Contact Details

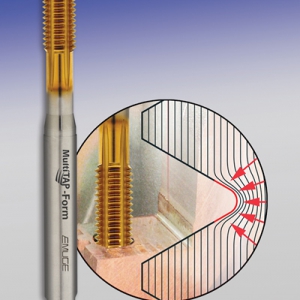
Emuge Corp., a leading manufacturer of high performance taps, thread mills, drills, end mills and other rotary tools, announced the introduction of its A-H family of taps, a new generation of Premium HSS-E and HSSE-PM Taps for hardened steel and cast iron materials. EMUGE has enhanced its H Series of Rekord-A style taps to provide more standard product solutions for threading hardened steel and cast iron material.
The EMUGE A-H family of taps is the best solution for tapping extremely abrasive materials and those materials with elevated hardness levels, such as cast iron, common in the heavy equipment and agricultural vehicle markets. EMUGE A-H Taps are now available with or without coolant through holes and with TiCN coating, or NT nitride surface treatment, for improved tool life.
Premium HSS-E A-H Taps can tap materials up to 48 Rc hardness. Emuge HSSE-PM A-HCUT Taps can tap materials between 44 and 55 Rc hardness and feature a hard, heat resistant, powdered metal substrate for enhanced cutting performance and extended tool life. The new generation of taps with TiCN coating enhance the surface hardness and help increase the tools' abrasion resistance. A new coolant-fed version with axial coolant holes help aid in chip evacuation.
The new EMUGE A-H family of taps is suitable for short chipping hardened steel and cast iron, and are offered in a Rekord A style for through and blind hole applications. UNC/ UNF thread sizes along with Metric and Metric Fine sizes are available.
Related Glossary Terms
- abrasive
abrasive
Substance used for grinding, honing, lapping, superfinishing and polishing. Examples include garnet, emery, corundum, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride and diamond in various grit sizes.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- hardness
hardness
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to surface indentation or abrasion. There is no absolute scale for hardness. In order to express hardness quantitatively, each type of test has its own scale, which defines hardness. Indentation hardness obtained through static methods is measured by Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop tests. Hardness without indentation is measured by a dynamic method, known as the Scleroscope test.
- tap
tap
Cylindrical tool that cuts internal threads and has flutes to remove chips and carry tapping fluid to the point of cut. Normally used on a drill press or tapping machine but also may be operated manually. See tapping.
- tapping
tapping
Machining operation in which a tap, with teeth on its periphery, cuts internal threads in a predrilled hole having a smaller diameter than the tap diameter. Threads are formed by a combined rotary and axial-relative motion between tap and workpiece. See tap.
- threading
threading
Process of both external (e.g., thread milling) and internal (e.g., tapping, thread milling) cutting, turning and rolling of threads into particular material. Standardized specifications are available to determine the desired results of the threading process. Numerous thread-series designations are written for specific applications. Threading often is performed on a lathe. Specifications such as thread height are critical in determining the strength of the threads. The material used is taken into consideration in determining the expected results of any particular application for that threaded piece. In external threading, a calculated depth is required as well as a particular angle to the cut. To perform internal threading, the exact diameter to bore the hole is critical before threading. The threads are distinguished from one another by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance that is specified. See turning.
- titanium carbonitride ( TiCN)
titanium carbonitride ( TiCN)
Often used as a tool coating. See coated tools.










 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS

