Contact Details
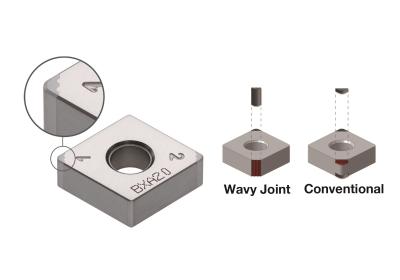
Tungaloy is introducing the WavyJoint PCBN inserts, an innovative PCBN brazing technology for higher productivity in hard turning operations.
Hardened steel parts are gaining broader acceptance in today’s automotive industry to meet the requirements of downsizing for less emission and energy. Manufacturers are seeking cost-effective solutions to improve productivity and machining efficiency. PCBN inserts are an effective solution to turn hardened steel parts.
However, a PCBN tip brazed with a conventional brazing technology is prone to detach, or debraze, from its carbide base insert when turned dry at a large DOC. Therefore, the operator has to use multiple, small cutting depth passes. The WavyJoint PCBN insert can significantly improve machining efficiency, enabling hard turning in a single pass at a large DOC and at a high feed rate.
At a glance:
Innovative brazing method allows for a large DOC, up to 1.6 times that of conventional PCBN inserts.
Larger PCBN mass of the cutting tip enhances thermal stability during deep and dry cutting.
Capable of a DOC up to 0.8 mm. Fewer turning passes for higher efficiency.
Reduced risk of debrazing allows for dry and interrupted cutting at a large DOC.
Reduces premature insert failures caused by thermal fatigue often seen in wet cutting.
Related Glossary Terms
- fatigue
fatigue
Phenomenon leading to fracture under repeated or fluctuating stresses having a maximum value less than the tensile strength of the material. Fatigue fractures are progressive, beginning as minute cracks that grow under the action of the fluctuating stress.
- feed
feed
Rate of change of position of the tool as a whole, relative to the workpiece while cutting.
- hard turning
hard turning
Single-point cutting of a workpiece that has a hardness value higher than 45 HRC.
- polycrystalline cubic boron nitride ( PCBN)
polycrystalline cubic boron nitride ( PCBN)
Cutting tool material consisting of polycrystalline cubic boron nitride with a metallic or ceramic binder. PCBN is available either as a tip brazed to a carbide insert carrier or as a solid insert. Primarily used for cutting hardened ferrous alloys.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.











 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

