ModuMini-Turn Q16 Line
ModuMini-Turn Q16 Line
The QC16 line offers toolholders with 16x16 mm square shanks and the matching modular cutting heads. The new line features an enhanced coupling that is capable of sustaining high cutting edge repeatability and tool rigidity when used for applications generating greater cutting loads that conventional QC12 line was not able to provide reliability with
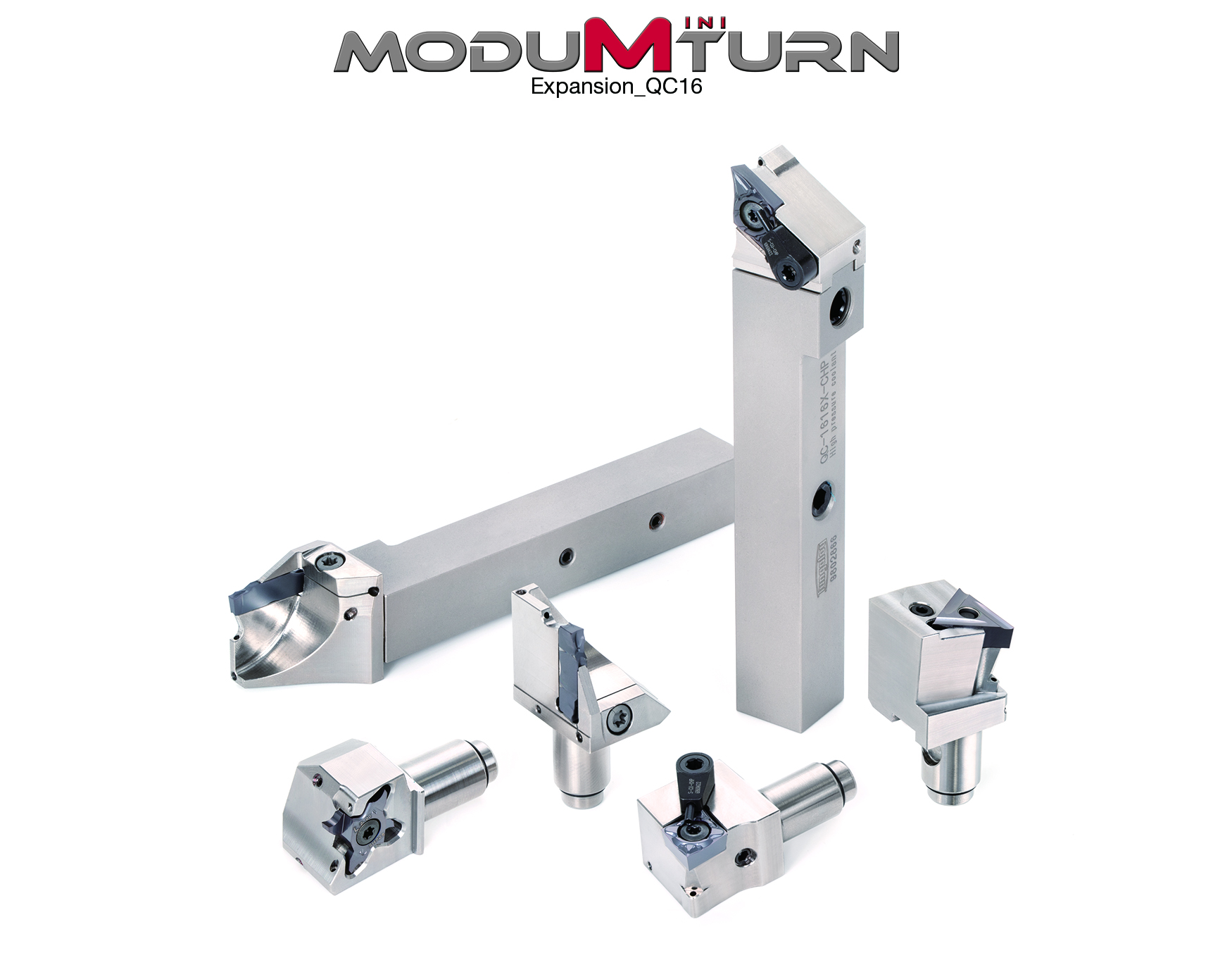
Tungaloy's ModuMini-Turn exchangeable head modular turning tool system for Swiss machines now includes new QC16 line that features 16x16 mm square shanks.
ModuMini-Turn features a unique coupling of the head and shank interface that boasts extremely high repeatability that provides the insert cutting point with a precision of five microns or smaller when the cutting head is re-assembled to the shank. This allows quick tool changes in Swiss machines for minimum downtime.
New QC16 line offers toolholders with 16x16 mm square shanks and the matching modular cutting heads. The new line features an enhanced coupling that is capable of sustaining high cutting edge repeatability and tool rigidity when used for applications generating greater cutting loads that conventional QC12 line was not able to provide reliability with. The QC16 line also offers an array of modular cutting heads to accommodate various types of inserts, including not only standard ISO positive inserts for forward and back O.D. turning, as well as grooving and threading inserts but also cost-efficient double-sided MiniForceTurn negative inserts with positive cutting edges. In addition, modular cutting heads for Y-axis turning are also available allowing shops to use elevated feeds and speeds to gain productivity of small part machining.
Integrating CHP internal coolant channel system that is capable of high pressure coolant supply, ModuMini-Turn toolholder directs the coolant jets precisely to the cutting point close to where it is required for better chip control and to extend insert tool life.





