CoroCut QD Concept for Grooving, Parting Off
CoroCut QD Concept for Grooving, Parting Off
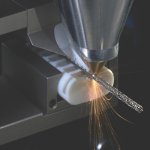
The CoroCut QD concept for deep external grooving and parting off from Sandvik Coromant adds internal machining to the application range of these secure and reliable tools.

The CoroCut QD concept for deep external grooving and parting off from Sandvik Coromant adds internal machining to the application range of these secure and reliable tools.
The CoroCut QD system now includes CoroTurn SL blades for deep grooves in internal machining. The modularity of the CoroTurn SL interface enables tool assemblies optimized for the specific application.
Internal grooving and parting off with long overhangs requires stability and tooling solutions that keep vibration to a minimum. CoroCut QD tools offer a stable clamping mechanism so that Silent Tools dampened boring bars can be used for vibration-free machining with long overhangs. For tube-shaped components, typically found in the oil and gas industry, this is welcome news enabling deep internal grooving to be machined with high process security.
As with the previously introduced CoroCut QD tools, the extended assortment features over- and under coolant. The over coolant easily handles chip control while the under coolant prolongs tool life further securing the machining process.