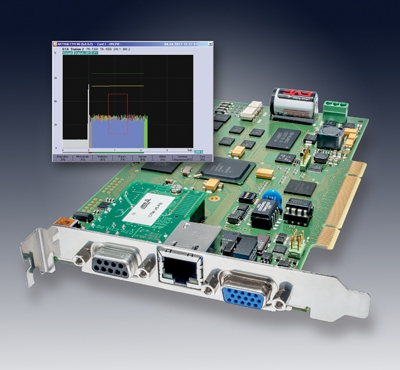
Marposs Corp. has introduced its new generation Artis CTM V6 tool, machine and process monitoring system. The CTM system safeguards and optimizes complex production processes thanks to aligned in-process monitoring. The flexible interface concept enables problem-free integration within many environments, from entry solutions with no fieldbus connections, to branched Ethernet architectures such as PROFINET, Ethernet/IP and Modbus.
Using the CTM system, evaluation and control are carried out with process-dependent strategies. Instead of searching for the smallest common denominator, CTM offers a range of strategies to optimally monitor the process. Each individual parameter can be very finely adjusted and precisely adapted to the process. Process monitoring operates precisely and reliably from the very first cut.
In the basic installation, the CTM system is interfaced with the machine control and accepts inputs from various measuring transducers. Data capturing is accomplished using a sensor-less digital torque adaptor (DTA), wherein a selection of drive data is collected by the control for the evaluation of the torque of the spindle and the feed axis. Additional or alternative sensors are available for measuring strain and force, true power, torque, vibration and acceleration, acoustic emission, and standard power or voltage signals.
Optionally, the CTM V6 system can provide Adaptive Control for adjusting the feed speed to compensate for material deviations. This function protects both machine and tool under high load by reducing the feed force.
For gear hobbing applications, the CTM V6 system improves quality and extends the productive life of hobbing tools by utilizing wear-based method safeguards as opposed to traditional replacement at fixed regular interval methods.
Monitoring of coolant flow using the CTM V6 system is especially useful for processes with small tools such as deep-hole drilling.
Tool related, automatic and process accompanying documentation provided by the CTM V6 system is based on precise data. Visualization software is a fundamental part of the CTM V6 tool and process monitoring system, enabling thorough evaluation of processes in a user-friendly manner.
Main benefits of the new CTM V6 system include comprehensive protection of tools and machines; process optimization; lower of unit costs by reducing the number of rejects; perfect adjustment even in the case of complex processes; and seamlessly documented component quality.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- drilling tool ( drill or drill bit)
drilling tool ( drill or drill bit)
End-cutting tool for drilling. Tool has shank, body and angled face with cutting edges that drill the hole. Drills range in size from “microdrills” a few thousandths of an inch in diameter up to spade drills, which may cut holes several inches in diameter. Drills may have tapered shanks with a driving tang and fit directly into a spindle or adapter, or they may have straight shanks and be chuck-mounted. The rake angle varies with the material drilled. Styles include twist drills, straight-flute drills, half-round and flat drills, oil-hole drills, indexable drills and specials.
- feed
feed
Rate of change of position of the tool as a whole, relative to the workpiece while cutting.









