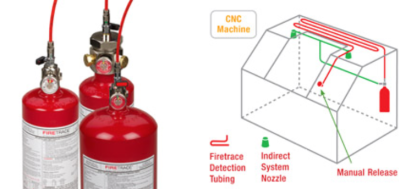
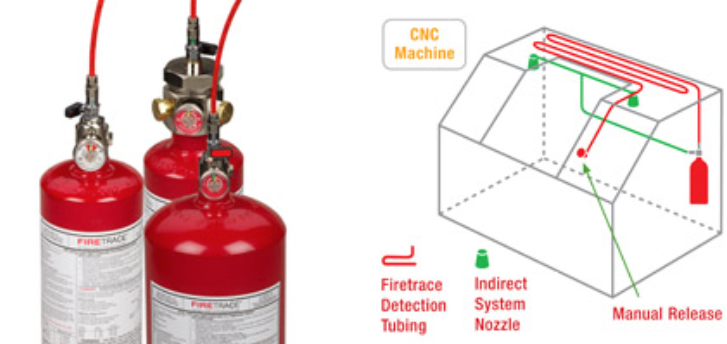
Firetrace International, Scottsdale, Ariz., offers CNC machinery fire suppression inside your machinery to instantly protect it from the risks of fire, the company reported in a Jan. 19 news release. Ultimately, these are re extinguishing systems designed to protect your machines by detecting when there is a re present and extinguishing it before it has chance to develop and cause extensive damage.
Automatic Fire Suppression Systems are ideal for CNC machines that use oil‐based lubricants that can overheat, ignite and cause a flash fire, according to the company. Featuring a flexible, polymer tubing that ruptures when exposed to a flame, the Firetrace systems detect and suppress a fire by flooding the machining area with a suppression agent.
Firetrace Automatic Fire Suppression Systems for CNC machines are UL listed, and the flexible polymer tubing can be installed in narrow spaces near the cutting or erosion head. Systems are capable of discharging from 3 lbs. to 20 lbs. of a fire suppression agent, such as CO2 (carbon dioxide) or ChemoursFM-200 or 3M Novec 1230 Fire Protection Fluid. These gaseous extinguishing agents are non‐conductive, non‐corrosive, leave no residue on the machine or workpiece, and will not contaminate expensive metalworking oils or fluids, according to Firetrace.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- flash
flash
Thin web or film of metal on a casting that occurs at die partings and around air vents and movable cores. This excess metal is due to necessary working and operating clearances in a die. Flash also is the excess material squeezed out of the cavity as a compression mold closes or as pressure is applied to the cavity.
- metalworking
metalworking
Any manufacturing process in which metal is processed or machined such that the workpiece is given a new shape. Broadly defined, the term includes processes such as design and layout, heat-treating, material handling and inspection.






