CAMWorks Version 2020 Software
CAMWorks Version 2020 Software
HCL Technologies announced the release of CAMWorks Version 2020 with several enhancements to assist machine shops in advancing their smart manufacturing practices. CAMWorks Version 2020 provides support for 3D printing of SolidWorks Assemblies, the CAMWorks ShopFloor product, intelligent probing functionality and automatic tab machining.
HCL Technologies announced the release of CAMWorks Version 2020 with several enhancements to assist machine shops in advancing their smart manufacturing practices. CAMWorks Version 2020 provides support for 3D printing of SolidWorks Assemblies, the CAMWorks ShopFloor product, intelligent probing functionality and automatic tab machining.
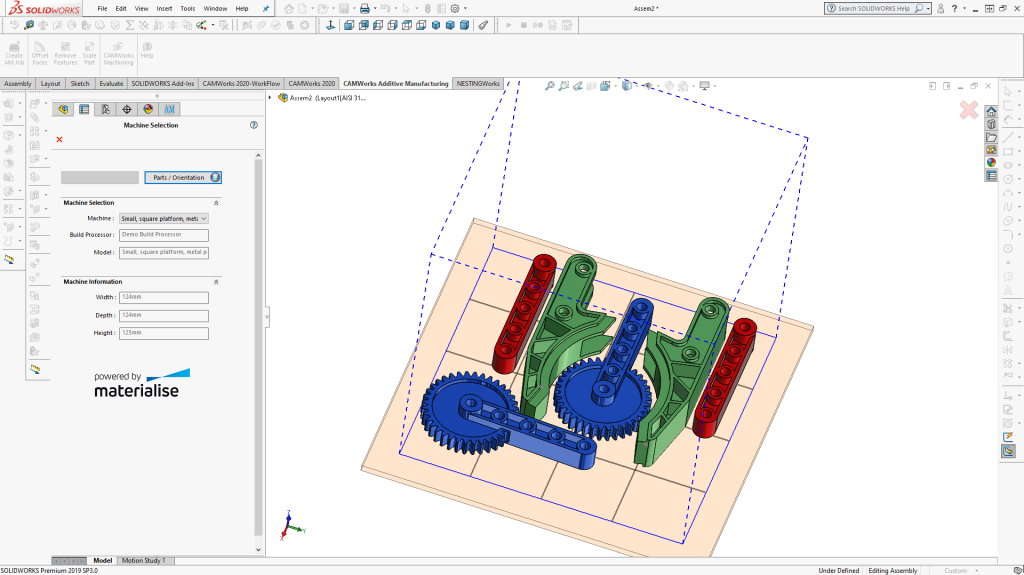
With Version 2020, the CAMWorks Additive Manufacturing module, powered by Materialise, has extended 3D printing functionality to SolidWorks Assemblies. Multiple parts from the same assembly or different assemblies can be nested onto the build platform, which saves time and increases efficiency, and CAMWorks Additive Manufacturing automatically generates the build supports. CAMWorks Additive Manufacturing is fully integrated into SolidWorks and allows 3D models to be printed directly from SolidWorks.
CAMWorks ShopFloor provides CNC machinists the ability to view solids models, view full simulations of CNC programs, and edit machining data on the shop floor, without the need to purchase a full shop-floor CAD/CAM system. With CAMWorks ShopFloor, all of the CAM data from the 3D digital models is captured and placed in a digital container, helping eliminate instances when parts are cut without the most recent edits. CAMWorks ShopFloor also supports 3D models with MBD (model-based definition) and PMI (product and manufacturing information) data for smart manufacturing to avoid errors that often occur when part data is transferred through 2D drawings or other formats. CAMWorks ShopFloor works in conjunction with other CAMWorks products and supports tooling lists and setup sheets generated within CAMWorks.
Touch probe support has been added to all CAMWorks base products in Version 2020, which saves time and eliminates the errors that often occur with manual part setting and inspection. CAMWorks automatically selects the probing cycle based on the face/feature selection, and a full set of touch probe tools has been added to the standard tool set with new parameters for probe shank and stylus. Probe support allows machinists to probe the stock or part features, set work coordinate offsets and measure a part to ensure part quality and create documentation for quality assurance. The probing toolpath is also displayed in the simulation to ensure collision avoidance.
Solutions for parts requiring additional support is provided with automatic tab machining. This eliminates the need to machine soft jaws or design special work-holding fixtures for subsequent machining operations. Programmers input the desired number of tabs, width and thickness, and CAMWorks automatically generates the tab machining details. Tabs can be equally spaced or precisely located using distance and/or offsets. Users can specify minimum segment and arc radius and are given multiple options for lead-in and lead-out.
Additional enhancements in CAMWorks Version 2020 include automatic feature recognition for chamfering and deburring, tapered multiple-point thread milling and an updated Universal Post Generator for users who want to make changes to their post processors.




