Automation and Turnkey Production Systems
Automation and Turnkey Production Systems
Machining customers examining the productivity benefits of multiple-spindle, high-precision machining centers from SW North America will find even further advantages in the full range of automation and turnkey production systems the company provides.
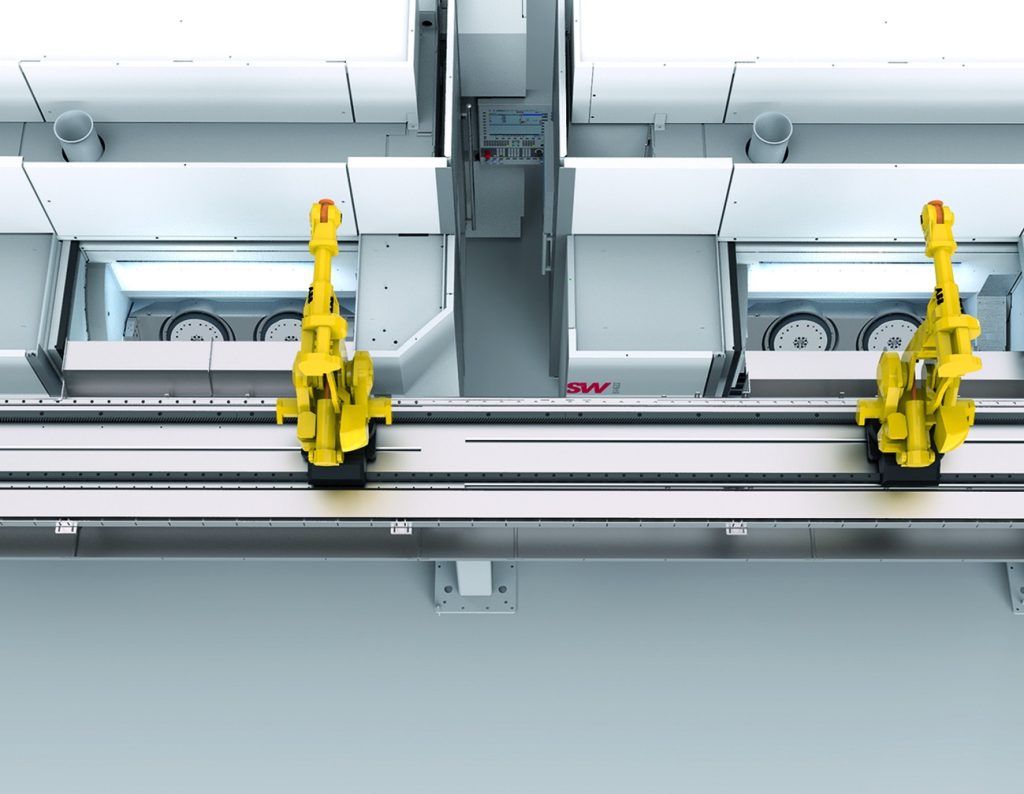
Machining customers examining the productivity benefits of multiple-spindle, high-precision machining centers from SW North America will find even further advantages in the full range of automation and turnkey production systems the company provides.
From the founding of bartsch GmbH in 1998, focusing on robot cells and assembly systems, to the renaming of bartsch to SW Automation GmbH in 2017, automation and assembly potential are an integral part of SW's equipment vision.
"Having the machine tool builder provide automation solutions provides significant benefits compared to third-party approaches," says Sven Makis, managing director of SW Automation. "First, SW takes on complete responsibility, including all layout planning, project design, and interface coordination through structured project management, technical expertise, and experienced and longstanding, reliable partners. Feasibility checks and layout definition are delivered in advance with the aid of cycle-time design and material flow analysis in a simulation model. Parts and processes can be traced using intelligent database solutions through suitable software and technical competence. Even perfect coordination of machining center, tool and gripper concept happens through know-how, experience, and close collaboration and coordination of individual components."
For example, overhead-mounted 7-axis robots supply a high level of flexibility and safety for loading and unloading at a low space requirement. Overhead mounting means the machine center is freely accessible with no protective fences. Partial automation can be engineered for maintenance or manual loading, if desired, as such modular systems can be easily expanded for increased volumes.
Assembly systems also are a specialty. In one system designed for inserting sleeves into a bearing cover, functions include automatic workpiece loading, pre-assembly of individual sleeves into the bearing cover, joining the sleeves while simultaneously monitoring force and distance, and robotic transfer of the bearing covers for the next process.
SW Automation expertise and experience also covers additional automation modules. Peripheral functions include brushing and component deburring with a deburring spindle; pressure and tightness testing and calibration; dimensional measurement and calibration; parts cleaning; and palletizing/packaging, all connected by transport systems, including accumulating conveyors, timing chains, pallet storage systems and lifting and lowering units. Use of RFID systems, cameras, and databases can also be accommodated.
In one example involving assembling transmission and clutch housings, SW Automation networked 48 machining centers with deburring, assembly, parts washing and pressure-testing modules to achieve a cycle time of 45 seconds per part. Benefits include a space-saving layout with walk-through access for operators and maintenance personnel and a high-degree of flexibility in arranging machining functions and workpiece handling.
In another example involving cylinder head covers, necessary tasks included sleeve assembly, bearing cover assembly and plain text labeling, all with force/distance monitoring during assembly. With a volume of 340,000 units per year, the system achieved a line cycle time of 26 seconds while maintaining specified quality metrics.





