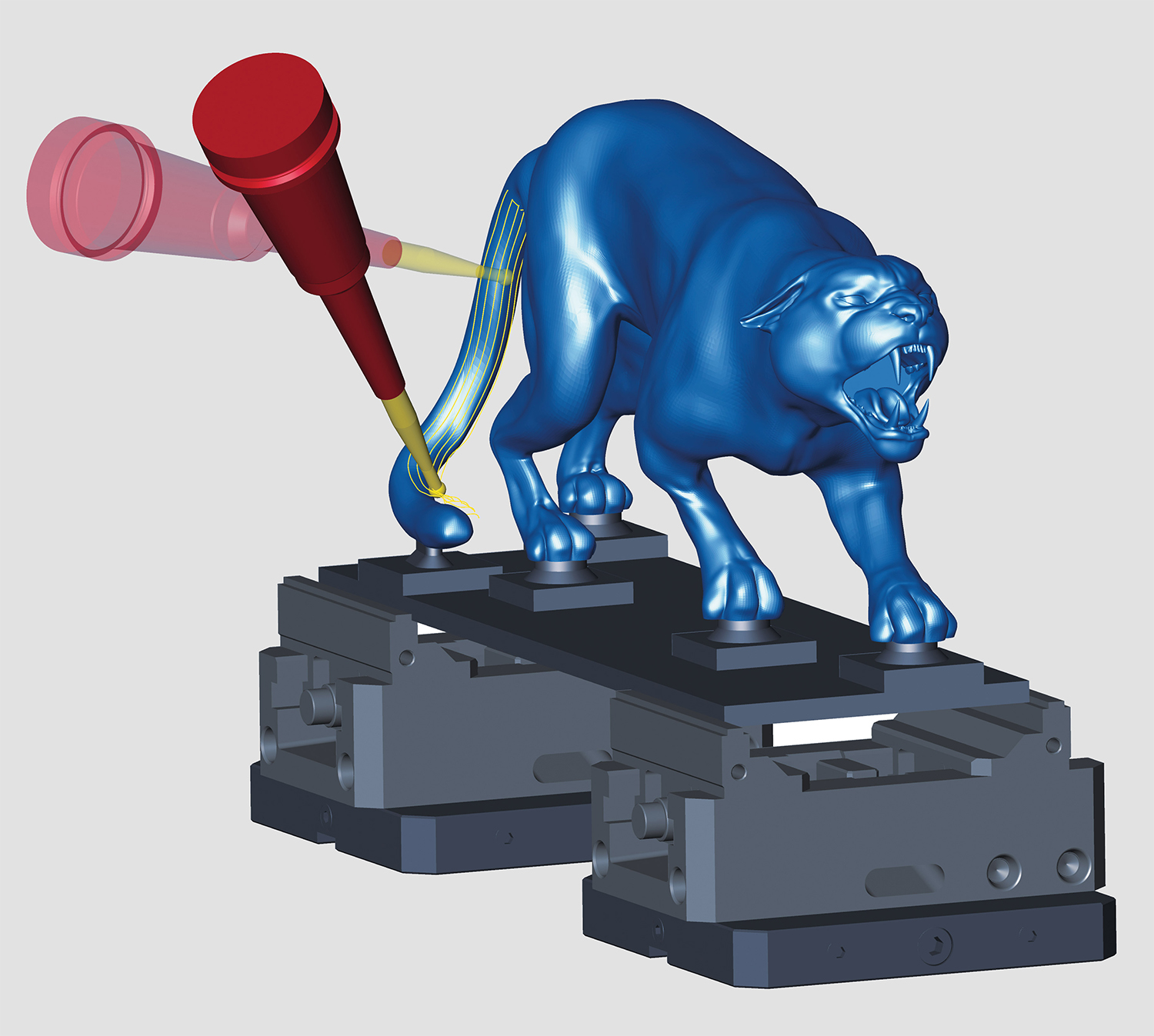 Jakob Nordmann, application engineer at Open Mind worked with Haimer applications engineer Daniel Swoboda to develop the programming and machining infrastructure. Due to the extremely detailed mouth and incisors, and the long and thin shape of the filigree tail section, two set-ups were required on a linear 5-axis DMG MORI HSC70 milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger." title="CNC machine tool capable of drilling, reaming, tapping, milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger." aria-label="Glossary: machining center">machining center.
Jakob Nordmann, application engineer at Open Mind worked with Haimer applications engineer Daniel Swoboda to develop the programming and machining infrastructure. Due to the extremely detailed mouth and incisors, and the long and thin shape of the filigree tail section, two set-ups were required on a linear 5-axis DMG MORI HSC70 milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger." title="CNC machine tool capable of drilling, reaming, tapping, milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger." aria-label="Glossary: machining center">machining center.
A four-flute cutter with a corner radius from the Duo-Lock Haimer mill Alu series was selected for the roughing, and tor the finishing process, the full radius version of the solid carbide end mill from the Haimer Mill Alu series was used because of its micro-geometrical properties, which are designed for smoothness and top surface quality.
"For especially detailed areas, such as the mouth and tail section or with the creases of the joints, we generated additional surfaces that can be combined with the STL network in hyperMILL, said Nordmann. For this, hyperCAD-S, the 'CAD for CAM' system specially designed by Open Mind to help meet all the programmers needs was used.
Equally imperative for milling the panther was the hyperMILL Virtual machining center, a process-safe NC simulation solution where virtual machine movements fully mimic real movements and ensure reliable collision detection. The Virtual machining center pre-emptively recognized that the component could not be processed in a basic orientation due to X-axis limited and automatically generated a solution for a workable position.





