Flexium+ CNC Platform helps Star Cutter
Flexium+ CNC Platform helps Star Cutter
NUM's latest-generation CNC systems are helping the Star Cutter Co. to maintain its position as a world leader in cutting tool machines. Star Cutter's new 5-axis tool and cutter grinding machine – the NTG 6RL – is based entirely on NUM's Flexium+ CNC platform, and fully automates the high-speed production and reconditioning of complex cutting tools.
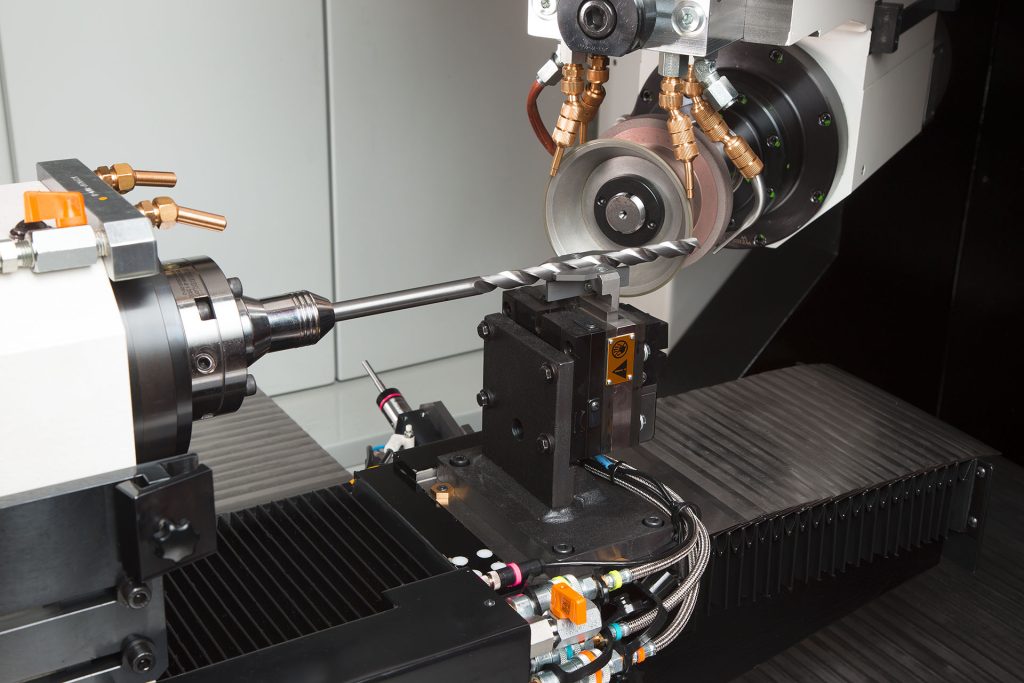
NUM's latest-generation CNC systems are helping the Star Cutter Co. to maintain its position as a world leader in cutting tool machines. Star Cutter's new 5-axis tool and cutter grinding machine – the NTG 6RL – is based entirely on NUM's Flexium+ CNC platform, and fully automates the high-speed production and reconditioning of complex cutting tools.
Star Cutter specializes in carbide and preform manufacturing, cutting tools and CNC machines for tool and cutter grinding and hob sharpening. Founded in Detroit in 1927, the company now operates six manufacturing facilities at strategic locations throughout Michigan.
Since 1998, Star Cutter has partnered with NUM for cooperative development of application-specific CNC hardware and software. During the course of this nearly 20-year collaboration, the two companies have advanced cutting tool machine technology significantly – Star Cutter currently manufactures seven highly specialized lines of machine tools, six of which are based on NUM's CNC systems.
Star Cutter originally used different controllers for its machines. However, with a goal to bring its customers even more capability and ease in realizing complex tool forms, as well as to gain more flexibility and speed in integration of third-party motors and simplify the development of control software, the company sought to transition from a proprietary control scheme to a more open CNC platform.
According to Bradley Lawton, chairman of Star Cutter, "NUM was an obvious choice. The company is renowned for the open architecture nature of its CNC solutions, and has done much to remove the 'black box' mystique that is endemic to many of the competitive CNC products on the market. And the quality and reliability of NUM's products is excellent, which is extremely important to us – over 99 percent of the machines that we have produced in the past 20 years are still in everyday use. On top of that, NUM's customer support is superb and we enjoy very responsive and helpful technical help".
NUM and Star Cutter's partnership has created dividends for both companies, and for their customers and machine end-users. Starting with its ETG and PTG series of tool and cutter grinders – which have an installed base of more than 200 – Star Cutter has steadily migrated nearly all of its CNC machines across to NUM's CNC hardware and NUMROTOplus software.
Star Cutter's latest NTG 6RL full linear 5-axis tool and cutter grinder machine can handle fluting, tertiary grinding, relief grinding and automated wheel change. It is based entirely on NUM's powerful Flexium+ CNC platform. The NUMDrive X modules that form part of this high-end CNC solution provide the drive flexibility that is needed to accommodate a variety of third-party linear and direct drive torque motors, as well as high frequency grinding spindle motors. As a consequence, the machines are capable of high grinding and surface finish accuracies, combined with high grinding speeds, and promise to be the most productive that Star Cutter has ever produced.
Steven Schilling, general manager of NUM Corporation in Naperville, Illinois, points out, "The higher bandwidth of the NUM's DriveX servo drive and improved internal processing of NUM's Flexium+ CNC platform, which is now managed by double-precision IEEE 754 floating point, provides capabilities that extend down to sub-picometer accuracy. This gives manufacturers like Star Cutter the opportunity to create machines that can grind even the smallest tools with superb accuracy."
Another key attribute of the Flexium+ platform is that it can run grinding programs as large as 40 MB directly from the NCK memory. And for complex grinding cycles, the CNC system can execute cycles directly from the system's disk drive, via a high speed data transfer protocol. This increased capacity and speed helps Star Cutter's customers to expand their CAD/CAM grinding operations. Application areas include the processing of advanced materials and aerospace components, in addition to medical devices and tools.
Star Cutter's new grinding machine also features a novel servo-assisted popup mechanical steady rest. This makes full use of the 'detachable axes' facility of Flexium+ systems equipped with NUMDrive X modules. It enables end users to simply place the rest into the machine for the production of longer parts, and to quickly remove the full motor/mechanical assembly when it is not needed.
Focusing on an intuitive user experience, the operator station features an entirely new design, which reduces button pushing, significantly simplifying machine setups and daily operations. The optional 6-axis robotic part loader essentially programs itself from the NUMroto tool files, requiring minimal user inputs. Notifications can be set to alert shop personnel of process completion or of issues encountered during unattended production.
The new machine is also designed for ease of integration with other forms of industrial automation and handling robots. NUM's Flexium+ platform offers a variety of system communication busses, including EtherCAT, CAN and EtherNet IP. Measured process or post-process data can be fed back to the CNC system's NUMRoto software to provide on-the-fly corrections, facilitating adaptive real-time control of the entire grinding process. Shop floor data can even be shared easily with the rest of the plant and to the cloud with NUM's built-in MTConnect interface.





