Eppinger Capto Base Holder
Eppinger Capto Base Holder
EXSYS Tool Inc. has introduced the EPPINGER CAPTO base holder, referring to it as "the world's smallest CAPTO interface with the fastest tool changeover times for enhancing efficiency and productivity in CNC turning operations."
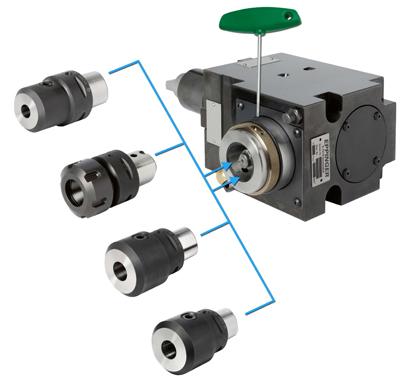
EXSYS Tool Inc. has introduced the EPPINGER CAPTO base holder, referring to it as "the world's smallest CAPTO interface with the fastest tool changeover times for enhancing efficiency and productivity in CNC turning operations."
When compared to traditional designs, the compact size of the EXSYS/EPPINGER CAPTO base holder provides more space for machining larger workpieces as well as offers improved torque transmission and rigidity for increased tool accuracy. The interface's cone-style shape further adds to the solution's precision and stiffness.
A special built-in release mechanism on the outer diameter if the EXSYS/EPPINGER CAPTO base holder's spindle provides optimal operator accessibility as well as makes it easy to lock and unlock the CAPTO adapters with a small Allen key for fast and virtually effortless tool changes. The automatic ejection of the CAPTO adapters also guarantees quick tool exchanges.
Available for bolt-on and VDI-style turrets, the EPPINGER/EXSYS CAPTO base holder accommodates fixed and rotary tools, including the EXSYS/EPPINGER PRECI-FLEX system, and accepts all standard CAPTO/PSC adapters. The same CAPTO adapters used in milling applications will now work in turning operations thanks to the versatility of the solution.
According to Scott Leitch, a representative for EXSYS Tool, for decades the EPPINGER name has been synonymous with innovation, precision and reliability, and its new CAPTO interface maintains the brand's premium legacy. "With the products superb rigidity, short tool changeover times and high accuracy, users will definitely experience enhanced productivity, profitability and an overall better machined component."





