Medical manufacturer prolongs tool life
Medical manufacturer prolongs tool life
Boost productivity and extend tool life when cutting cast aluminum surgical light housings. A special PCD endmill with laser-machined cutting edges.
END USER: Simeon Medical GmbH & Co. KG, +49 74-61-900-68-0, simeonmedical.com.
CHALLENGE: Boost productivity and extend tool life when cutting cast aluminum surgical light housings.
SOLUTION: A special PCD endmill with laser-machined cutting edges.
SOLUTION PROVIDERS: J.M. Sales USA, (248) 321-6170, www.jmsales-usa.com; Johs. Boss GmbH & Co. KG (JBO), +49 74-32-9087-0, www.johs-boss.de.
It's common knowledge that superhard materials can be used to make cutting tools with exceptionally long life. But a medical device maker really hit the jackpot when it replaced a solid-carbide endmill with a PCD one and experienced a more than 5,600 percent improvement in tool life, while efficiently producing high-quality parts. Simeon Medical GmbH & Co. KG, Tuttlingen, Germany, experienced that outcome when the manufacturer of surgical light housings needed a longer lasting endmill to more productively mill circular pockets in the cast aluminum housings. Depending on the model, each housing has 24 to 36 pockets to hold LED lights.
The parts manufacturer was applying uncoated solid-carbide endmills that had roughing teeth with a chipbreaker geometry. Tool life averaged from 12 to 14 housings. Simeon tested a coated carbide tool, but tool life increased only three to five housings.

A special PCD endmill from JBO mills a circular pocket in cast aluminum at Simeon Medical.

Seeking to reduce costs and further extend tool life, Simeon commissioned Johs. Boss GmbH & Co. KG (JBO), Albstadt, Germany, to develop a solution. (J.M. Sales – USA, Troy, Mich., is JBO's U.S. representative.) The toolmaker selected PCD as the cutting tool material and produced an endmill with chipbreaking roughing teeth. The 3-flute tool measures 16mm (0.63 ") in diameter and 90mm (3.54 ") in total length and has 24.90mm-long (0.98 "), 1.60mm-thick (0.06 ") PCD cutting edges with a 0.80mm (0.03 ") end radius.
In addition, JBO laser-machined the cutting edges. Compared to the conventional method of wire EDMing the edges, laser machining produces an ultrasharp cutting edge with minimal chipping and edge rounding, according to JBO. For example, if the EDM's eroding wire is 0.3mm (0.01 ") in diameter, the cutting edge radius is 0.15mm, whereas laser machining can generate an edge radius as small as 0.02mm (0.0008 "), explained Sandro Conzelmann, application technician for JBO. "And we can produce more filigree geometries than is possible with wire erosion," he said.
Within a week of the inquiry, Conzelmann noted JBO was able to provide a tool. According to JBO, the initial PCD endmill lasted from mid-July 2013 to the end of November, producing more than 800 housings. In addition to reducing frequent and time-consuming tool changes, the PCD tool cut cycle time 18 minutes compared to the solid-carbide tool by running at higher speeds and feeds. The PCD endmill runs on a Hermle machining center at a spindle speed of 17,000 rpm, a cutting speed of 855 m/min. (2,805 sfm) and a feed rate of 8,000 mm/min. (315 ipm).
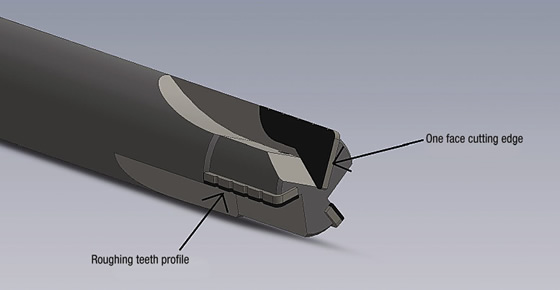
JBO designed the PCD endmill for Simeon Medical with roughing teeth on the external diameter and a face cutting edge.
The total cost for two special PCD tools is $886 compared to $82 to $109 for one standard solid-carbide tool, Conzelmann noted.
Also, the stability of the PCD tool edge eliminates burr formation, according to JBO. Therefore, Simeon eliminated the 10 minutes required to manually deburr a part after machining it with a solid-carbide endmill.

