Contact Details

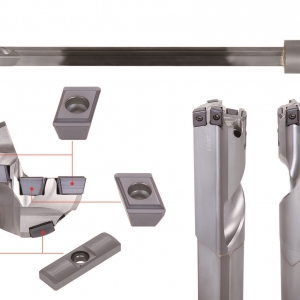
Tungaloy has announced the expansion of its AddMeisterDrill small diameter exchangeable head drills. The expansion includes the introduction of DMC high precision drill heads and addition of the drill diameters range from 4.0 mm to 4.4 mm (or from .157″ to .173″) to the existing DMP general-purpose drill heads, increasing the entire size range from 4.0 mm to 5.9 mm (from .157″ to .232″).
Featuring superior cutting performance of solid carbide drills and the ease-of-use of the DrillMeister exchangeable head drill series, AddMeisterDrill small-diameter exchangeable head drills allow quick and secure exchanges of extremely small drill heads thanks to its dedicated key. In addition, unique coolant outlets furnished on the drill body provides an increased ratio of through-coolant supply for improved chip evacuation and process security.
AddMeisterDrill now offers DMC high precision drill heads. Featuring a unique self-centering edge geometry, DMC drill heads facilitate quick penetration into materials, allowing high precision and stable drilling. The drill heads are available from 5.0 mm to 5.9 mm (from .197″ to .232″) in diameters in AH9130 PVD coated grade optimized for drilling applications. Extremely wear resistant, the grade provides extremely long tool life in carbon steel and alloy steel applications.
Also, with the addition of the new DMP drill head diameter range of 4.0 to 4.4 mm, AddMeisterDrill provides an optimized tool geometry for customers’ applications that need a boost in productivity.
Related Glossary Terms
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
physical vapor deposition ( PVD)
Tool-coating process performed at low temperature (500° C), compared to chemical vapor deposition (1,000° C). Employs electric field to generate necessary heat for depositing coating on a tool’s surface. See CVD, chemical vapor deposition.









 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

