Purge Coolant Filtration System
Purge Coolant Filtration System
MP Systems has launched a new coolant filtration system designed to prevent chips from accumulating inside a CNC machine tool's coolant tank and causing coolant starvation of the machine tool's flood pump and the high pressure coolant pump.
MP Systems has launched a new coolant filtration system designed to prevent chips from accumulating inside a CNC machine tool's coolant tank and causing coolant starvation of the machine tool's flood pump and the high pressure coolant pump.
"Experienced machine tool operators have learned to accept the work stops created by these issues as normal byproducts of the machining process," MP Systems Engineer Brian Jalbert says, "but with the Purge they don't have to anymore."
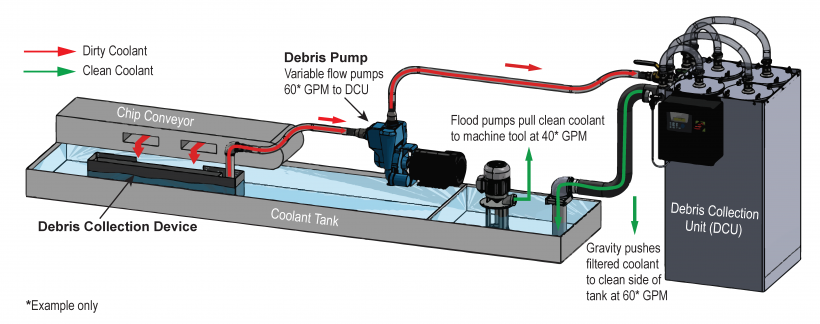
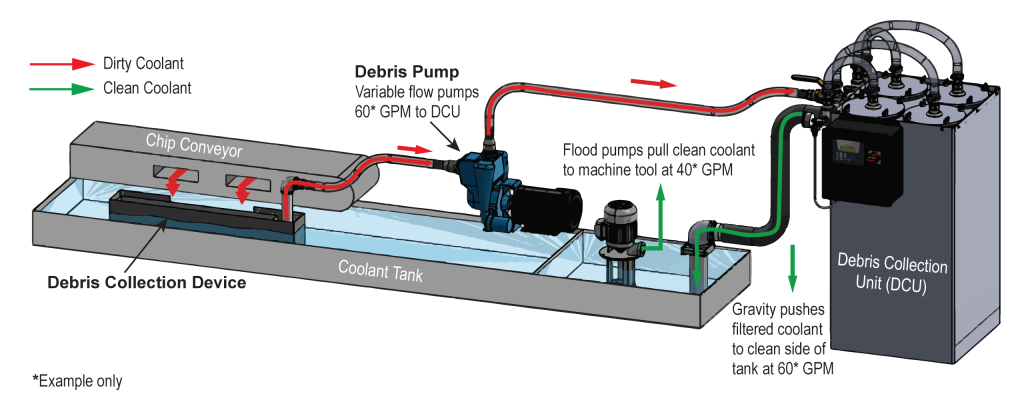
To understand how the Purge eliminates these problems, Jalbert says it's important to first understand how a typical CNC machine tool manages coolant filtration.
A machine tool's coolant tank has two sides: a clean coolant side and a dirty coolant side, Jalbert explains. The dirty side contains a basket that catches larger chips, preventing them from settling on the dirty side of the tank. But this basket allows smaller chips and fines to pass through its walls, where they can settle into the dirty side of the tank. To keep them from flowing into the clean side, there's a screen between the two sides of the tank. However, many of the smaller chips and fines can pass through this screen or get trapped in it and clog it.
"That's when the trouble starts," Jalbert says. "These small chips and fines build up in the coolant tank where they consume space, which reduces the coolant volume in the tank. In addition, the clogged screen prevents coolant from flowing into the clean side, which compounds the problem."
When coolant volume drops on the clean side of the tank, the machine tool's flood pump can't pump enough coolant through the machine to avoid sucking air. If the machine is running with a high pressure coolant system, that pump will also become coolant starved, which triggers an alarm to shut down. When this happens, the machine tool shuts down.
"The Purge prevents these problems," Jalbert says. "It's a full-flow system. It pulls coolant from the dirty side of the coolant tank, filters it and returns it to the clean side of the coolant tank faster than the flood and high-pressure coolant pumps draw from it. This prevents coolant starvation of the pumps."
In addition to preventing coolant starvation of the flood and high pressure coolant pumps, the Purge keeps small chips and fines from clogging the machine tool's nozzles and lines. By keeping the coolant cleaner, part quality is improved and cutting tool life is extended.
As an added bonus, the machine's coolant tank doesn't need to be cleaned nearly as often. "Cleaning a coolant tank is a nasty job that nobody wants to do," Jalbert says. "It's also time consuming and you have to shut the machine down to do it. If the machine is inside a caged cell, it's a task than can take days. If you can eliminate this job even once, the Purge will pay for itself."
The Purge can hold up to 20 gallons of debris. When it's full, users simply lift out the filter bags. The cost of the filter bags depends on the desired level of filtration and the type of bag used. A standard 5-micron felt bag costs four dollars.
"Changing filter bags is faster, more convenient, and a lot safer than sticking your hands in a tank full of chips," Jalbert says.





