ISCAR is introducing the IC5400 carbide grade, featuring an effective means of parting and grooving stainless steel. The new grade has a tough substrate, like the one used for IC830. It is MTCVD TiCN and alpha aluminum-oxide coated, with the SUMO TEC advanced post-coating treatment. This considerably improves resistance to flaking, chipping and abrasion, preventing built-up edge and this providing prolonged tool life.
The ISO application range of the new grade is M30. It was designed for parting and grooving stainless steel at low to medium cutting speeds under stable or unstable machining conditions.
Field tests clearly show the advantages of IC5400 machining. The new grade features substantial improvement in tool life. It was found that by using IC5400, cutting speed can be raised by 15 percent in comparison with IC830.
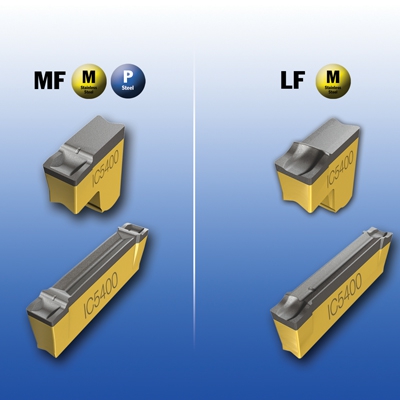
ISCAR is expanding its range of parting with LF, LFT and MF chipformers, for parting and grooving stainless steel and also for ductile materials. The new LF chipformer design features a positive rake inclination and sharp cutting edge. It exerts low cutting forces and reduces built-up edge. In addition, it efficiently narrows the chips, leaving a clean cut surface.
The LFT chipformer features basically the same design as the LF chipformer, except that it was reinforced by a T-land to improve its durability and its resistance to chipping of the cutting edge and corners. It can be applied at higher feed than the LF chipformer.
The MF chipformer has the basic design of the C chipformer with high deflector and smaller T-land, most suitable for medium to high feeds, suitable also for steel (ISO P).
ISCAR's new chipformers are available in grade IC5400 for general stainless steel applications and in grade IC830 for interrupted cut and high load applications. IC808 is also available. In the initial stage, the DGN LF and LFT and TAG LF are available in 2 and 3mm widths.
The combination of the new chipformers with IC5400 grade is ISCAR's first-choice recommendation for parting and grooving stainless steel.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- built-up edge ( BUE)
built-up edge ( BUE)
1. Permanently damaging a metal by heating to cause either incipient melting or intergranular oxidation. 2. In grinding, getting the workpiece hot enough to cause discoloration or to change the microstructure by tempering or hardening.
- cutting speed
cutting speed
Tangential velocity on the surface of the tool or workpiece at the cutting interface. The formula for cutting speed (sfm) is tool diameter 5 0.26 5 spindle speed (rpm). The formula for feed per tooth (fpt) is table feed (ipm)/number of flutes/spindle speed (rpm). The formula for spindle speed (rpm) is cutting speed (sfm) 5 3.82/tool diameter. The formula for table feed (ipm) is feed per tooth (ftp) 5 number of tool flutes 5 spindle speed (rpm).
- feed
feed
Rate of change of position of the tool as a whole, relative to the workpiece while cutting.
- grooving
grooving
Machining grooves and shallow channels. Example: grooving ball-bearing raceways. Typically performed by tools that are capable of light cuts at high feed rates. Imparts high-quality finish.
- interrupted cut
interrupted cut
Cutting tool repeatedly enters and exits the work. Subjects tool to shock loading, making tool toughness, impact strength and flexibility vital. Closely associated with milling operations. See shock loading.
- parting
parting
When used in lathe or screw-machine operations, this process separates a completed part from chuck-held or collet-fed stock by means of a very narrow, flat-end cutting, or parting, tool.
- rake
rake
Angle of inclination between the face of the cutting tool and the workpiece. If the face of the tool lies in a plane through the axis of the workpiece, the tool is said to have a neutral, or zero, rake. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge more acute than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is positive. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge less acute or more blunt than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is negative.
- titanium carbonitride ( TiCN)
titanium carbonitride ( TiCN)
Often used as a tool coating. See coated tools.







