Contact Details
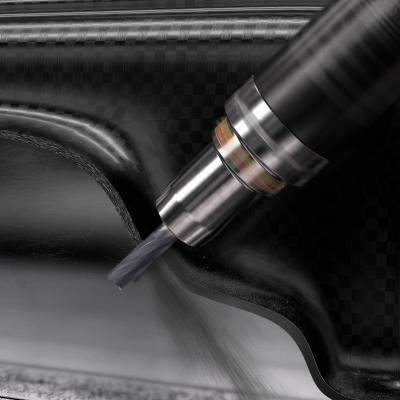

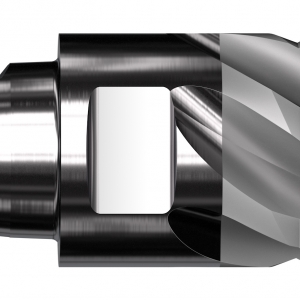
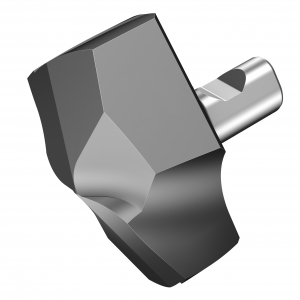
New CoroMill Plura routers unveiled by Sandvik Coromant offer optimized milling and slotting operations in composite materials such as CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced plastic) and GFRP (glass fiber reinforced plastic). Production engineers, machine shop managers and operators will all benefit from the patented geometries provided by the new routers, particularly those in the aerospace industry, where these materials are increasingly prevalent, as well as others in sectors such as automotive, motorsport, wind power and marine.
Machining solutions dedicated to specific composite materials are becoming an increasingly important factor at machine shops looking to achieve improvements in quality, cycle time and costs. The abrasive content of many composites causes issues such as rapid tool wear, compromised cutting quality, elevated temperatures, vibration and unstable cutting conditions. With these challenges in mind, the latest CoroMill Plura generation from Sandvik Coromant has been developed to improve CFRP and GFRP machining on three-, four- and five-axis CNC machining centers, as well as gantry-type CNC machines and stand-alone robotic arm systems.
“The CoroMill Plura brand is a well-established and proven solution across many industries. With this latest generation of routers, patented geometries are designed specifically to boost the machining of composite aerospace parts that include fuselage, wings, stabilizers, stringers, spars, ribs, frames, substructures, floor beams, struts and pressure decks,” says Aaron Howcroft, global product manager, composites, Sandvik Coromant. “The routers offer high productivity and have the longest tool life on the market. Furthermore, they are available as standard items for fast ordering, thus delivering benefits to procurement/purchasing teams.”
When milling and slotting composite materials, the new routers are used primarily in full radial engagement and at full depth of cut. In some cases, finishing passes can also be deployed. Helix angles have been carefully designed for ideal sharpness and cutting edge strength, thus ensuring longer tool life and high-quality surface, edge and slot finishes. The range comprises three cutters: the CoroMill Plura compression router, CoroMill Plura low-helix router, and CoroMill Plura serrated router.
The CoroMill Plura compression router, with its dual 40° helix, works best with special woven glass layers on both sides of CFRP components. As there is an overlap between compressed flutes, the router performs well in thin, flat materials by reducing material vibration.
Specifically designed for smooth and burr-free finishing passes in CFRP workpieces, the CoroMill Plura low-helix (5°) router features a high number of teeth and a coating that is designed to aid quick cutting and protect from heat. Right and left helix options allow flexibility in material with challenging support conditions, such as weak or compromised fixturing.
Finally, the CoroMill Plura serrated router, with its large flute form, allows for high material-removal rates. The geometry also offers a dual cutting action to reduce delamination and vibration, ultimately providing a single-pass solution to minimize stress on composite parts.
All three CoroMill Plura routers can be used with or without coolant.
Related Glossary Terms
- abrasive
abrasive
Substance used for grinding, honing, lapping, superfinishing and polishing. Examples include garnet, emery, corundum, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride and diamond in various grit sizes.
- centers
centers
Cone-shaped pins that support a workpiece by one or two ends during machining. The centers fit into holes drilled in the workpiece ends. Centers that turn with the workpiece are called “live” centers; those that do not are called “dead” centers.
- composites
composites
Materials composed of different elements, with one element normally embedded in another, held together by a compatible binder.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- depth of cut
depth of cut
Distance between the bottom of the cut and the uncut surface of the workpiece, measured in a direction at right angles to the machined surface of the workpiece.
- flat ( screw flat)
flat ( screw flat)
Flat surface machined into the shank of a cutting tool for enhanced holding of the tool.
- flutes
flutes
Grooves and spaces in the body of a tool that permit chip removal from, and cutting-fluid application to, the point of cut.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- slotting
slotting
Machining, normally milling, that creates slots, grooves and similar recesses in workpieces, including T-slots and dovetails.







 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

